Goniometer
What is the Goniometer?
A goniometer is an essential instrument used in several fields, including science, engineering, medicine, and meteorology. A goniometer’s principal function is to measure the angles between two or more objects. The name “goniometer” is derived from the Greek words “gonia,” which means angle, and “metron,” which means measure.
The measuring of joint area at each joint surface is known as goniometry. As a result, the study of angles is known as goniometry. It refers to the measuring of angles in any plane of the body’s joints in rehabilitation facilities.
A goniometer is the tool that therapists most commonly use to measure range of motion. In the event that a patient has a modified range of motion in a specific joint, the therapist will use a goniometer to measure the patient’s range of motion at the first assessment and again in later sessions to make sure the therapy is functioning and to evaluate its efficacy.
Anatomy and Physiology
The amount of mobility around a certain joint or body component is measured by its range of motion. Doctors, osteopaths, physical therapists, and other medical practitioners utilize goniometers, which measure the angular motion of a joint, to assess a patient’s range of motion.
He can move in three different ways, depending on the evaluation’s goals.
- Passive
- Active
- Active assistive
Types of Goniometers
Inclinometer
Among all of them, universal goniometers are the most widely used variety.

Universal Goniometer
It has two distinct formats: short arms and long arms. Short arm goniometers are used for measurements of small joints such as the wrists, elbows, and ankles. For joints like the knee and hips with lengthy levers, long arm goniometers provide greater accuracy.

Gravity Goniometer/Inclinometer
Despite the pull of gravity, an arm holding a weighted pointer stays erect.

Software/Smartphone-based Goniometer
Using a smartphone as a digital goniometer has a number of advantages, such as one-handed use, measurement ease, accessibility, and measurement tracking through applications.
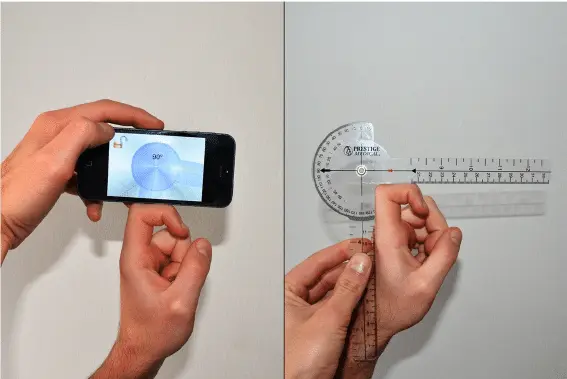
Arthrodial Goniometer
Ideal for determining the cervical spine‘s rotation, lateral flexion, and anteroposterior flexion.
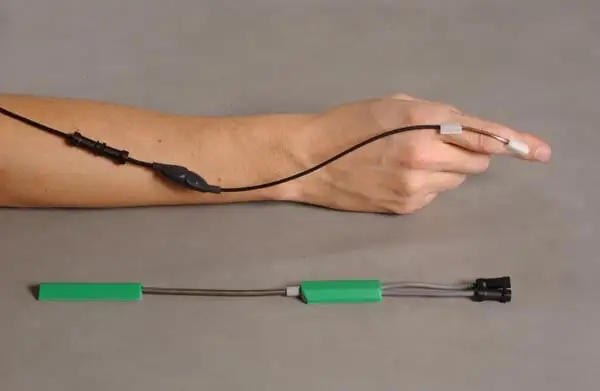
Twin Axis Electro-goniometer
Even though the inter- and intra-rater reliability of electrical and universal goniometers differs and is higher for the former, their greater usage for research makes them challenging to adapt to patient clinical assessments.
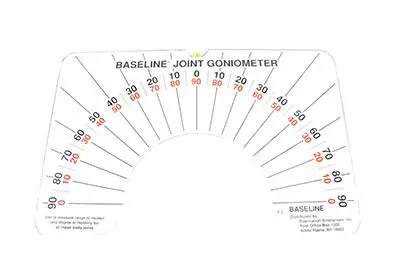
Validity and Reliability
It is questionable if goniometers are a reliable and useful tool for determining how effective a therapy is.
Measurements of knee joint angle relative to radiography joint angle have been rigorously confirmed, despite the paucity of research on goniometric validity. Universal goniometers typically offer good to exceptional reliability and are more trustworthy than visual assessment, especially for untrained examiners. Reliability varies depending on the joint and motion being assessed.
While some studies reveal no discernible variations between particular equipment, others assert that the type of goniometer used determines how reliable the data are. Overall, the study demonstrates that the universal goniometer has good intra- and inter-rater reliability and that providing explicit instructions about goniometric position enhances non-expert dependability. The marine therapist must thus take all necessary steps and guarantee that there is a chance to improve accuracy. Regarding the number of activities to do and if average ratings for repeated actions increase ratings, we’ve received conflicting input.
When using goniometry, expectations for a range of motion, readings on the incorrect side of the scale, shifts in patient motivation, or performing successive measurements at various times of the day can all be sources of inaccuracy. That is a potential.
As a result, measures taken by the same therapist at the same time of day, with the same tools, and according to a uniform protocol tend to be more accurate overall.
Goniometry Technique
A standard nomenclature should be used in goniometrics. On a broad scale, the most popular approach is the neutral zero method (0-180 degree system). The therapist has to use the same goniometer every time in order to reduce the possibility of instrumental errors.
- Align and stabilize joints correctly.
- Perform each body part’s recommended range of motion (ROM). establishes how the ends of the joints and the range of mobility feel.
- Feel around for the right bone markers.
- Align the goniometer with the reference point.
- Make sure you read the meter accurately.
- Precisely document and take the measurements (they need to measure and record the appropriate amount for both passive and active range of motion for future use).
- To prevent trick motion, which involves moving several joints simultaneously, or flaws that might skew measurements, each joint’s range of motion (ROM) needs to be maintained independently.
Indications
Uses for goniometers include:
- existence of dysfunction pertaining to the muscles, tendons, or joints.
- Establish the diagnosis
- Establish treatment objectives.
- Assessing progress
- Adapt the course of treatment based on the patient’s development.
- Manufacturing of braces
- Measurements used in research
Contraindications
The following circumstances should not be measured with a goniometer for determining an active range of motion:
- Dislocation of the joints
- fracture that continues to heal
- Osteoporosis or regions of brittle bone (because forced measures might lead to iatrogenic damage) should be avoided if movement impedes the healing process following surgery. This is especially important right after injury, when soft tissue may be damaged.
Under what conditions and with what extra care are goniometers appropriate?
- Inflammation or periarticular infection
- the severe ache that worsens while moving
- Unstable or very mobile
Parts of the goniometer
Three parts make up a universal goniometer:
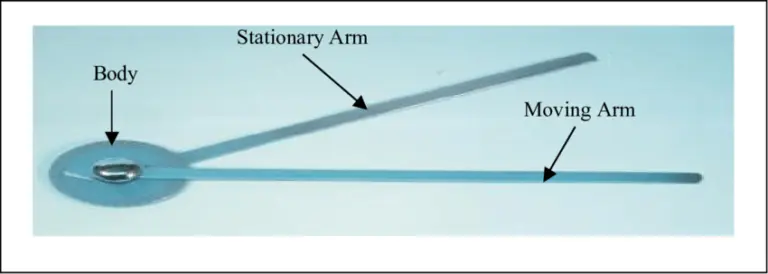
Body
Its protractor-like shape allows it to make either a complete or semi-circle. It has a scale for measuring angles.
For half-circle models, the scale goes from 0 to 180 degrees; for full-circle models, it goes from 180 to 0 degrees; and for all three, it goes from 0 to 360 degrees. The angle between ticks varies from 1 to 10 degrees.
Fulcrum
The articulated arm may move freely inside the device’s body thanks to a screw located in the middle of the casing. The moveable arm has a screw-like mechanism that may be tightened to lock it in place or released to give it more freedom of movement. The measuring joint is positioned above the body’s fulcrum.
The fixed arm
The fixed arm of the goniometer is the arm that is positioned in line with the fixed part of the measuring joint. It is structurally a part of the body and is unable to move on its own.
The moving arm
“Moving arm” describes the goniometer arm that is positioned in line with the moving component of the joint under measurement.
In goniometry, what is the physical therapist’s role?
Only professionals with the necessary training, such as licensed physicians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and others, should do goniometer tests and evaluations.
Professionals must be able to:
- Correctly align and stabilize joints.
- Perform each body part’s recommended range of motion (ROM).
- establishes how the ends of the joints and the range of mobility feel. Feel around for the right bone markers.
- Align the goniometer with the reference point.
- Make sure you read the meter accurately.
- Make sure you accurately record your dimensions.
Patient preparation
There is no need for significant preparation while using the goniometer. The patient has to provide their agreement for the examination and be informed beforehand. The connection to be inspected and its surroundings should be sufficiently exposed during the examination, which should take place in broad daylight. Please have a pre-discussion about this with the assistant if needed.
Technique or Treatment for Using the Goniometer
Goniatrimers are used to measure the range of motion in both active and passive motion. Positioning is important in goniometry because it establishes an empty start or neutral position for the joint and stabilizes the proximal joint segments.
After stabilizing the proximal joint component, the examiner gradually expands the distal joint component’s range of motion until the desired distal feel is reached.
Upon evaluating the range of motion that is accessible, the examiner puts the distal component back in its initial position. By palpating the relevant bone landmarks, the examiner signs the goniometer.
Important things the patient should know while applying the goniometry method.
- The patient moves the joint through its range of motion while the examiner removes the goniometer and takes the initial reading.
- The examiner replaces and repositions the goniometer, records the measurements, and reads them once the joint is out of range.
- After three measures are made, the appraiser determines the average. This determines the active range of motion.
- When rotating the joint, care must be made to maintain the patient still in order to obtain precise measurements. The joint capsule, surrounding muscles, and ligaments are examples of soft tissue components whose tension is greatly affected by placement.
- Employ the positions where the soft tissue structures are tense since these postures limit the range of motion more than those where the tissues are loose.
- To make sure that the soft tissue stress level doesn’t change from measurement to measurement, it’s critical to make sure the same test position is utilized each time.
- This method guarantees comparable outcomes. Any shift in position will result in inaccurate measurements. Each individual, age, and joint has a different range of motion.
Complications
There are very few goniometry-related difficulties, which are caused by technological shortcomings. These include:
- Inaccurate measurements caused by technological flaws, or measurement mistakes, can seriously affect patient care.
- Iatrogenic injury: In weak osteoporotic bones, excessive joint motion during goniometry may cause iatrogenic fractures.
Clinical Significance
Measurements of goniometry are helpful in a variety of therapeutic situations. The scope includes anything from assessing the range of motion of the spine following fusion surgery for scoliosis to tracking pine mobility in Bechterew’s illness. Goniometric testing allows us to measure how much a patient’s limb joints’ range of motion has improved.
Everyone agrees that further research is needed to evaluate whether goniometers are a legitimate and reliable enough tool to assess treatment effectiveness. The type of goniometer that is used can have an impact on how reliable the readings are. They haven’t always seen a statistically meaningful change.
Conclusion:
Goniometers can compare the efficacy of various therapies and assist in clinical decision-making for post-use care and outcome analysis of certain interventions. In circumstances when this information is meaningful and measurable, this technique assists medical experts in identifying the most effective therapies for certain diseases, ultimately optimizing and enhancing health outcomes.
FAQs
Is the purpose of a goniometer flexible?
One instrument used to assess the range of motion of different joints throughout the body is the goniometer. It is a useful tool for figuring out how flexible a joint is. Sports scientists, chiropractors, physical therapists, doctors, physical therapists, and physiologists frequently utilize it.
What are the goniometer joint’s angles?
The angles that are utilized for goniometric measurements include acute angles (less than 90°), right angles (less than 90°), and obtuse angles (more than 90°). Several practicing environments are using smartphones to monitor joint range of motion (ROM).There exist several elements that may impact the validity of the generated measurements.
What is the purpose of an eye goniometer?
In many glaucoma instances when the angle may narrow or shut, it is highly helpful. The anterior chamber angle is determined in degrees using the goniometry procedure. Using the camera below, capture an image of the anterior chamber. anterior chamber angle.
What are the advantages of using a goniometer?
The simplicity, convenience of use, and validation of the device for usage in dogs and cats are among the benefits of employing a universal goniometer to assess the range of motion. However, there are many disadvantages to this strategy.
A protractor or goniometer?
Voting and adding new comments are not permitted. A goniometer is a specialist tool used in several industries such as chemistry and medicine.
What are the goniometer’s limitations?
The universal goniometer has a drawback in that it takes two hands to operate, which makes it challenging to stabilize other body parts, particularly when there is only one practitioner present.
How is a finger goniometer used?
The Stainless Steel Short Finger Goniometer makes it simple to measure the range of motion in the metacarpal, phalangeal, and interphalangeal joints. Protractor with linear marks in inches and centimeters oriented in opposing directions on both sides. In 5° increments, the protractors measure 0-150°.
What do a goniometer’s two arms stand for?
A goniometer has two arms: one that is fixed to the circle with the angle degrees on it, and the other that moves to take measurements. To precisely measure the range of motion, make sure you comprehend how the moving arm points to the angle degrees.
What does an orthogoniometer mean?
A goniometer is a device that measures the angle of motion at a joint and is frequently used by physicians, osteopaths, physical therapists, and other health professionals to assess range of motion. Depending on the goal of the evaluation, there are three different forms of range of motion: passive, active, and active assistive.
What is the goniometer’s working principle?
It is believed that the angle formed by the proximal and distal bones making up the joint is accurately represented by the angle formed by lining up the arms of a general-purpose goniometer using bone markers.
What unit of measurement is being applied to ROM?
One common movement in joints is rotation. This is known as an “angular motion.” ROM measures employ degrees rather than inches or millimeters due to angular motion.
What is a goniometer’s contact angle?
An angle of engagement One tool for figuring out a droplet’s contact angle with an external surface is a goniometer. This might serve as a stand-in for the dampness of the surface. The droplet’s contact angle decreases to less than 90° as it starts to spread across the surface.
What is a goniometer’s basic principle?
An instrument for measuring angles is a goniometer. A physical therapist can ascertain a joint’s range of motion using the use of goniometry. A therapist trained in goiometry may assess both active and passive range of motion.
What is the range of motion in goniometry?
A goniometer is the most common tool used to measure the range of motion of a body joint. Measurement of the joint angle from the joint axis is done using a moving arm, fulcrum, and fixed arm. For accurate results while utilizing a goniometer for ROM measurements, appropriate training is necessary.
Why is ROM measured?
The term range of motion, or ROM, refers to a measurement of the suppleness of muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, and joints. For this reason, it is imperative to examine the ROM in order to evaluate the appropriateness and potential damage.
What are the applications of goniometry in physical therapy?
A goniometer is one tool used in physical therapy to measure range of motion (ROM). Its arms are both stationary and movable. The points of connection for them are joints. Each is positioned such that the center of the goniometer and the joint of interest are on the same side of the body.
References
- Parmar, D. (2023, December 13). Goniometer – Type, Technique, Indication. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/goniometer/


3 Comments