Muscle Stiffness
Introduction
Muscle stiffness refers to a sensation of tightness or reduced flexibility in the muscles, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. It can occur due to various reasons such as overuse, lack of movement, injury, or conditions like arthritis. Stiffness typically results when muscles are unable to relax fully, leading to tension and restricted movement.
While it is a common issue, it can be particularly troubling if it interferes with daily activities or exercise. Understanding the causes and remedies for muscle stiffness is essential for improving mobility and reducing discomfort.
Causes of Muscle Stiffness
Some common causes of muscle stiffness are:
Overuse and Strain: Excessive workouts can cause muscle fatigue and stiffness.
Dehydration: Inadequate water intake impairs muscular function.
Poor Posture: Sitting or standing wrongly causes muscle strain over time.
Lack of activity: Prolonged periods of inactivity can cause stiffness.
Stress and Tension: Emotional stress may cause muscular tension.
Muscle Damage: Tears or strains in muscle fibers induce stiffness.
Inflammation: Conditions like arthritis cause muscle and joint stiffness.
Medication Side Effects: Some drugs can induce muscle stiffness as a side effect.
Cold temperature: In cold weather, muscles might get strained and tense.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome is a chronic condition that affects muscles and the thin connective tissue (fascia) that holds them in place, resulting in tight and tender knots (trigger points) in the muscle.
Risks of Muscle Stiffness
Muscle pain and stiffness can be more likely in certain situations. Tightness can have several harmful effects on the body if it is not treated. The following are some possible dangers related to muscle stiffness:
Fibromyalgia: The chronic illness known as fibromyalgia is the cause of all musculoskeletal pain and fatigue.
Reduced range of motion: Tight muscles can limit the range of motion in the joints, which makes it difficult to perform everyday activities like reaching, lifting, and bending.
Multiple Sclerosis: Muscle stiffness and spasms result from immune system attacks on the neurological system.
Tunnel syndrome: Tunnel syndrome is the term used to describe the pinched nerves or severe nerve compression caused by certain disorders.
Symptoms of Muscle Stiffness
Muscle stiffness is most commonly indicated by the ongoing pain you feel. You need to consult a doctor for symptoms like tight leg muscles. Other cautionary indicators to be aware of are:
Muscle cramps: Sudden, involuntary contractions cause considerable pain and discomfort, frequently disrupting activities.
Muscle spasms: Quick, sudden muscle spasms cause pain and temporary paralysis in the affected area.
Joint pain: Persistent joint pain, ranging from mild to severe, typically exacerbated by activity.
Aching and stiffness: Prolonged, dull pain and restricted joint and muscle flexibility that impairs all day-to-day activity.
Pain worsens with movement: Increased pain during physical exercise, reduced mobility, and impact on routine tasks.
Burning sensation in muscles: A persistent, painful burning sensation, frequently associated with overuse or nerve problems.
When to see a doctor
Consult a doctor if muscle stiffness lasts longer than a few days. Your doctor can inspect your muscles to check for underlying causes.
If muscle stiffness is associated with red-flag symptoms such as:
- Fever.
- Muscle weakness.
- Neck stiffness.
- Swelling.
Diagnosis of Muscle Stiffness
To determine muscle stiffness, your doctor will:
- Request your past medical records.
- Perform a physical examination.
- Order laboratory tests to detect muscle injury and rule out any underlying causes.
Tests can include:
- Blood tests
- MRI and CT
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Ultrasound
How is muscle stiffness treated?
If at-home treatments fail to ease tense muscles, your doctor can suggest more therapy.
Your healthcare practitioner may also suggest physical therapy. With a series of recommended exercises, a physical therapist can help you improve your strength and mobility while easing your pain. You may need additional treatments to address the underlying cause of your muscle stiffness if you have an underlying illness that contributes to stiffness.
For pain treatment, over-the-counter drugs are typically effective; however, if stronger medications are required, prescriptions may be provided.
Physical Therapy Treatment
Muscle stiffness physical therapy addresses the root causes of pain and tension, such as underuse, mobility abnormalities, postural issues, and traumas. Your physical therapist develops a personalized treatment plan to ease tight muscles, encourage healthy function, and improve the range of motion in parts of your body that are stiff after performing an initial evaluation to determine how and why you hurt.
Physical therapy for muscle tension may involve the following methods and treatments:
Therapeutic exercise and stretching: Stretching and therapeutic exercise to increase muscle strength, enhance mobility and flexibility, and promote good posture.
Cross-friction massage to improve tendon, ligament, and muscle mobility.
Strain-counterstain technique: The strain-counterstain method gradually moves problematic joints and muscles into more comfortable positions.
Dry needling releases active stimulation points increases blood flow, and relaxes tense muscles.
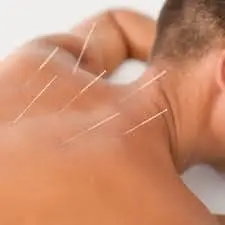
Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold therapy to the afflicted area can lessen muscle stiffness and soreness. While cold can help to lessen inflammation, heat may help to relax tense muscles.
Exercise: Frequent exercise helps ease stiffness and soreness by strengthening and stretching muscles. To assist avoid muscular strains, it’s critical to warm up before working out and to select exercises that are suitable for your level of fitness.

Stretching: By increasing flexibility and lengthening tense muscles, stretching helps lessen pain and stiffness. To allow the muscles a chance to relax and extend, it’s crucial to perform gentle stretches and hold them for at least 30 seconds.
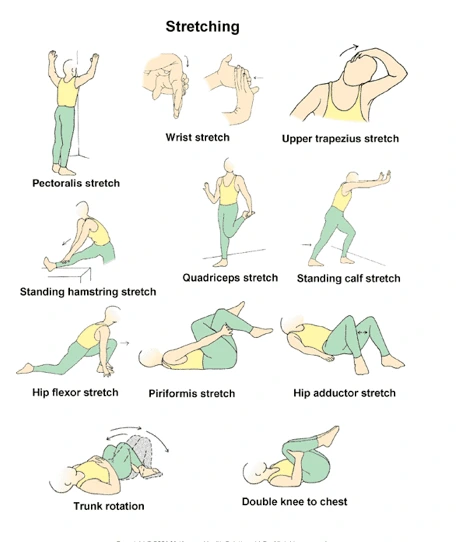
Home Treatment for Muscle Stiffness
Most people can use home treatments or over-the-counter medications to ease stiff muscles. You could try:
- Many times during the day, switch between heat and cold therapy for 20 minutes at a time.
- Rest till the stiffness lessens.
- Stretching all day long, particularly before and after physical activity.
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen etc.
Prevention
To avoid increasing muscle stiffness, people may make a few simple modifications to their lifestyles. These consist of:
- Regular exercise.
- Stretching the muscles.
- Putting on appropriate footwear when working out.
- Putting on warm clothes when it’s freezing outside.
- Maintain proper posture and make sure that the furnishings in your home and office provide support and comfort.
Summary
The feeling of tightness or pain in the muscles is known as muscle stiffness. Muscle stiffness is a common side effect of prolonged inactivity or vigorous exercise. The patient should visit a doctor when symptoms appear. Generally, at-home treatments for muscular stiffness include chilling or stretching the afflicted area.
FAQ’s
What causes muscle stiffness?
Numerous factors, such as strain on the muscles, overuse, inactivity, bad posture, and underlying medical diseases like fibromyalgia, may lead to muscle stiffness.
How long does muscle stiffness last?
Depending on the cause and intensity, muscle stiffness can persist for a few minutes to many days.
Can exercise help with muscle stiffness?
Yes, regular exercise helps improve blood flow and flexibility, which in turn can help minimize muscle stiffness.
Can muscle stiffness be prevented?
However, avoiding overuse or repetitive motions, stretching frequently, and maintaining proper posture can all help reduce muscle stiffness.
Which homemade remedies can be done for stiff muscles?
Muscle stiffness can be treated at home by using heat or cold packs.
References
- Seymour, T. (2023, October 24). What causes muscle soreness and stiffness? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320545#treatments
- Professional, C. C. M. (2024a, May 1). Muscle Stiffness. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/25147-muscle-stiffness
- Seidenburg, M. (2024, September 30). Causes of Muscle Stiffness & Treatments. BenchMark Physical Therapy. https://www.benchmarkpt.com/blog/causes-of-muscle-stiffness-treatments
- Hospitals, M. (n.d.). Muscle Stiffness – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Home Remedies. Best Hospitals in India | Medicover Hospitals. https://www.medicoverhospitals.in/symptoms/muscle-stiffness
- PhysioTattva. (n.d.). Relieve Muscle Stiffness: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions. https://www.physiotattva.com/symptoms/muscle-stiffness

4 Comments