Supraspinatus Muscle
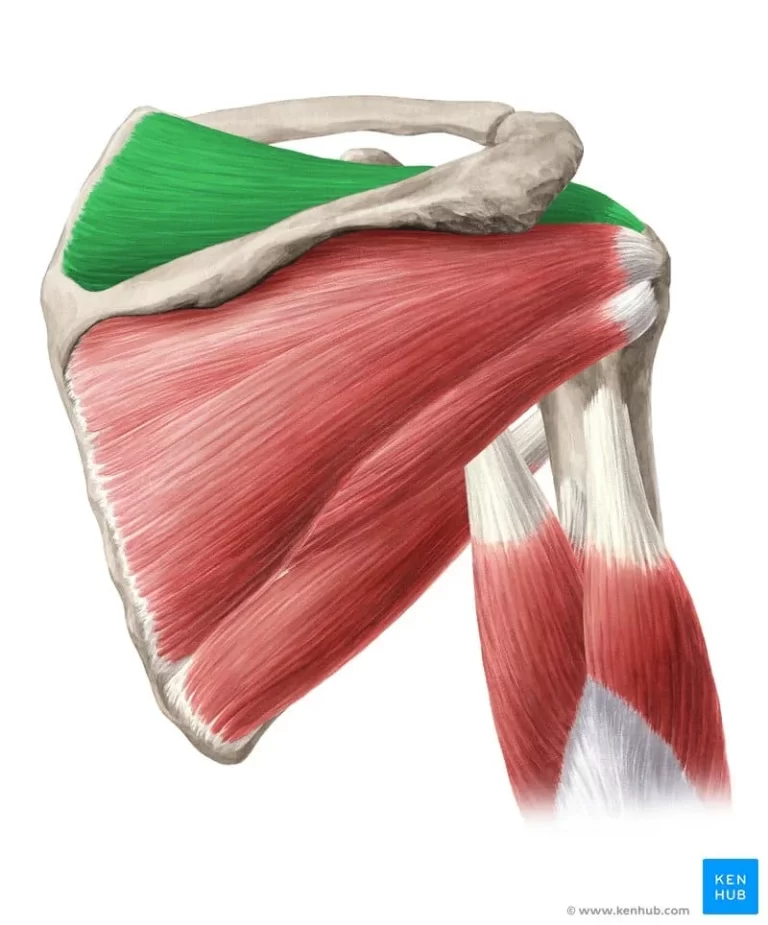
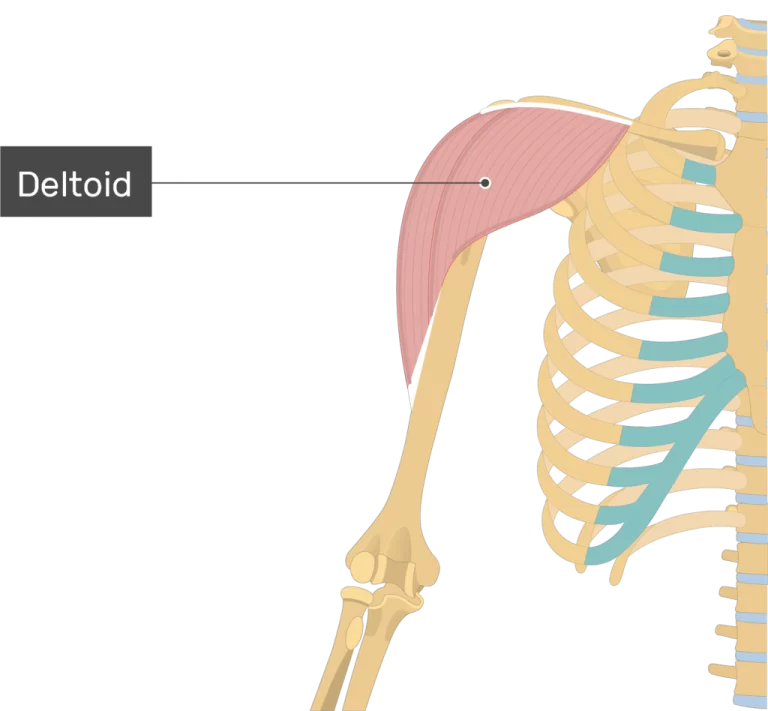
What Is The Supraspinatus Muscle? The supraspinatus muscle is one of the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and facilitate its movement. It is located on the superior aspect of the scapula (shoulder blade) and plays a crucial role in initiating the…