Rockwood Test for AC Joint Injury
Introduction
Rockwood Test is a clinical shoulder examination used to assess acromioclavicular (AC) joint instability or separation. The test helps identify injury to the AC joint by evaluating pain, prominence, and abnormal movement of the clavicle, commonly seen after a direct fall or shoulder trauma.
Rockwood Classification
- Type I: Joint intact, minor ligament strain.
- Type II: Slight joint separation and a tear in the ligament.
- Type III: Significant joint dislocation and total tear of the AC and coracoclavicular (CC) ligaments (usually treated non-surgically or surgically).
- Type IV: Clavicle displacement posteriorly (behind) is Type IV.
- Type V: The clavicle is considerably raised (pushed up).
- Type VI: The clavicle is positioned inferiorly, or beneath the acromion.
Purpose of the test:
The test’s objective is to assess anterior shoulder instability.
This test is designed to evaluate the GH [Glenohumeral] joint’s stability.
It is used to assess the fundamental traumatic instability of joint issues.
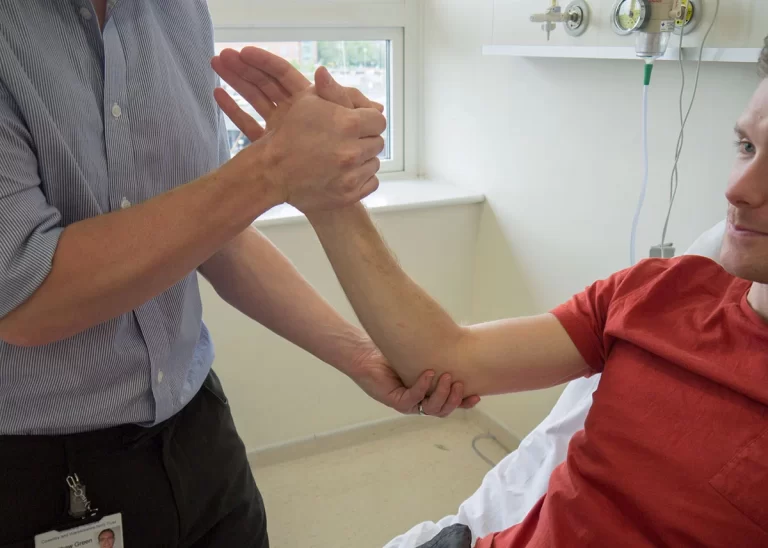
How to perform this test?
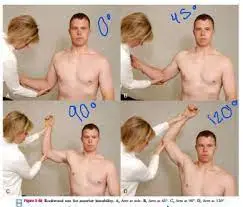
- Sitting is the starting posture for this test.
- With their arm on the patient’s side, the examiner stands behind them.
- The examiner then rotates the shoulder laterally.
- The arm is then abducted to a 45-degree angle and passively rotated laterally.
- This test is performed at 90 and 120 degrees to the arm’s abduction.
- The test’s various postures are crucial since the shoulder’s stabilizers change as the angle of abduction increases.
Interpretation of the test?
- When the arm is at a 90-degree angle, the patient has anxiety due to posterior discomfort.
- Patients have a little pain at 45′ and 120′.
- The patient rarely feels anxious at 0′.
- This test is positive in every scenario.
FAQs
What is the shoulder Rockwood protocol?
The Rockwood Protocol is a thorough surgical approach designed to stabilize the shoulder joint, particularly when there is substantial ligamentous laxity or multidirectional instability. The supporting structures of the shoulder are reconstructed and tightened using a mix of arthroscopic and open methods.
What is the anterior instability Rockwood test?
Anterior instability is assessed using the Rockwood test, where the crank test is positioned similarly, except that the shoulder is rotated laterally at 0, 45, 90, and 120 degrees. The anterior instability Rowe test: The patient is in a supine position with their hand behind their head. The examiner applies a downward push to the arm while clenching their hand behind the humeral head.
What is the Rockwood classification?
Rockwood used radiographs to categorize acromioclavicular (AC) joint injuries based on joint displacement. The treatment paradigm for acute AC dislocation has been shaped by this categorization. In acute injury, the relationship between Rockwood grade and symptoms has not been established.
References
- Ladva, V. (2021, December 31). Rockwood test : Shoulder Joint Examination Test – Mobile Physio. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/rockwood-test/