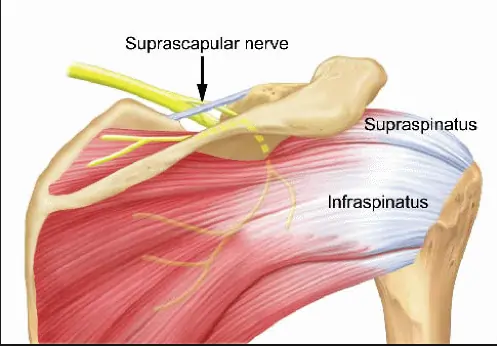
Suprascapular Nerve
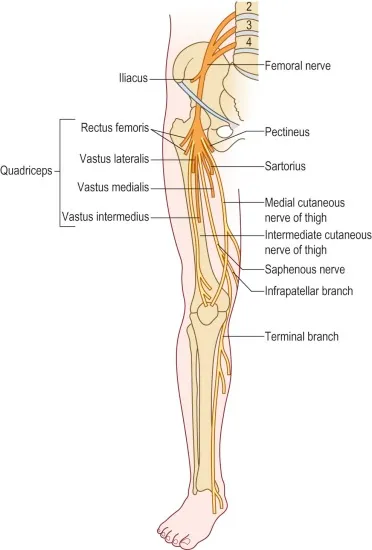
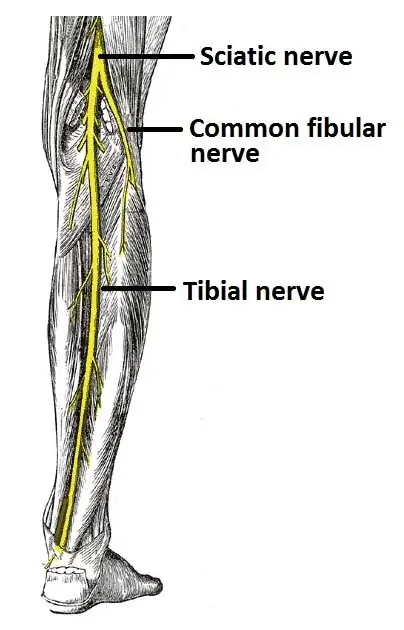
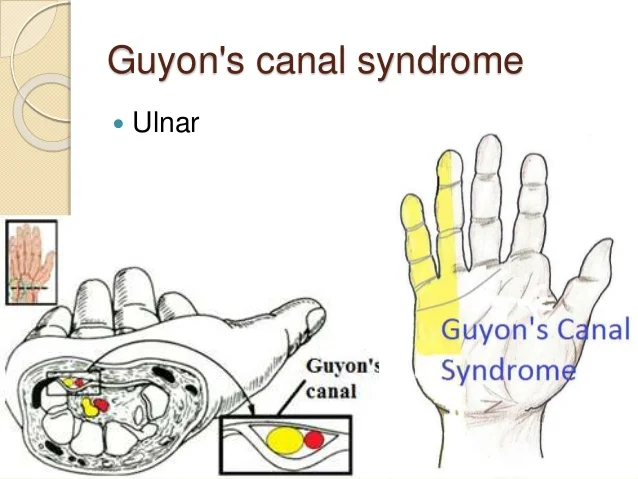
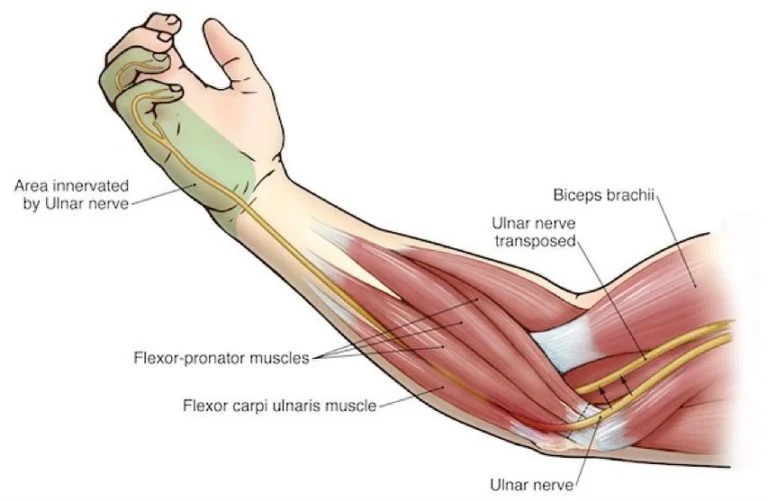
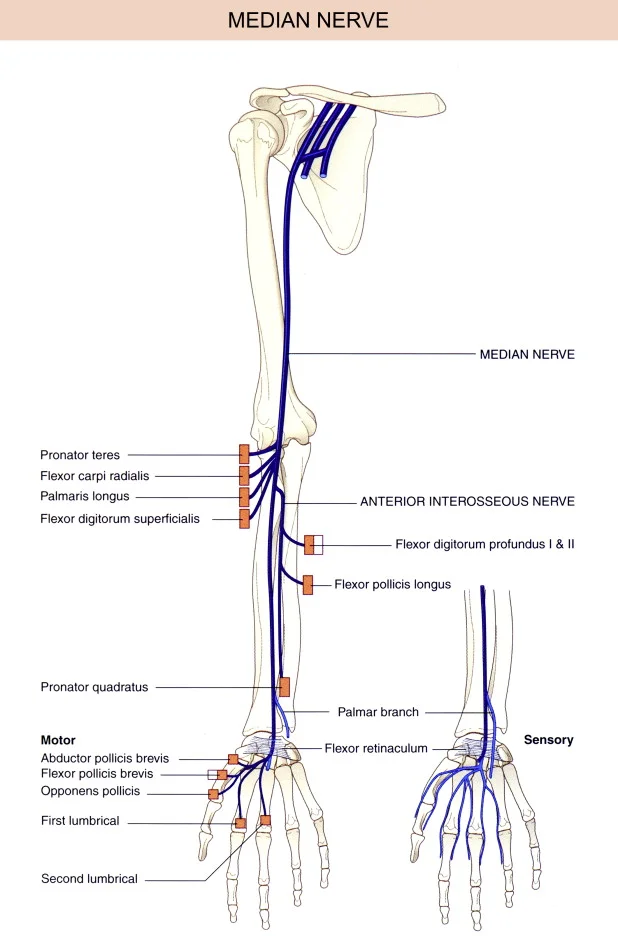
Introduction The suprascapular nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus (C5-C6) that supplies motor innervation to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, which are key for shoulder movement and stability. It also carries sensory fibers to the glenohumeral joint and surrounding ligaments. The nerve passes through the suprascapular notch, where it is susceptible to compression…