Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
What is a Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)?
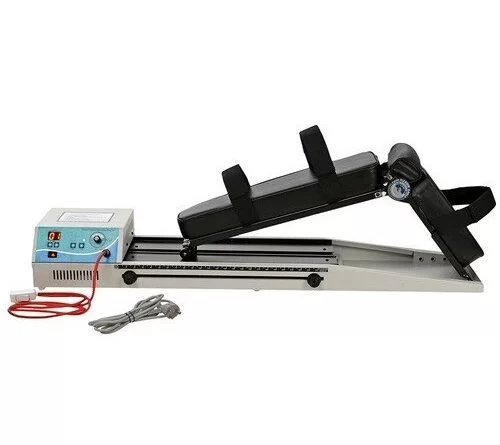
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), also known as cold laser therapy or photobiomodulation, is a therapeutic technique that employs low-power lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to treat various conditions.
LLLT’s (low-level laser treatment) objectives are to decrease inflammation and speed healing by applying low-level lasers to the layers of skin or bruises. It is beneficial for disorders like lymphoedema and complicated wounds that don’t respond to conventional therapies.
An applicable wavelength of sunlight diminishes during minimally invasive light-based laser treatment (LLLT). It doesn’t generate any heat, vibration, or sound. Biological stimulation or photobiology are other names for it. The cells that make up connective tissue, known as fibroblasts, are thought to be affected by the activity of low-level laser therapy, which also has anti-inflammatory qualities and speeds up the healing process.
Light may penetrate hard and soft tissues, especially the skin, between 660 and 905 nm.
Class III lasers are referred to as LLLTs, or low-power lasers, whereas class IV lasers in the USA are known as High Power Laser Therapies (HPLTs), lasers with an output power of 500 mW or higher. Heat is generated on the outermost layer of the skin by HPLTs because of their higher power density (the illumination). As LLLT therapy doesn’t result in a heating tactile sensation, they are commonly called “Cold Lasers.”
Mechanism of low-level laser therapy:
The mechanism underlying LLLT is still being studied. It appears that the effects of LLLT are restricted to a particular range of laser wavelengths and that LLLT administered below the dosage range is ineffective. Photosynthetic reactions are well-studied in biology, and light-loving plants (LLLTs) make use of the Grotthuss-Draper law, which stipulates that a chemical reaction cannot take place unless a chemical component absorbs light. Consensus holds that the respiratory enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, which is part of the chain of electron transportation in mitochondria, is the chemical substance implicated in low-level laser therapy.
The adverse effects of low-level laser therapy:
Notable benefits of low-level laser therapy for physiotherapy include the following, and this instrument can be used to enhance other therapies like therapeutic exercise:
The lowering of inflammation:
- Within hours or days, it can occur.
Alleviation of pain:
- Faster tissue Regenerating: LLLT stimulates the development of endothelium, keratinocyte, lymphocyte, and fibroblast cells.
Effectiveness for difficult wounds:
- In comparison to standard therapy alone, LLLT has been demonstrated to accelerate ulcer healing and reduce the need for amputations in individuals with diabetes.
Efficacy in treating lymphedema:
- Research has demonstrated that lymphoedema patients, especially those whose lymphoedema is associated with breast cancer, can greatly reduce their arm volume and circumference with LLLT. The total number of patients in the study, meanwhile, can occasionally reach an upper limit, and the results can vary.
low-level laser therapy for regenerating your skin:
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been associated with skin tissue exposure to red and near-infrared (NIR) light, whereas typical laser treatments such as ablation and cutting require powerful light. The electron transport system is then activated by an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), nitric oxide generation, and the activation of many signaling pathways.
LLLT has been utilized more frequently in recent years to treat psoriasis, inflammatory acne, scars, and fine wrinkles. The stimulation of stem cells promotes tissue healing and repair. The main advantage of LLLT for the skin is the lack of side effects or the presence of very minor ones.
Paleness in specific body areas is a common sign of vitiligo, a disorder that changes the color of the skin. Patients experience skin that is patchy with white areas. Additionally, by preventing autoimmunity, this treatment also lessens depigmentation.
The use of LLLT to treat acne shows a lot of potential. Mechanistically, light—especially blue light—is absorbed by porphyrins made by Propionibacterium acnes as part of their regular metabolic process. This light consumption initiates several photochemical responses that have an antibacterial impact.
low-level laser treatment for hair growth:
On the epidermis, hair follicles (HF) are tunnel-shaped structures that go through repeated regenerative cycles. In this cycle, there are three phases here; anagen, catagen, and telogen.
Rapid cell division characterizes the anagen stage. Apoptosis drives the telogen arrangement, sometimes referred to as the resting stage, which follows the catagen arrangement.
Through a change in the hair phase, LLLT reduces androgenetic alopecia (AGA) in both genders. Mechanically speaking, LLLT brings telogen HFs back into the anagen phase. By increasing the generation of antioxidants and reactive oxygen species, it could promote keratinocyte and fibroblast mitosis. The cytochrome c oxidase (COX) gene facilitates the previously listed processes and is in charge of absorbing low-intensity light.
Whenever LLLT and functioning anagen cycle HFs are connected, cell division grows faster and the stage of anagen widens. It is known that exposure to lasers restores the physiological regeneration of hair follicles (HFs) on the scalp. These HFs may have been affected by chemotherapy-induced cancer medicines that cause alopecia areata (AA), AGA, and hair misfortune.
The findings indicate that scalp hair loss was reduced and hair thickness and diameter were increased during the LLLT-modulated hair period. Furthermore, LLLT has been demonstrated in multiple studies to lower inflammation, which is what initiates hair growth.
In general, LLLT improves alopecia patients’ clinical condition. AGA can be safely and effectively treated with LLLT, as multiple clinical studies have demonstrated. Significantly, individuals with non-scarring alopecias and those who did not respond to conventional hair loss therapies were found to benefit from this treatment.
How might low-level laser therapy work in conjunction with gradual hair loss?
First off, LLLT makes use of a light source that emits a certain wavelength (usually between 630 and 670 nanometers) with a unique capacity to absorb the chemicals found in hair follicles. This kind of light permeates the scalp and activates the epidermal stem cells that are in charge of hair follicle regeneration. In summary, DHT accumulation in the follicles is inhibited by LLLT because it promotes the metabolic activities required for hair production.
afterwards Treatment
Depending on your health, the number of alternative therapies you are receiving, the extent of your hair loss, and other factors, the success of laser hair therapy varies widely from person to person. The first noticeable effects of LLLT hair loss treatment become apparent in the second month following treatment initiation.
The results of the therapies become clear after the first four to six discussions. The sessions are held once a week. There are twenty-four sessions in a whole therapy cycle. The outcomes of the LLLT can be sustained for a long time with home maintenance after the entire course of treatment is finished.
Potential Advantages of Low-Level Laser Therapy:
Research and clinical trials on low-level laser therapy point to several advantages, such as:
Promotes detoxification and eliminates fat that could encourage weight loss:
- Low-level laser treatment causes the fat inside fat cells to soften and become damaged, which makes it easier for the body’s lymphatic drainage system to start removing the fat from those areas.
- At Restoration Healthcare, an Irvine functional medicine center, we reset the body’s metabolism for long-term health advantages by using low-level laser therapy as part of a medically supervised detox, fat-reduction, and/or weight-loss plan.
Reduces pain (analgesic):
Below are several ways that low-level laser therapy reduces pain:
- reduces the sensitivity of nerves
- lessens inflammation
- increases the brain’s and the adrenal glands’ synthesis of endorphins, enkephalins, and opioids, among other painkilling substances.
- Non-invasively stimulates acupuncture and muscle trigger points to release tensed muscle fibers.
Reduces inflammation:
- By widening blood vessels and stimulating the lymphatic system, low-level laser therapy helps swollen areas caused by inflammation or trauma to drain.
Accelerates tissue healing and cell proliferation:
- Deep tissue penetration of low-intensity light increases cell energy availability and speeds up cell growth and reproduction. By raising the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ADP), it promotes cell nourishment and waste removal, which is particularly useful in the regeneration of tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
- LLLT is particularly useful in healing burns and open wounds because it also promotes the growth of fibroblasts in injured tissue. Fibroblasts are the key proteins needed to replace old tissue or repair tissue injuries.
Improves vascular activity:
- Two methods that low-level laser therapy lessens scarring and expedites the healing process are by:
- promotes the formation of new capillaries in damaged tissue at a much faster pace and widens and dilates blood vessels to increase blood flow to those areas.
Boosts metabolic activity:
- In addition to promoting the synthesis of particular pro-healing enzymes in blood cells, low-level laser therapy also enhances the transportation of nutrients and oxygen.
- Reduces the production of scar tissue: Surgery, wounds, scratches, and burns all cause fibrous (scar) tissue to form less frequently when low-level laser therapy is used.
Promotes nerve function and regrowth:
- Axon growth and nerve cell reunion are accelerated by low-level laser therapy.
Supports immune system function:
- By increasing the synthesis of lymphocytes and immunoglobulins and by making it easier for white blood cells to enter injured tissue, low-level laser therapy directly influences immunological function.
Lessens dependency on drugs:
- Low-level laser therapy is thought to be a secure, organic, and efficient substitute therapy that can assist in lowering or doing away with the need for opioids other analgesics, and anti-inflammatories, alongside other drugs having unfavorable side effects that could be dangerous.
Uses for Low-Level Laser Therapy:
There are several uses for low-level laser therapy, such as the following:
- Detoxification, fat loss, and weight management: Low-level laser therapy, such as the protocol now offered at Restoration Healthcare, can help the body get rid of extra fat that may be causing dysfunction or long-term illness when used as a complementary component of an integrative plan of care.
- Musculoskeletal injuries and pain: Tendonitis, bursitis, tennis elbow, neck discomfort, lower back pain, knee pain, muscular spasms, and joint swelling are examples of musculoskeletal ailments and pain.
- swelling: Examples of swelling include dental swelling, carpal tunnel syndrome, and autoimmune swelling (from a condition known as rheumatoid arthritis, for instance).
- Skin rejuvenation: it includes treating edema (swelling), dermatitis, vitiligo, burns, psoriasis, and rashes.
- Wound healing: For injuries that don’t respond to therapy, such as diabetes-related injuries.
- Acupuncture: For patients who are uncomfortable with needles, consider acupuncture.
The limitations of low-level laser therapy:
- Eyes: Wear the proper safety glasses for everyone in the room, and avoid pointing laser beams directly into people’s eyes.
- Cancer: Unless the patient is receiving chemotherapy and LLLT can be used to lessen side effects such as mucositis, do not treat over the site of any known primary carcinoma or subsequent metastasis.
- Pregnancy: Avoid applying direct treatment to the growing fetus.
- Epileptics: Be advised that individuals who are photosensitive and/or epileptic may experience seizures in response to low-frequency pulsed visible light (<30Hz). According to reports, patients who received placebo devices in trials had the same negative effects from LLLT.
Low-Level Laser Therapy’s minor side effects:
Abnormalities associated with LLLT are quite rare. Early on in the course of treatment, a few months after starting LaserComb, some patients had a transient case of telogen effluvium. However, after using LaserComb consistently, this issue went away.
There have been instances where LLLT in the skin developed a slight redness that disappeared on its own without further treatment. Some patients treated skin became somewhat pigmented, swollen, and itchy. Patients may have blisters, burns, or scars on the treated skin if laser treatments are not done properly.
Evidence
2017 saw the publication of a comprehensive study and meta-analysis that determined LLLT to be a successful therapeutic approach for reducing pain in adult muscular and skeletal disorders individuals. Likewise, it was established that implementing the correct dosage requirements provided by the World Association of Laser Therapy (WALT) strengthened productivity.
Inconsistent data about the effectiveness of laser therapy for treating acute or chronic neck pain or shoulder discomfort were discovered in a 2017 study titled “A systematic overview of current evidence addressing effective treatment options for musculoskeletal pain in primary care.” Low-level laser therapy may be used in conjunction with physical therapy and/or surgery to treat knee discomfort.
FAQs
What does low-level laser treatment aim to achieve?
In photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT), also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), red or near-infrared (NIR) light is utilized to regenerate, recover, and stimulate different biological systems as well as to fix effects caused by injury or illness.
What is the low-level laser therapy success rate?
Participants in a clinically controlled study reported a 39% increase in hair growth, leading the researchers to conclude that low-level laser therapy considerably increased the number of hairs. Numerous further studies have confirmed that the laser cap is a secure and reliable method for enhancing both men’s and women’s hair growth.
What drawbacks does LLLT have?
For treatments, patients frequently need to see their doctors two or four times a week at the latest. After treatments, old injuries may get worse for a few days, but for most patients, this feeling only lasts for a few days.
References
- Low-level laser therapy. (2024, April 12). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-level_laser_therapy
- Low-Level Light Therapy for Hair Growth and Skin Rejuvenation. (2024, January 31). News-Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Low-Level-Light-Therapy-for-Hair-Growth-and-Skin-Rejuvenation.aspx
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): What are the benefits? | Top Doctors. (2023, December 18). Top Doctors. https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/medical-articles/low-level-laser-therapy-lllt-what-are-the-benefits
- Top 10 Health Benefits of Low-level Laser Therapy. (2024, May 28). Functional Medicine Doctor Irvine. https://rhealthc.com/low-level-laser-therapy/top-10-health-benefits-of-low-level-laser-therapy/
- Best Low Light Laser Therapy in Chennai | Laser Therapy in Chennai | Laser Hair Removal in Chennai | Laser Hair Removal Treatment in Chennai | Skin Laser Treatment in Chennai | Skin Lightening Treatment in Chennai | Skin Lightening Treatment Cost in Chennai | Laser Treatment for Facial Hair Removal in Chennai. (n.d.). https://www.radianceskinandhaircare.com/home/low-light-laser-therapy.html