Vagus Nerve
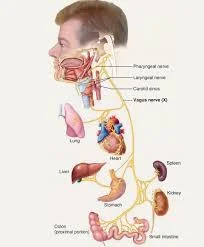
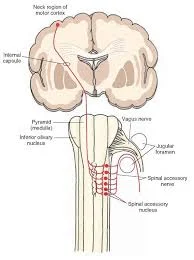
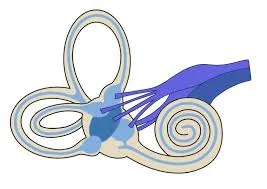
Introduction The vagus nerve, also known as the 10th cranial nerve or CN X, is one of the longest and most complex nerves in the human body. It starts in the brainstem, travels through the neck, chest, and abdomen, and branches out to the heart, lungs, digestive tract, and even the tongue and ears. The…