When Knee Pain is Serious?
Introduction:
Adults frequently complain of knee pain, which is typically caused by normal wear and tear from daily activities, including walking, bending, standing, and lifting. Knee pain and issues are also more common in athletes who run or participate in sports requiring rapid pivoting or jumping.
However, knee pain can be annoying and even incapacitating in some situations, regardless of whether it is caused by aging or an injury.
Which knee problems are common?
An injury or a sudden action that strains the knee can cause other knee issues. The following are examples of common knee issues:
Torn cartilage: Sprains can frequently result in cartilage tears. Wearing a brace during an activity may be part of the treatment to prevent future damage to the knee.
Tendonitis: Overuse of a tendon during specific activities, such as running, leaping, or cycling, can lead to tendon inflammation. Jumper’s knee is the term for patellar tendonitis. In sports like basketball, this frequently happens when the force of landing on the ground after a jump strains the tendon.
Arthritis: The most prevalent kind of arthritis affecting the knee is osteoarthritis. The degenerative process of osteoarthritis causes the joint’s cartilage to progressively deteriorate. People in their middle and older years are frequently affected. Excessive joint stressors, like obesity or recurrent injuries, might result in osteoarthritis. By inflaming the joint and eroding the knee cartilage, rheumatoid arthritis can also have an impact on the knees.
Symptoms of knee pain:
An infection or inflammatory disease may cause pain or swelling throughout the entire knee, whereas a bone fracture or torn meniscus only manifests symptoms in one area.
Knee joint pain or knee problems can range in severity from a little ache to a more severe and incapacitating pain. Additional symptoms and indicators associated with knee pain include:
- Limping because of the pain
- Walking up or down stairs is difficult because of a sprain (ligament injury).
- Knee swelling, stiffness, and redness
- Crunching or popping sounds.
Ten Warning Signs Not to Be Ignored:
Deformity of the Joint:
A fracture, dislocated kneecap, or patella damage could be the cause of any abnormality you observe in your knee joint, such as a distorted appearance in comparison to the healthy knee.
Difficulty Walking:
It’s critical to get medical help if you start to limp or purposefully avoid walking because of worsening knee pain. Such severe pain could be an indication of a degenerative disease or an underlying bone damage that needs to be evaluated and treated by a physician.
Inability to Hold Weight:
Your affected knee’s incapacity to support weight could be a sign of a number of knee disorders, all of which require immediate medical attention for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Knee Instability:
Joint instability, which is frequently associated with ligament issues, is indicated by a wobbling sensation or a sense that your knee might collapse. Ignoring knee instability and carrying on with daily tasks could make the issue worse.
Less Sensation in the Knee:
Although knee problems frequently result in pain, the lack of pain can also be worrisome. Absence of pain, particularly while applying pressure to the knee, could be a sign of a significant medical condition, such as sciatica or another problem unrelated to the knee.
Pain That Affects Your Daily Activities:
Any knee pain that becomes a difficulty in your everyday activities, such as walking, jogging, working, or commuting, should be evaluated by a specialist.
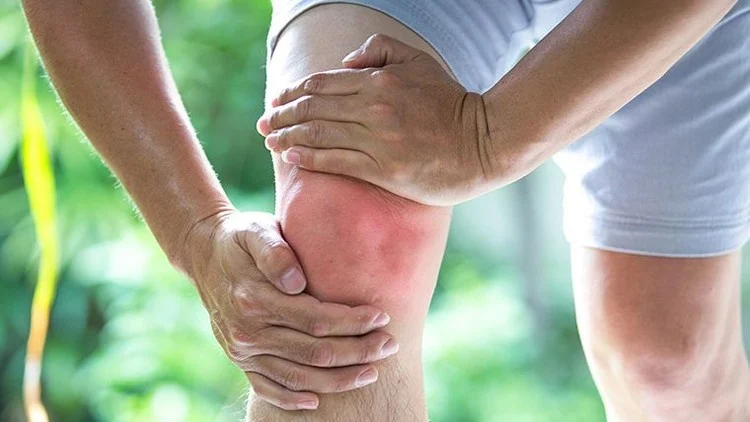
Redness or Swelling Around the Joints:
Examine the region for warmth or soreness if you notice redness or swelling, as these signs could indicate an infection.
Your range of motion may be limited after a knee injury due to internal edema. You should be concerned if you have trouble fully bending or straightening your leg. See a physician for a thorough assessment if you observe a chronic reduction in range of motion that lasts longer than twenty-four hours.
Treatment of knee pain:
Medications:
You should see your doctor for a thorough review if you frequently take over-the-counter anti-inflammatory pain relievers for knee pain.
Physical Therapy:
Strengthening the muscles surrounding your knee through physical therapy or physical therapy sessions can occasionally increase its stability and aid in mechanical movements. Seeing a physical therapist might also help prevent injuries or make existing ones worse.
Injections:
In certain cases, administering medication directly into the knee may be beneficial. The two most popular injections used to treat knee pain are lubricants and corticosteroids. Injections of corticosteroids can help reduce knee inflammation and pain associated with arthritis. While lubricants that are identical to the fluid that is already in your knee joint aid in pain reduction and movement restoration, they typically need to be repeated every few months.
Surgical Treatment:
Arthroscopic Knee Surgery:
A typical outpatient surgical technique is arthroscopic knee surgery, which allows a surgeon to view inside the knee through a few tiny incisions using a fiberoptic camera.
Partial knee replacement:
The surgeon may use metal and plastic components to replace the damaged areas of your knee during this treatment. Compared to total knee replacement (TKR), this treatment has a shorter recovery period because it only replaces a portion of the knee joint.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR).
What are some homemade remedies to get rid of knee pain?
Even though over-the-counter pain relievers frequently relieve knee pain, if you take them frequently, you should consult an orthopaedic physician to prevent any negative effects from frequent pharmaceutical usage.
The R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) technique is frequently beneficial for minor knee injuries:
- Rest: Give your joint some rest.
- Ice.
- Compress: Please be aware that the compression band must be taken off at night and shouldn’t be overly tight.
- Elevate: While applying ice, elevate the damaged or aching knee, ideally on a pillow.
How to prevent knee pain?
Knee pain can have several causes. Therefore, there are several ways to avoid knee pain based on the underlying cause. If your pain is from overuse, you may find it helps to run or walk less or on softer terrain. To prevent traumatic knee injuries, avoid any direct injuries to your knee, such as uneven and slick surfaces when walking, and use a seatbelt when driving. If you are overweight, losing weight may also help relieve a variety of knee pain symptoms.
Conclusion:
To sum up, knee pain becomes severe if it occurs suddenly, is severe, persists for a long time, or is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, locking, deformity, or inability to bear weight. To prevent further harm and ensure proper treatment, these symptoms should be taken seriously, as they may indicate underlying conditions such as ligament tears, fractures, or joint infections.
FAQs
Which sleeping posture is ideal for people who have knee pain?
The elevation can aid in reducing knee edema if there is any. It’s normally easiest to sleep with your knees straight if you have stiff knees.
Which sleeping posture is ideal for people who have knee pain?
The elevation can aid in reducing knee edema if there is any. It’s normally easiest to sleep with your knees straight if you have stiff knees.
What is the reason of knee pain?
It may contribute to the development or worsening of knee pain by causing weakening of the bones, soreness in the muscles, and even inflammation of the joints. Joint problems and bone health can also be impacted by other deficiencies, such as calcium.
How can knee pain be relieved the quickest?
Combining rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) is frequently the quickest strategy to reduce knee pain. For an accurate diagnosis and course of therapy, it is essential to see a healthcare provider if the pain is severe or does not go away with home treatments.
Can walking help with knee pain?
Indeed, walking is typically thought to be an effective approach to ease knee pain, particularly in those with osteoarthritis. By preserving joint flexibility, strengthening supporting muscles, and aiding in weight control, this low-impact exercise can reduce knee pain.
Can knee pain be alleviated by walking?
Yes, walking is usually seen to be a good way to relieve knee pain, especially if you have osteoarthritis. It is a low-impact exercise that can lessen knee pain by strengthening supporting muscles, maintaining joint flexibility, and helping with weight control.
How can one determine whether knee pain is severe?
Knee pain can indicate a number of problems, some of which need to be treated right once. chronic pain that doesn’t go away with rest or medicine, or pain that gets in the way of everyday activities, are further signs of severe knee pain.
References:
- How to identify if your Knee Pain is serious? | Apollo Hospitals. (2025, February 18). Apollo Hospitals. https://www.apollohospitals.com/health-library/how-to-identify-if-your-knee-pain-is-serious
- Center, O. O. (2024, April 29). Is Your Knee Pain Serious? 10 Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore. Orlando Orthopaedic Center. https://www.orlandoortho.com/is-your-knee-pain-serious-10-signs-you-shouldnt-ignore/
- Askinazi, O., PhD. (2025, April 28). What your knee pain may indicate based on its location. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/knee-pain-location-chart