How to Cure Severe Back Pain?
Introduction:
Severe back pain can significantly impact daily life, making even simple tasks challenging. It often results from muscle strain, poor posture, spinal issues, or underlying medical conditions.
Effective treatment begins with identifying the root cause, followed by a combination of rest, physiotherapy, exercise, and medical interventions. Early care and proper guidance are key to long-term relief and recovery.
A prevalent presently crippling disease, severe back pain can interfere with everyday activities and restrict movement. Poor posture, spinal disc disorders, strained muscles, or underlying medical conditions can all cause it. This manual offers tried-and-true strategies for pain management, healing, and avoiding recurrences by integrating lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and medical guidance.
Various strategies to reduce your back pain:
Strengthen your core muscles:
- Since we hardly ever engage our core muscles in daily activities, we must tone them with targeted, specialized exercises.
Stretch daily:
- Tight muscles are the root cause of many back issues.
Avoid sitting with poor posture:
- Your lower spine’s discs are under considerably more strain when you sit poorly than when you stand.
Lift correctly:
- It is quite easy to twist in the wrong direction when lifting something heavy.
Watch your weight:
- Your back is strained by excess weight. Over time, the spine may become unnaturally curved, and the back may lose its appropriate support.
Quit smoking:
- Smoking reduces blood flow to the vertebral discs that provide cushioning. This might cause disc degeneration to occur more quickly. This raises the possibility of a fracture caused by osteoporosis, a disorder that makes bones brittle and weak.
Sleep Better:
- Because your back pain may worsen when you don’t get enough sleep, it can be a vicious cycle. Back pain can also be made worse by sleeping in a bad position. Attempt to lie on your side.
Good Posture:
- Additionally, bad posture may worsen back pain, particularly if you spend a lot of time sitting down. Avoid hunching over your keyboard. Consider placing a rolled towel or pillow between your seat and lower back.
Medication From the Store:
- Some people might not be able to take either due to their side effects. Consult your physician before using painkillers. Research indicates that you will most likely require multiple forms of treatment.
Prescription Pain Relievers:
- For pain management, to prevent overdosing on specific active ingredients, it is crucial to discuss any additional drugs you are taking, including over-the-counter ones, with your doctor or pharmacist. To lessen terrible muscle spasms, your doctor might also recommend muscle relaxants.
Antidepressant Medications:
- Your doctor may prescribe antidepressant drugs to manage chronic low back pain, even if you’re not depressed. How antidepressants alleviate chronic pain is unclear. The impact of antidepressants on chemical messengers is thought to have an impact on the body’s pain signals.
Physical Therapy:
- You can learn from physical therapists how to move, sit, and stand in ways that maintain the right alignment of your spine and reduce back pain. Additionally, they can teach you specific exercises to build stronger back-supporting core muscles. Research indicates that improving your strength, flexibility, and endurance can help reduce back pain, but it takes time.
Don’t Rest an Achy Back:
- For back pain, doctors used to recommend bed rest. However, we now know that one of the worst things you can do is to lie motionless. It may worsen back pain and cause additional issues. It’s critical to stand up and gradually resume your activities. Try yoga, walking, or swimming.
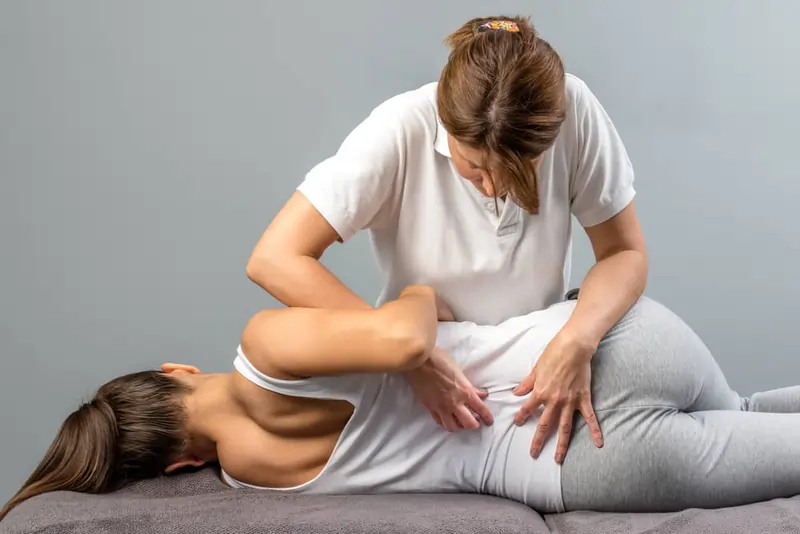
Hands-On Therapy:
- According to a recent study, patients with chronic back pain experienced better pain and functionality after receiving a massage once a week for ten weeks. After a year, the benefits diminished after roughly six months. Spinal manipulation is another manual method. When administered by a qualified practitioner, this treatment can help restore lost mobility and alleviate structural issues with the spine.
Nerve Stimulation:
- Certain methods that activate nerves to lessen chronic back pain are being researched. If more conservative treatment isn’t working for you, your doctor could think about including acupuncture in your regimen.
Talk Therapy:
- Seeing a psychologist for back pain might sound odd. However, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is highly beneficial for chronic back pain both in the short and long term. For instance, CBT might focus on how individuals with back pain perceive exercise and the reasons behind their avoidance of it to assist in altering their reaction to physical activity. Significant reductions in pain and impairment have been reported by CBT participants.
Biofeedback:
- A unique device called biofeedback helps you teach your brain to regulate how you react to pain. According to some research, it reduces back pain by roughly 30%, making it more effective than medicine.
Spinal Injections:
- To alleviate your back pain, a specialist might suggest a spinal injection. Physicians who specialize in pain management may employ a variety of injectable techniques. For instance, the inflammation causing the pain may be reduced by a corticosteroid injection. To prevent potential side effects, your doctor may restrict the number of injections you receive annually, depending on the type.
Back Surgery:
- Your surgeon may suggest a discectomy to remove some disc material if a bulging disc is pressing against a nerve. These procedures are risky and not always effective, just like any other.
Conclusion:
Accurate diagnosis, temporary pain management, and long-term rehabilitation through physical therapy and lifestyle modifications are all necessary to cure chronic back pain. The best and longest-lasting effects come from strengthening your core, correcting your posture, and continuing to be active under medical supervision, even though medicine and rest can assist at first. See a doctor to rule out serious problems and look into cutting-edge treatment options if the pain is ongoing or getting worse.
FAQs
Which back pain symptoms are warning signs?
“Red flags” for back pain are indications of a significant underlying illness that frequently calls for prompt medical intervention. These include neurological symptoms, including numbness or weakness, fever or infection symptoms, loss of control over the bowels or bladder, severe or increasing pain, and inexplicable weight loss. Red flags may also include steroid use, fatigue, pain at rest or night, trauma, and signs of brain malfunction.
What is the duration of back pain?
Some people, though, might endure agony for several months. It is advised to see a healthcare provider for additional assessment and therapy if back pain lasts more than a month.
What makes women’s backs hurt?
Women’s back pain can result from several things, such as strained muscles, lifestyle decisions, changes in hormones, and certain medical disorders. Back pain can also be caused by pregnancy, premenstrual syndrome, and endometriosis.
Are muscles or the spine responsible for back pain?
Its duration: Back muscle inflammation can last for more than three days. Compared to muscular pain, spinal pain is less frequent and occurs intermittently. Spinal pain frequently radiates to other bodily areas.
Why is paracetamol not recommended for back pain?
Although various forms of pain and fever can be effectively treated with paracetamol, the mechanisms of action for back pain may differ, and the evidence is being used to evaluate therapeutic guidelines.
How can someone with back pain sleep?
Using pillows for support and getting a firmer mattress can also help reduce pressure and enhance the quality of your sleep.
What symptoms indicate disc or back muscle pain?
There are many different causes of back pain, and it can be difficult to tell the difference between disc and muscular problems. Whereas disc pain can be incapacitating, tingling, and radiate down the legs, muscle pain is typically isolated, similar to soreness after a workout.
How can severe back pain be managed?
Chronic back pain may be alleviated by nonsurgical spine treatments such as electrical nerve stimulation, laser therapy, biofeedback therapy, massage, and acupuncture. All things considered, these tactics are worthwhile to investigate because their possible advantages greatly exceed their possible drawbacks.
References
- Ways to relieve back pain. (n.d.). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/ss/slideshow-relieving-back-pain
- Cultivating Health. (2025, May 5). 8 tips to help ease your back pain | Cultivating Health. cultivating-health. https://health.ucdavis.edu/blog/cultivating-health/8-tips-to-help-ease-your-back-pain/2022/06
- 7 ways to treat chronic back pain Without surgery. (2025, April 4). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/back-pain/7-ways-to-treat-chronic-back-pain-without-surgery