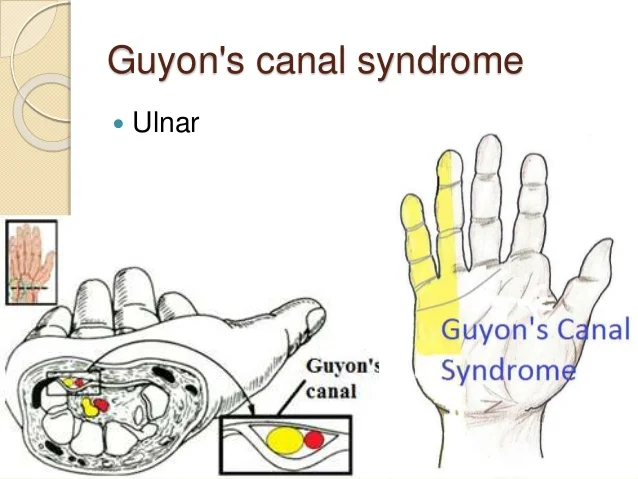
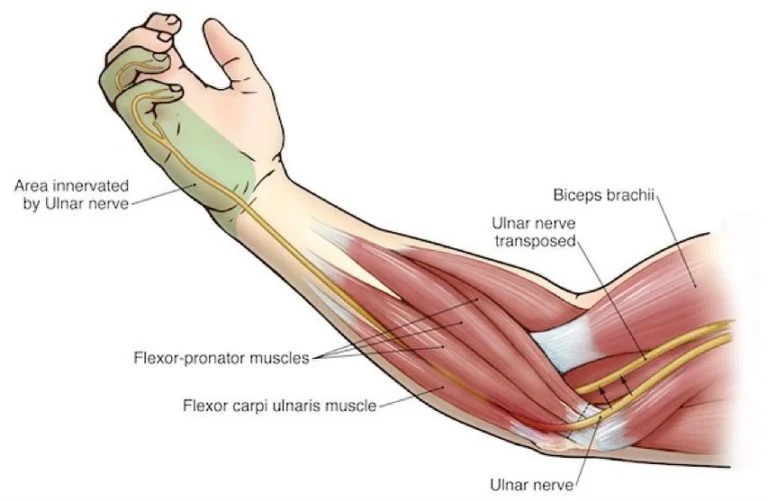
Tibial Nerve
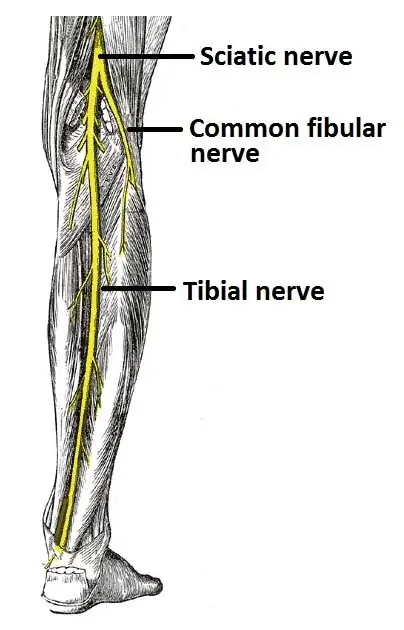
Introduction The tibial nerve is a major branch of the sciatic nerve and is part of the lumbosacral plexus. It originates from the L4-S3 spinal nerves and runs down the back of the leg. From the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve descends into the leg’s posterior compartment. Along with the posterior tibial vessels, it travels…