Vestibulocochlear nerve
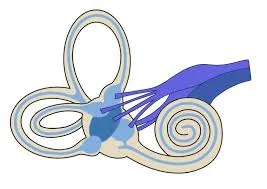
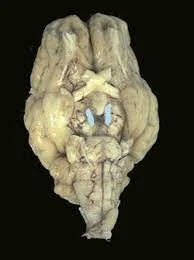
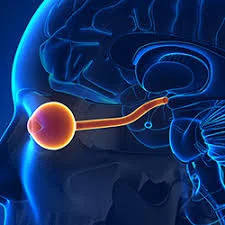
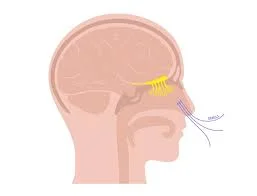
Introduction The vestibulocochlear nerve is also called cranial nerve eight (CN VIII). The vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) connects the vestibular and cochlear nerves. It is situated within the internal auditory meatus (internal auditory canal). The cochlear nerve controls hearing, while the vestibular nerve controls balance and eye movements. CN VIII injuries are caused by pathological…