Swollen Knee
Introduction:
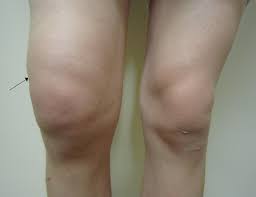
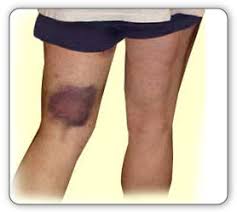
When too much fluid builds up in or around your knee joint, you have a swollen knee. This problem may be referred to as an effusion in your knee joint by medical specialists.
The pain and stiffness caused by the edema might be lessened by removing some of the fluid. Treatment can start as soon as the root cause is identified.
Causes of Swollen Knee:
Injuries:
- Torn ligament.
- The meniscus cartilage is ruptured.
- Irritation from overuse.
- Broken bones.
Diseases and conditions:
- Osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Gout.
- Pseudogout.
- Bursitis.
- Cysts.
- Tumors.
Infections:
The following infections can result in knee swelling:
- The chronic illness known as lupus makes the immune system target healthy tissues, including the joints.
- A doctor can use testing to identify whether the swelling is due to an infection.
Bursitis:
Swelling is subsequently caused by an inflammatory reaction in the knee. If bursitis is the reason, a mix of the following treatments may be used:
- compression
- using ice packs
- Elevating the knee
- resting
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Arthritis:
Another common reason for knee swelling is arthritis. The five essential indicators of acute inflammation may be present in an individual with arthritis, despite the presence of underlying chronic inflammation.
- The two most prevalent types of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammatory condition where the immune system unintentionally targets the joints, and osteoarthritis, which is caused by a loss of cartilage in the knee.
Symptoms of a Swollen Knee:
Typical signs and indicators include:
- Swelling: There may be a noticeable increase in the skin surrounding your kneecap, particularly if you compare the affected knee to your other knee.
- Stiffness.
- Pain.
Risk Factors of Swollen Knee:
- Age.
- Sports: The kinds of knee injuries that produce swelling are more common in those who play sports like basketball that require twisting the knee.
- Obesity: A swollen knee can result from tissue and joint overload, degeneration, and additional stress on the knee joint caused by carrying too much weight.
Treatment of Swollen Knee:
Nontraumatic knee edema can be initially treated at home. Acetaminophen and NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) are examples of over-the-counter pain relievers that can lower inflammation and ease pain.
As soon as you experience pain or other symptoms, use the RICE method:
- Rest: Avoid the action that hurts you. While your knee heals, avoid overusing it.
- Ice: Several times a day, apply ice packs or a cold compress wrapped in a small towel to your knee for 15 minutes at a time.
- Compression.
- Elevation: As much as possible, raise your leg and knee above your heart.
If you have a particular injury or medical condition, your healthcare professional may recommend other treatments. You may require:
- Crutches.
- A brace that secures your knee.
- Physical therapy.
- Corticosteroids.
Surgery for knee swelling:
If you have arthritis and your knee pain and swelling make it difficult or impossible for you to go about your everyday activities, your doctor may suggest a knee replacement, or arthroplasty. Surgery is typically only recommended by your doctor if no other therapies can alleviate your problems.
Your doctor or surgeon will explain what to anticipate and the recovery period if you require knee surgery.
Complications of a Swollen Knee:
- Muscle loss: The presence of fluid in the knee can impair muscular function and weaken thigh muscles.
- Fluid-filled sac (Baker cyst): Although a bloated Baker cyst can hurt, it normally gets better with compression and cooling. You may require a needle to extract fluid if the swelling is significant.
Prevention of Swollen Knee:
Usually, an injury or long-term medical problem causes a swollen knee. To control your general well-being and avoid accidents:
- Make the muscles surrounding your knee stronger. Pressure on a joint can be lessened by having strong muscles surrounding it.
- Select low-impact workouts. Swimming and water aerobics are two exercises that don’t put your knee joints under constant weight-bearing strain.
- Keep your weight in check. A swollen knee can result from wear and strain, which is exacerbated by excess weight.
Prognosis:
The underlying reason, severity, and promptness of treatment all have a significant impact on the prognosis of a swollen knee. Swelling usually goes away with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) in a few days to a few weeks when there are minor injuries or excessive use.
However, the prognosis may include physical therapy and long-term maintenance if the edema is caused by persistent illnesses like meniscal tears or arthritis.
A good recovery is typically the result of early diagnosis and effective treatment, but chronic swelling may be a sign of infection or structural damage, necessitating prolonged rehabilitation and maybe surgery.
Conclusion:
To sum up, a swollen knee may indicate several underlying problems, from minor wounds to more serious illnesses. Effective recovery and the avoidance of additional difficulties depend on prompt examination, precise diagnosis, and suitable therapy. Maintaining knee health and mobility requires paying attention to signs and getting medical assistance when swelling intensifies or continues.
Knee swelling can be the consequence of an injury or an underlying medical condition like arthritis or an infection. Using an ice pack and taking NSAIDs are two home care techniques that can help reduce swelling. However, it is crucial to seek professional attention if someone believes that the swelling is caused by an underlying condition.
FAQs
Does a swollen knee respond well to deep heat?
This facilitates the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to your aching joints. In addition to relieving pain and muscular spasms, heat helps relax tense muscles and joints. It’s advisable to apply ice for a full day before moving on to heat if you have swelling. When you initially feel knee pain, applying heat is OK if swelling is not an issue.
Do I need to massage my swollen knee?
If you have knee pain, stiffness, or edema, it might be quite helpful to massage your knee.
For knee swelling, what blood test is performed?
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test
While a high ESR denotes significant levels of inflammation, a low ESR level may suggest low levels of inflammation. There is no need for specific preparation, but if you are taking any drugs, let your healthcare provider know.
Which medication works best for reducing swelling?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, help cure sprains, strains, and inflammation and associated symptoms, such as arthritis-related swelling.
Is using hot water to reduce knee swelling possible?
You could try adding heat once the periodic ice has been in place for 72 hours. Cut the heat off if the edema gets worse.
Is it possible to minimize knee swelling with hot water?
After 72 hours of periodic ice, you could try adding heat. Use a heated cloth, heating pad, or warm bath for 15 to 20 minutes many times a day.
Can knee swelling be reduced by hot water?
You might try introducing heat after periodic icing for 72 hours. Stop the heat if the swelling gets worse.
Does ice help with swelling?
After an injury, ice can indeed help reduce swelling. By helping to constrict blood vessels in the damaged location, ice can minimize swelling by slowing down blood flow and minimizing fluid leakage into the surrounding tissues.
Should I walk with my knee swollen?
In certain cases, walking might alleviate knee pain, but in others, it can exacerbate the condition. For instance, you should stay in bed and give your knee total rest if you injured it in a fall so that the swelling doesn’t worsen.
Is a swollen knee a serious condition?
If you have suffered a sports injury or trauma, see a doctor. Consult a healthcare professional if you have excruciating pain, are unable to move your knee, or if the swelling doesn’t go down in a few days.
How can I quickly minimize swelling?
Focus on R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) and lifestyle changes to rapidly reduce edema. To promote fluid drainage, elevate the swollen area above the heart, employ compression with a bandage or support stocking, rest the affected area, and apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes at a time.
Can knee swelling be reduced by exercise?
Knee swelling can be considerably decreased and mobility increased by including mild yet efficient activities in your recuperation regimen.
What is the duration of knee swelling?
The root cause will determine this. The swelling might only last a day if it developed rapidly as a result of an injury. See your doctor if the swelling doesn’t go away in a few days. Treatment may be necessary to address the underlying cause of your swelling, such as an infection, underlying disease, or more serious injury.
How should a swollen knee be treated?
Elevation and ice.
Every two to four hours, apply ice to your knee for 15 to 20 minutes to reduce pain and swelling. Make sure to elevate your knee above your heart when applying ice to it.
References:
- Swollen knee – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic. (2022, June 16). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/swollen-knee/symptoms-causes/syc-20378129
- Professional, C. C. M. (2025c, June 12). Swollen knee. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/17678-swollen-knee
- Swollen knee – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2022, June 16). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/swollen-knee/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20378134
- Cole, J. D., MD. (2020, August 10). What causes a swollen knee (Water on the knee)? Arthritis-health. https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/general/what-causes-swollen-knee-water-knee
- Gotter, A. (2024, February 6). 8 home remedies to reduce knee swelling quickly. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-reduce-swelling-in-knee-quickly