Knee Joint Stiffness
Introduction
Knee joint stiffness is a common issue that can affect people of all ages, often resulting in reduced mobility and discomfort. This condition occurs when the knee joint becomes rigid or difficult to move, which can be caused by factors such as injury, arthritis, prolonged inactivity, or overuse. Stiffness in the knee can make everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or sitting down challenging, impacting one’s overall quality of life.
Knee joint pain and edema are frequently accompanied by knee joint stiffness. Knee joint stiffness is a typical finding in arthritic diseases and can be caused by joint injury or illness.
Due to the presence of two cartilage pieces known as menisci, the knee joint bones may glide easily against one another. Additional traumatic reasons for stiff knee include bone fractures, bursitis in tendons or bursae, or injury to the kneecap’s cartilage.
While rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune illness that produces inflammation in the joints, is due to immune system malfunction, osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joint.
If you sprain your knee, you might have more serious joint problems later on. Emergency care might be required.
Serious symptoms, such as paralysis, loss of feeling, absent foot pulses, total incapacity to move the knee joint, elevated temperature, significant bleeding, or unbearable pain, should be checked by a doctor.
Movements
Four movements are allowed by knee joint
Extension and Flexion, Rotation laterally
Rotation medially
| Knee flexion | 0-135 to 140 |
| Knee extension | 140 to 135-0 |
Pathophysiology
Knee joint stiffness and its surrounding pain can include
Inflammation due to arthritis, infections, or autoimmune systemic inflammatory diseases.
Non-inflammatory issues that are often mechanical (e.g., internal derangements, trauma)
An injury is more likely to result in meniscal pain.
What are the causes of Knee Joint stiffness?
Injured ligaments
Ligament injury might result from a strained or overextended knee. These injuries frequently occur in athletes or persons who have very busy lives. A sprained, torn, or ruptured knee ligament might result in internal bleeding.
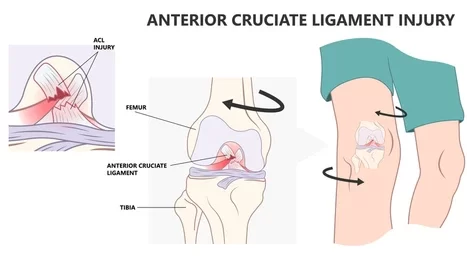
Injured meniscus
A meniscus injury arises from tearing or damage to the cartilage that separates the bones in your knee joint. This can occur when you apply pressure to the knee or rotate it, which frequently happens when playing sports that require quick spins and pauses. Even something as basic as utilizing stairs or rising too quickly from a squat might cause a meniscus tear.
Meniscus tears can cause pain and edema. It could be difficult to move your knee through its full range of motion and appear to be held in one place. As a result of these mobility limitations, the knee may become stiff.
- Stiffness after knee surgery
- Knee surgeries most often performed are:
- ACL repair
- arthroscopy of the knee
- knee ligament reconstruction
- Lateral release
- meniscus replacement or repair
- microfracture, plica excision, tendon repair, meniscectomy, complete knee replacement
Following surgery, you must follow the right procedures to promote complete healing and avoid knee stiffness. Spend time performing rehabilitation exercises to strengthen, stabilize, and flex your knee.
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee causes cartilage degradation, leading to misalignment—inflammation results from rheumatoid arthritis’s degeneration of the joint lining. Deformity, stiffness, reduced function, and range of motion are possible outcomes.
Muscles, weak and strong
It is maintaining knee muscles that are both flexible and strong enough to support your entire body while minimizing or eliminating knee pain. It is believed that having strong legs, hips, and buttocks would lessen knee stiffness.
In a 2010 research, nearly 2,000 knees of men and women with osteoarthritis or at risk for the condition were examined. The results showed that neither quadriceps nor hamstring strength was a predictor of common knee symptoms including pain, aching, or stiffness.
Nonetheless, as stronger muscles can aid in supporting the knee joint, having strong quads may help lower the chance of developing knee issues.
When to see your doctor
Seeing a doctor is crucial while seeking medical attention. Your doctor can identify the reason behind your knee stiffness and you two can work out a plan of care to get well. Imaging examinations, physical examinations, or laboratory testing can be required.
A physician who specializes in physical therapy, musculoskeletal and joint issues, or rheumatology may be recommended to you. If surgery is required, you will be sent to an orthopedic surgeon.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a diagnosis of knee stiffness made?
To rule out arthritis, your doctor will most likely prescribe knee X-rays. The X-rays need to show:
The kind of arthritis.
Any alterations to your skeletal structure.
The spurs are on the bones.
The slenderness of the interosseous membrane. As cartilage decreases, the space gets smaller. The pain increases with space restriction.
An MRI or computed tomography scan may be necessary for medical specialists.
How would a medical professional diagnose knee stiffness?
Your medical professional will give you details when you report your symptoms. Some questions might include:
- Is your skin often red?
- Does your knee swell up?
- Is your skin often warm?
- How long have you had these symptoms?
- What medications do you take?
- How severe is your pain?
- Do you struggle to walk?
- Do the symptoms interfere with your daily activities?
How is knee stiffness treated?
However, they provide some advice that may lessen the intensity of your symptoms and perhaps prevent the stiffness from growing worse, such as:
Sustain a healthy weight.
Instead of engaging in high-impact exercises like jogging or tennis, choose low-impact ones like cycling or swimming.
- Put in shock-absorbing shoe inserts.
- Treat the area with ice or heat.
- Use a brace or knee sleeve.
- Use a cane
- Plasma high in platelets.
Medications
- Acetaminophen
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (ibuprofen)
- Ointments or creams that relieve pain.
- Corticosteroids (cortisone shot).
- COX-2 inhibitors
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
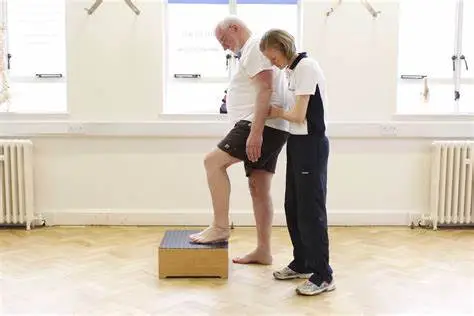
PT Exercises for Knee Stiffness
The knee may be strengthened and made more mobile with targeted workouts.
For the treatment of your knee stiffness, your physical therapist may suggest the following exercises:
Straight leg lifts and quad sets
Quads with short arcs
Exercises for building hip strength. Your hip flexors assist in regulating your knee posture. Knee pain might result from weakness here.
Stretches for the lower extremities
exercises for balance
PT Treatments for Knee Stiffness
- Ultrasound
- Electrical activation
- Kinesiology taping
- Using cold or heat
- massages using soft tissues
- mobilization of the knee joint
- Exercises and stretches that may help
However, exercise may benefit a stiff knee resulting from an arthritis-related condition.
Continuous Passive Motion (CPM): CPM machines enhance the range of motion; a maximum of five to six hours per day, with a two-hour interval between sessions, are preferred. The patient may easily modify it according to their range of motion because it’s passive.

Mobilization of the knee joint:
Anterior Glide
Indication: Anterior glide increases knee extension.
Patient Position: The patient is placed in a crook-laying position to adopt the drawer test posture. The knee joint is gradually stretched to the limit of its range when kept in a resting posture.
Posterior Glide:
Indication: to increase knee flexion.
The mobilizing force and hand location are arranged so that the force used during the mobilization is parallel to the tibia’s line. This technique is most frequently used in the closed-packed posture, comparable to the PCL’s posterior drawer test. As an alternative, you can perform it with your knee nearly fully bent.
Knee Muscle Stretching exercise:–
Calf Muscle Stretching
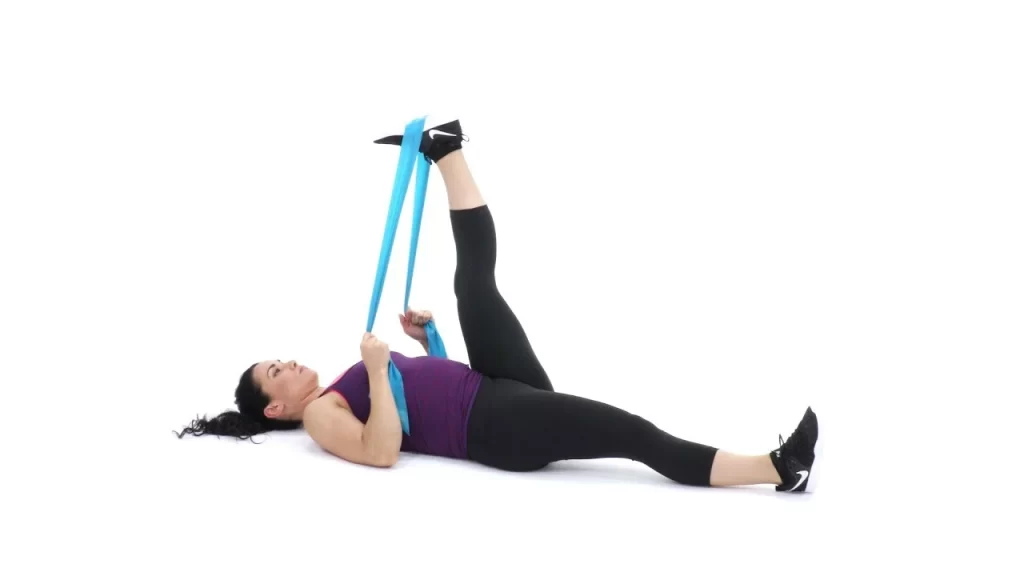


Exercises for strengthening: Raising the strength of the muscles surrounding the knee helps to lessen joint stress—activities like leg lifts and hamstring curls.
ROM exercise: Stretches and activities that extend the knee’s range of motion help keep the joint moving and relieve stiffness. These workouts involve stretching with a yoga strap and heel slides.

Aerobic exercises can increase a person’s energy levels and help them lose any additional weight that could put undue strain on their knees. These workouts include swimming and cycling.
Exercises for balance: These build muscle around the knee and lessen the chance of falling, which might cause more injury to the joint.
Summary
Knee stiffness is a frequent problem. It is especially prevalent in elderly folks and those with much physical activity.
However, if a person’s stiffness is accompanied by additional symptoms or a history of knee damage, they should see a physician. For a diagnosis and a course of treatment, individuals who think they may have knee arthritis should also consult a physician. Painkillers, various physiotherapy exercises, stretches, and flexibility exercises are all part of the treatment.
FAQs
Why does my knee feel tight and stiff?
Joint tightness may arise from damage to the knee’s interior cartilage, tendons, or ligaments.
How do I know if my knee is stiff?
Knee stiffness is an experience of difficulty bending or extending your knee’s range of motion, which impairs your leg’s overall flexibility, strength, and stability.
Should you stretch a stiff knee?
Range of motion and flexibility may be enhanced while the pain is reduced with mild stretching and strengthening activities.
Which exercise is best for knee joint stiffness?
Strength and Flexibility First
Water aerobics. Cycling is a great kind of physical activity for those with knee pain. Another option is water aerobics. Strength, flexibility, and range of motion can all be greatly increased by biking.
Yoga. Yoga is great for increasing flexibility, particularly in the potentially stiff regions surrounding the knee.
Strolling.
References:
- Fletcher, J. (2020, January 15). What to know about knee stiffness. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/327499#causes
- Knee pain – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2023, January 25). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20350849
- Gambrah-Lyles, C. (2018, March 18). Knee Stiffness | Causes, Home Relief, & When to See a Doctor. https://www.buoyhealth.com/learn/knee-stiffness
- Holland, K. (2022, August 5). Stiff Joints: Why It Happens and How to Find Relief. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/stiff-joints
- Physiotherapist, N. P. (2022b, September 24). Knee Joint stiffness : Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/knee-joint-stiffness-physiotherapy-exercises/




4 Comments