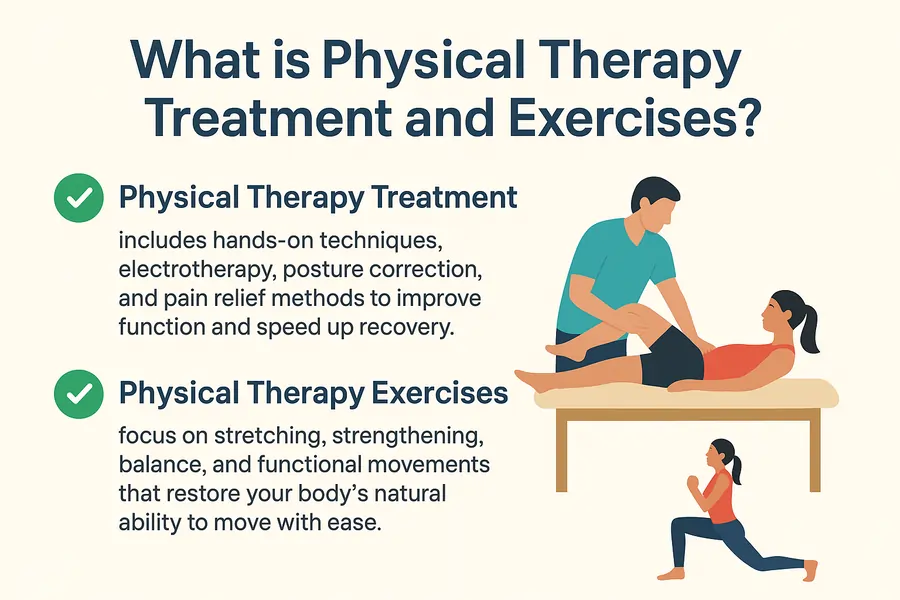
Physical Therapy Treatment and Exercise
What is a Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy is a branch of healthcare that focuses on helping individuals restore and improve their physical function and mobility. It involves the use of various therapeutic techniques, exercises, and interventions to address a wide range of conditions, injuries, or disabilities.
Physical therapy Treatment includes
- Exercises where you actively do certain movements on your own
- Guided passive motions performed by the therapist, pressure (massage) application
- therapies utilizing electrical currents, ultrasound, heat, or cold as physical stimulation.
These methods are applied in the treatment of both acute and chronic symptoms, as well as in the prevention of new issues and in the rehabilitation process following long-term illnesses, surgeries, or traumas.
The best course of physical therapy treatment will be determined by the patient’s unique medical condition, symptoms, and length of time they have experienced pain, among other factors. Both his or her preferences and general level of physical fitness will be important factors.
A wide variety of healthcare locations, such as outpatient clinics, private practices, hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, home health, schools, sports and fitness facilities, hospices, occupational settings, government organizations, research centers, and Sports where the licensed physical therapist works.
Here are some key aspects of physical therapy treatment and exercise:
Assessment and Diagnosis:
Physical therapists begin by assessing the patient’s overall health, medical history, and specific physical issues.
They perform a thorough examination to identify impairments, limitations, and functional deficits.
Based on the assessment, a diagnosis is made, and a personalized treatment plan is developed.
Goal Setting:
Clear, measurable goals are established in collaboration with the patient to track progress and guide the treatment process.
Goals may include pain reduction, improved range of motion, increased strength, enhanced balance, or restoration of functional activities.
Therapeutic Exercises:
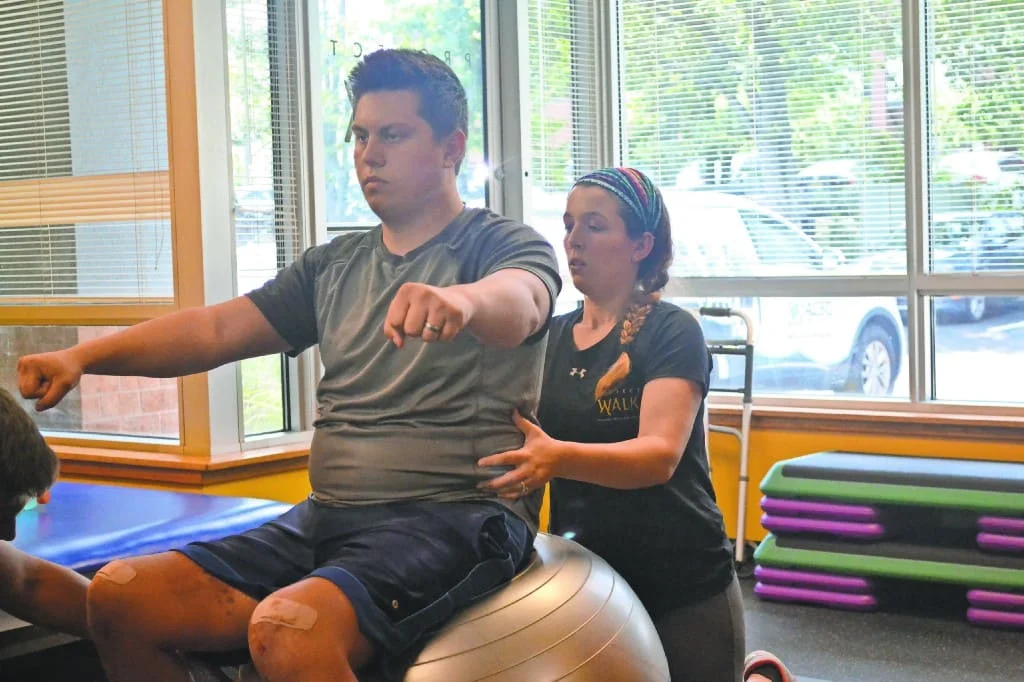

Physical therapists prescribe specific exercises tailored to address the patient’s condition.
Exercises may focus on strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, enhancing coordination, and promoting overall fitness.
Patients are usually provided with a home exercise program to reinforce in-clinic treatments.
Manual Therapy:
Hands-on techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and soft tissue manipulation may be employed to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Manual therapy can help address muscle tightness, joint stiffness, and other physical impairments.
Modalities:
Physical therapists may use modalities like heat, ice, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or traction to complement their treatment and manage pain.
Education:
Patients are educated about their condition, proper body mechanics, and strategies for preventing future issues.
Lifestyle modifications and ergonomic recommendations may be provided to support long-term well-being.
Functional Training:
Therapy often includes activities and exercises that mimic daily tasks to improve functional abilities.
Functional training helps patients regain the skills necessary for daily living and work activities.
Cardiovascular Exercise:
Depending on the patient’s needs, cardiovascular exercises may be incorporated to improve endurance and overall cardiovascular health.
Progress Monitoring:
Regular assessments are conducted to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Communication between the patient and therapist is crucial for optimizing outcomes.
Prevention and Maintenance:
Physical therapists often provide guidance on injury prevention strategies and ongoing exercises to maintain gains achieved during therapy.
It’s important to note that physical therapy is a highly individualized process, and the specific approach varies based on the patient’s condition and goals. Compliance with the prescribed exercises and active participation in the rehabilitation process are key factors in achieving successful outcomes.
When is Physical Therapy Treatment Required?
The following conditions where Physical Therapy Required:
- Back pain
- Age-related Wear-and-tear or injuries of the muscles, tendons or joints
- Osteoarthritis
- Pelvic floor problems such as Bladder-Bowl Incontinence
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Cardiovascular Conditions (heart and blood vessel)
- Respiratory diseases
- Neurological (nerve-related) conditions mainly related Paralysis, Parkinson’s, stroke
- Delay Developmental issues in kids, like those that impact their bones or muscles
People who require assistance or nursing care can also benefit from physical therapy. For example, it can help strengthen muscles, practice specific actions in a specific order, and prevent falls.
Types of Physical Therapy
Physical therapists have access to a wide range of techniques, and they frequently decide to specialize. Among these kinds are:
Orthopedic physical therapy:
This takes care of injuries to the muscles, bones, ligaments, fascia, and tendons that affect the musculoskeletal system. It is appropriate for conditions like sprains, fractures, tendinitis, bursitis, long-term medical issues, and orthopedic surgery recovery or rehabilitation.
Joint mobilizations, manual therapy, strength training, mobility training, and other techniques may be used to treat patients.
Geriatric physical therapy:
This can assist senior citizens who experience conditions like arthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, hip and joint replacement, balance issues, and incontinence that limit their range of motion and bodily functions. The objectives of this kind of intervention are to improve physical fitness, lessen discomfort, and regain mobility.
Neurological physical therapy:
Neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury, and stroke can benefit from this.
Increased limb responsiveness, better movement patterns, tone management, strength development, and balance promotion may all be the goals of treatment.
Cardiovascular and pulmonary rehabilitation:
Those impacted by certain cardiovascular diseases and surgical procedures may find this beneficial. Therapy can improve cardiovascular and muscle stamina and endurance.
Sports Physical Therapy:
Specialized for athletes, focusing on sports-related injuries, performance enhancement, and injury prevention.
Women’s Health Physical Therapy:
Targets conditions specific to women, such as pelvic floor dysfunction, pregnancy-related pain, urinary incontinence, and post-mastectomy rehabilitation.
Therapy for wound care:
Improving circulation, can assist in guaranteeing that a healed wound receives enough blood and oxygen. Manual therapy, e-stim, compression treatment, and wound care are all possible components of physical therapy.
Vestibular therapy:
This provides to treat inner ear diseases that may cause balance issues. Many exercises and manual techniques are used in vestibular physical therapy to assist patients restore their balance and coordination.
Decongestive therapy:
Patients with lymphedema and other disorders involving fluid collection may benefit from this as a means of draining collected fluid.
Pelvic floor rehabilitation:
This can aid in the treatment of pelvic floor disorders, including fecal or urine incontinence, urinary urgency, and pelvic pain brought on by certain illnesses or traumas.
What is Pediatric Physical Therapy?
The goals of pediatric physical therapy include the diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions affecting newborns, kids, and teenagers.
- developmental delays
- cerebral palsy
- spina bifida
- torticollis
- various musculoskeletal disorders
The goals of pediatric physical therapists include increasing function, reducing discomfort, enhancing mobility, and preventing or lessening physical problems that are permanent.
To increase a child’s capacity for autonomous and active functioning at home and in school, they collaborate closely with kids, their families, and caregivers.
Physical Therapy Courses
In the US, completing a doctorate in physical therapy and passing a state licensing exam are prerequisites for working as a physical therapist.
The following topics are studied by physical therapists:
- Biology
- Anatomy
- Histology of cells
- Exercise physiology
- Biomechanics
- Physiology
- Neuroscience
- Pharmacology
- Pathology
- Behavioral sciences
- Electrotherapy
- Cardiovascular research
- Musculoskeletal, metabolic, endocrine, and lung studies
Physical therapists may focus on areas of expertise like:
- Cardio-Pulmonary health
- Clinical electrophysiology
- Health for older adults
- Orthopedics, neurology, pediatrics
- Sports physical therapy
Who offers physical therapy?
Physiotherapists, or physical therapists with specialized training, administer physical treatment. Other medical practitioners can also perform some aspects of physical therapy, such as massages and treatments based on physical stimuli (such as heat therapy or electrotherapy). These include massage therapists and hydrotherapists, who utilize water to treat medical conditions.
Physical therapy can be provided in a variety of venues, including hospitals, rehabilitative care facilities, nursing homes, and physical therapy practices.
What are the educational requirements to become a Physical Therapist?
In the US, licensure and training are prerequisites for all physical therapists. A doctor of physical therapy (DPT) degree is required. Typically, obtaining a DPT requires three years. Bachelor’s degrees are also held by physical therapists.
To practice physical therapy in the United States, one must pass the National Physical Therapy Examination. Certain states demand further tests or licenses.
Is a physical therapist a doctor?
Physical therapists obtain a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree, although they are not physicians of medicine (MD) or doctors of osteopathy (DO). They are unable to conduct surgery, write prescriptions for medication, or diagnose illnesses.
When you visit a physical therapist, you will often get better movement after receiving a diagnosis from another medical professional.
Difference between physical therapy, physiotherapy, and kinesiotherapy
Physical therapy, physiotherapy, and kinesiotherapy are all the same.
These names all relate to the same kind of medical care. Whatever you name it, your physical therapist will assist you in becoming a better, more self-assured mover.
In the United States, physical therapy is typically referred to as the treatment, and physical therapists as the providers who carry it out by patients and providers.
Outside of the United States, physiotherapy and physiotherapists are more frequently mentioned. Outsiders refer to physical treatment as kinesiotherapy on occasion.
Physical therapy vs. occupational therapy
Both occupational therapy and physical therapy assist you in moving your body more effectively and safely. Their ultimate objective separates them from one another.
The goal of physical therapy is often to treat a particular body part. Physical therapy may be necessary for the treatment of certain medical conditions, such as pain and stiffness, or for recovery following surgery or an injury.
The main goal of occupational therapy is to assist patients become more capable of performing routine, daily tasks and leading as independent a life as possible. In occupational therapy, “occupation” does not always imply loss of function or return to work following an injury.
Providers use the term “occupation” to refer to all of your daily tasks. A skilled occupational therapist can assist you with activities such as using a computer, grocery shopping, and dressing yourself.
Conclusion
One crucial person on your medical team may be a physical therapist. They’ll assist you in increasing the range and comfort of motion in your body.
Short-term physical therapy may be necessary as part of your post-operative rehabilitation or while you’re healing from an injury. Some people manage chronic diseases that limit their capacity to move and regulate their bodies by working with physical therapists.
Speak with a medical professional if you experience any new symptoms, such as pain or stiffness, particularly if it’s preventing you from moving a body part as normally.
FAQs
What is called physical therapy?
Physiotherapy helps people who have been affected by illness, injury, or disability regain their capacity to move and work. It might also reduce your likelihood of being sick or hurt in the future. It calls for a comprehensive approach in which the patient takes an active role in their own treatment.
What is the job of a physical therapist?
Physical therapists assess and report the advancement of their patients. Physical therapists help with diseases or injured patients to relieve pain and improve mobility and strength. They frequently play a significant role in patients’ treatment for chronic illnesses, injuries, and conditions as well as in rehabilitation and preventive care.
Which type of physiotherapy is best?
Orthopaedic physiotherapy is the most often used kind of physical treatment. It addresses the greatest range of subjects. Sports physiotherapists use orthopaedic treatment to treat injuries caused during sports. However, we recommend this course of therapy to patients recovering from muscular or orthopedic surgeries.
Which field of physiotherapy is best?
Compared to regular physiotherapists, orthopaedic, neurologic, pediatric, and sports physiotherapists might make more money. In general, physiotherapists in India make respectable salaries and have excellent opportunities for professional advancement.
Is physical therapy good for you?
Physical therapy offers several advantages. It consists of practical exercises and teaching about how your body moves. Physical therapists can assist you with injury recovery, managing chronic pain, and even improving your performance in your preferred sport.





35 Comments