Top 9 Anti-Aging Exercises to Keep Young
Introduction:
While aging is a natural process, maintaining an active lifestyle can greatly reduce its physical effects and give you a sense of vitality, strength, and youth. Frequent exercise enhances cardiovascular health, muscle strength, flexibility, and balance—all important aspects of healthy aging. In addition to increasing posture and muscular tone, anti-aging workouts help increase metabolism, mental clarity, and general vitality.
Benefits of Anti-Aging Exercises:
Anti-aging workouts are essential for preserving your physical and mental health as you age. Frequent exercise increases bone density, slows down the loss of muscle, and maintains joint flexibility, which lowers stiffness and injury risk.
Additionally, anti-aging exercises increase metabolism, which aids in controlling body weight and preventing age-related fat growth. They also enhance posture, balance, and coordination, which reduces the chance of falls and increases the effectiveness of daily movement.
Beyond the physical advantages, regular exercise lowers stress, enhances the quality of your sleep, sharpens your memory, and elevates your mood, which over time makes you feel more youthful, confident, and full of energy.
Top 9 Anti-Aging Exercises Video:
Anti-Aging Exercises to Keep You Fit and Young:
Squats:
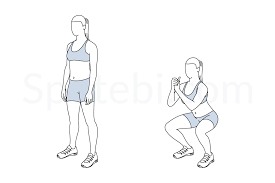
Because they improve general mobility and balance while strengthening the lower body, squats are among the best anti-aging workouts. Major muscular groups like the glutes, quads, hamstrings, and calves are targeted by this strong exercise, which helps to maintain functional strength for everyday tasks like sitting, standing, and lifting while preventing age-related muscle loss.
By using several muscles at once, squats also increase bone density, strengthen the hips, knees, and ankles, and increase metabolism. Squats help improve posture, balance, and core stability, which lowers the chance of falls and keeps your body strong, energetic, and young as you age.
Plank:

Without putting undue strain on the joints, the plank is a very powerful anti-aging exercise that increases core strength, stability, and endurance. It helps maintain a strong core that promotes proper posture and spinal alignment as you age by focusing on the muscles of the lower back, shoulders, chest, glutes, and abdomen.
In addition to improving balance and total body control for daily motions, a stronger core lowers the chance of back pain. Additionally, plank exercises increase metabolism, strengthen muscles, and promote attentive breathing, all of which enhance concentration and lower stress. Regular plank practice keeps your body resilient, steady, and young over time.
Push-ups:
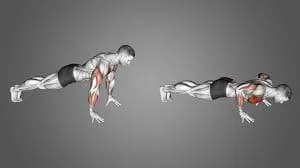
Push-ups are a great anti-aging workout that helps preserve joint stability, muscular tone, and upper body strength. They mostly target the arms, shoulders, triceps, and chest, but they also train the glutes, lower back, and core to maintain proper alignment. This full-body engagement supports everyday functional activities like pushing and lifting, maintains muscular mass, and enhances posture.
When done regularly, push-ups also increase metabolism, improve cardiovascular endurance, and increase bone density. Push-ups help maintain your body’s strength, balance, and youthful appearance as you age by simultaneously developing several muscle groups.
Jumping Jacks:
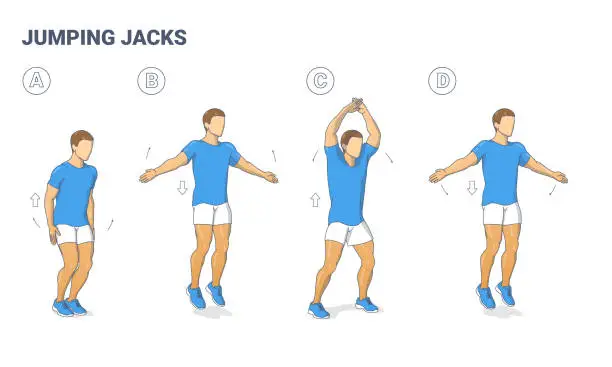
A straightforward but effective anti-aging workout, jumping jacks improve cardiovascular health, coordination, and general vitality. This full-body exercise enhances blood circulation and oxygen supply throughout the body by using the arms, legs, shoulders, and core.
Jumping jacks help maintain a healthy metabolism, improve endurance, and promote heart health—all of which are critical for controlling age-related weight gain. Jumping jacks are a dynamic exercise that promotes everyday mobility and vitality, keeping the body youthful, supple, and energetic.
Marching in Place:

All fitness levels can benefit from Marching in Place, a mild yet powerful anti-aging workout that enhances mobility, balance, and cardiovascular health. This low-impact exercise improves coordination and joint flexibility while strengthening the legs, hips, and core.
Additionally, marching in place enhances blood circulation, raises heart rate, and promotes greater endurance without straining the lower back or knees. Frequent practice lowers the risk of falls as you age by enhancing walking skills, stability, and posture. Marching in place is an easy and accessible way to maintain a youthful, energetic, and active body over time.
Walking Lunges:

Walking lunges are an effective anti-aging exercise that improves coordination, strength, and balance while encouraging functional movement. Additionally, walking lunges strengthen the core, increase hip mobility, and improve posture, making daily tasks like bending, walking, and climbing stairs safer and easier.
They promote healthy aging and lower the chance of falls by testing balance and joint control. Regularly performing walking lunges keeps your body strong and youthful by increasing muscular tone, bone density, and general movement confidence.
Tree Pose:

A great anti-aging yoga pose that enhances stability, balance, and mental clarity is the tree pose. In addition to improving joint stability and posture—both crucial for a healthy aging process—this position strengthens the legs, ankles, and core. Additionally, Tree Pose enhances body awareness and coordination, which lowers the chance of falls and increases general mobility.
The nervous system is calmed, stress is decreased, and mental clarity is improved by deliberate breathing and focus. Frequent Tree Pose practice promotes improved alignment, inner balance, and a sense of calm confidence—all essential components for maintaining stability, youth, and physical fitness as one ages.
Bicycle Crunches:
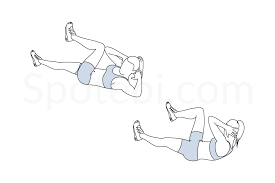
Bicycle crunches are a powerful anti-aging workout that enhances spinal mobility, coordination, and core strength. By focusing on the abdominal muscles, particularly the obliques, this dynamic exercise helps maintain a strong midsection that promotes good posture and lessens lower back pain.
By using several muscle groups simultaneously, bicycle crunches help improve body control and balance. They help prevent age-related core weakening, improve movement efficiency, and increase muscle endurance when done regularly. Bicycle crunches increase stability, lessen back pain, and create a more youthful, athletic body by maintaining a strong and flexible core.
Bridges:

Bridges are a very powerful anti-aging exercise that improves hip mobility and spinal stability while strengthening the glutes, lower back, and core. By stimulating the posterior chain, which is necessary for proper posture and fluid movement, this exercise helps mitigate the consequences of extended sitting and age-related muscle weakening.
Additionally, bridges improve overall balance and coordination, lessen lower back pain, and promote improved pelvic alignment. Bridges assist in preserving functional strength for everyday activities like walking, bending, and standing by enhancing lower body muscular activation and blood circulation. This keeps your body strong, stable, and youthful as you age.
Conclusion:
One of the best methods to remain active, fit, and young at any age is to incorporate anti-aging workouts into your daily routine. Exercises that enhance strength, balance, flexibility, and cardiovascular health include squats, planks, push-ups, jumping jacks, marching in place, walking lunges, tree posture, bicycle crunches, and bridges.
Frequent exercise lowers the risk of age-related weakness and stiffness while maintaining muscle mass, promoting joint health, improving posture, and increasing energy. You may encourage longevity, self-assurance, and general well-being by being consistent and selecting exercises that meet your level of fitness. This will enable you to feel stronger, move more effectively, and live a healthier, younger life.
FAQs:
Which muscle is the hardest to develop?
Due to their high endurance fibers and frequent daily use, the calves are typically the hardest muscles to grow. These are followed by stubborn areas like the forearms, rear deltoids, and occasionally the upper chest, biceps, or hamstrings, which require concentrated, intense training to grow due to genetics, neglect, or how they are integrated into other movements.
What is the most athletic body type?
Most people consider mesomorphs to be their “athletic” body type. These guys have no trouble burning fat and gaining muscle. Mesomorphs should maintain a high-protein diet to sustain lean muscle mass and can afford a moderate amount of carbohydrates to power their training.
What should I consume to quickly increase muscle?
After an exercise, milk and dairy products like yogurt and cottage cheese are frequently consumed as sustenance. Due to the high protein content of milk, which aids in muscle rehabilitation. Furthermore, carbohydrates included in milk and dairy products can help build muscle when paired with protein.
Which foods are naturally high in creatine?
Red meat, fish (herring, salmon, tuna), and fowl (chicken) are the main sources of natural creatine, with dairy products containing lower amounts. Plant-based diets give the body the building blocks it needs to produce its own creatine. Vegetarians can obtain building blocks from legumes, nuts, and seeds, but the best sources are beef and herring.
Which protein is the best for building muscle?
Whey protein for muscle growth: This protein encourages muscle growth and increases muscular mass. Because protein supplements increase muscle strength and enhance performance, many trainers favor them for guys who are bodybuilders, athletes, and frequent gym patrons.
In the gym, which muscle grows the fastest?
Due to their size, frequent participation in daily activities, and capacity to handle heavy loads with compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and rows, the legs (Glutes, Quads, Hamstrings) and back (Lats, Traps) typically grow the fastest in the gym. This results in faster visible gains, especially for beginners, though individual genetics, diet, and consistency are crucial.
What is the key to gaining muscle after the age of fifty?
The best method for gaining muscle at any age is resistance training. This can involve challenging muscles with free weights, resistance bands, or even your own body weight. Aim for exercises like squats, which are excellent for strengthening the lower body.
What is the simplest muscle to develop?
Because they are large muscle groups that are frequently used in daily life and respond well to heavy compound lifts like squats, rows, and deadlifts, the quadriceps (thighs) and traps are involved. Additionally, arms (biceps/triceps) grow relatively quickly due to isolation work.
Why do bodybuilders avoid cardio?
Reaching your bodybuilding objectives requires more than just lifting heavy weights; it also entails maintaining overall health, optimizing muscle definition, and ensuring cardiovascular fitness. Fearing that cardiovascular conditioning will impede muscle growth, many bodybuilders are reluctant to include it in their regimen.
At what age is it most difficult to grow muscle?
Building muscle beyond 40 is considerably more challenging due to hormonal changes. Men begin to gradually lose the muscle-building hormone testosterone in their 30s, whereas women experience this hormonal shift more quickly after menopause.
Which muscle is the most difficult to develop?
Due to their high endurance fibers and frequent daily use, the calves are typically the hardest muscles to grow. These are followed by stubborn areas like the forearms, rear deltoids, and occasionally the upper chest, biceps, or hamstrings, which require concentrated, intense training to grow due to genetics, neglect, or how they are integrated into other movements.
Does physical activity slow down the aging process?
Although it can’t stop biological aging itself, exercise does significantly slow the effects of aging and promote “healthy aging” by preserving bone, muscle, brain, and cellular function. It may even reverse some biological markers of aging, such as telomere shortening, lowering the risk of chronic diseases, and prolonging active life. Frequent exercise keeps you physiologically younger and more energetic by preventing age-related decreases in strength, metabolism, and cognitive function.
Which workout gives you a nine-year-younger feeling?
What they discovered is as follows: The longest telomeres were found in adults who engaged in high levels of activity, which were defined as jogging for 30 minutes (for women) or 40 minutes (for males) five days a week. In terms of biology, this group was 7 years younger than moderately active individuals and 9 years younger than sedentary individuals.
What are the seven anti-aging pillars?
Inflammation, stem cell regeneration, macromolecular damage, stress, proteostasis, metabolism, and epigenetics are the seven pillars. The interwoven network illustrates the connections between the pillars. Age-related illnesses and aging share these cornerstones.
What is the best anti-aging exercise?
Resistance exercise: Resistance exercise is the best option if you wish to genetically reverse your age! This kind of workout maximizes your level of endurance and strengthens your muscles. You can accomplish this by including bands, weights, bars, dumbbells, and other such equipment in your regular exercise routine.
References:
- The 14 best exercises to keep you young. (2016, August 1). Men’s Health. https://www.menshealth.com/uk/building-muscle/a750252/14-best-exercises-to-stay-young/
- Motion, B. T. (2021, May 20). Top 10 Anti-Aging exercises. Back to Motion. Denver Physical Therapy. https://backtomotion.net/top-10-anti-aging-exercises/
- Homestead Village. (2023, September 26). 9 Great exercises to help you feel young. https://www.homesteadvillage.org/blog/9-great-exercises-to-help-you-feel-young/
- Crain, E. (2025, December 15). 15 ways exercising can make you look younger. Health. https://www.health.com/fitness/15-ways-exercise-makes-you-look-and-feel-younger
- Bhattacharya, S. (2024, September 26). 14 effective strength training and flexibility exercises to combat ageing. Healthshots. https://www.healthshots.com/fitness/muscle-gain/anti-ageing-workout/