Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
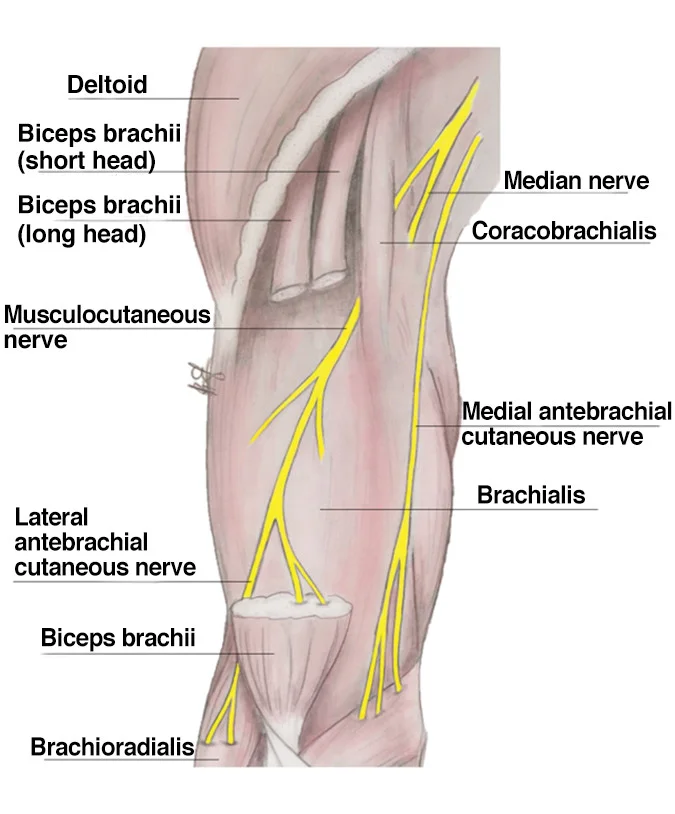
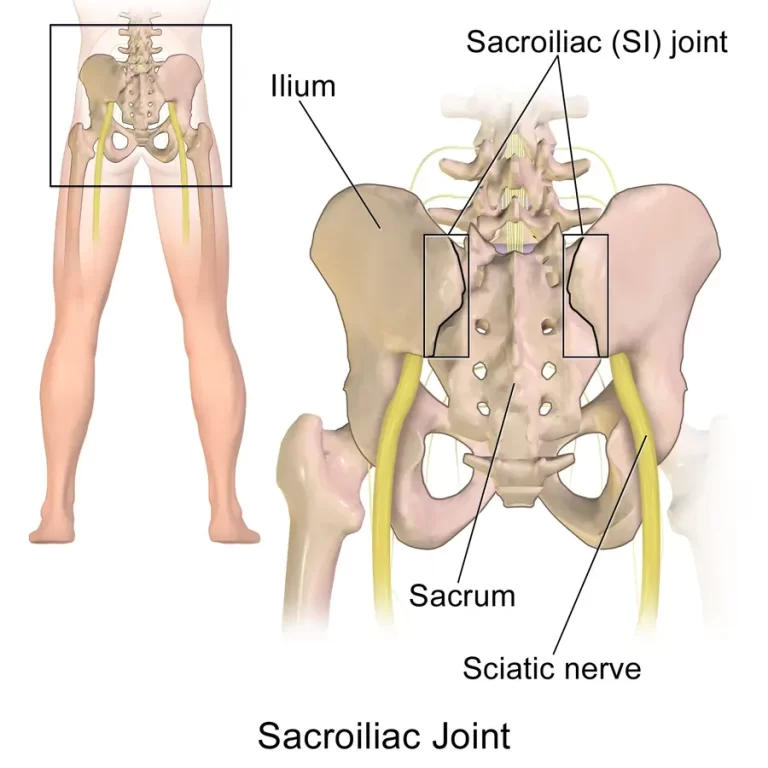
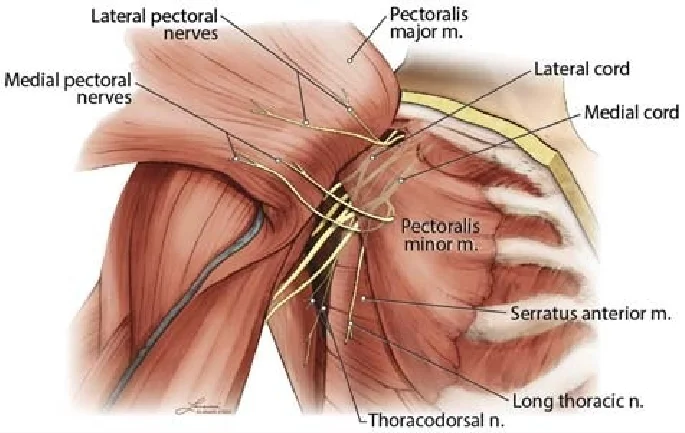
Introduction The medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve is a sensory nerve originating from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, primarily carrying fibers from the C8 and T1 nerve roots. It supplies sensation to the skin of the medial (inner) side of the forearm. The nerve descends along the arm, often near the basilic vein, and…