Poor Posture
What is a Poor Posture?
Poor posture is a common issue affecting many people in today’s sedentary lifestyle. It refers to the incorrect alignment of the body while sitting, standing, or lying down. Over time, poor posture can lead to a range of health problems, including back pain, neck pain, and even headaches.
A person’s regular activities often cause certain muscles to shorten or tense, while others overstretch and become weak, resulting in poor posture. It could result in pain, harm, or other medical issues.
Posture may be affected by a variety of variables, such as biomechanical elements like force and repetition and occupational tasks. Psychosocial variables, such as occupational stress and strain, are additional risk factors for bad posture.
Additionally, improving your balance can help you become more proficient in almost any sport or activity, including tennis, golf, jogging, dance, and skiing.
Types of Poor Posture:
One can exhibit bad posture in a number of ways:
- The upper extremities move differently as a result of a decrease in the stability of the shoulder blades.
- Lumbar lordosis
- It may manifest as a projecting abdomen, a forward tilting of the hips, and an increase in the lumbar spine’s curvature. The hip joints and lower back are both strained in this position.
- Kyphosis: Other names for kyphosis include arcuate, round back, and Kelso’s hunchback.
- The most common ailment seen in older women is known as “dowager’s hump.”
- Swayback
- Individuals with a swayback posture have forward-tilting hips, excessive spine curvature, and a backward-leaning look when standing.
Does Poor Posture Cause Back Pain?
If the pain in your back persists, this is one of the things that might lead to poor posture. When you’re fatigued or focused on something, it’s incredibly simple to inadvertently stoop down. Nevertheless, sitting incorrectly all the time strains the surrounding muscles and the spine unnecessarily. These are the negative effects of bad posture and the steps you may take to avoid them.
Adopting an incorrect posture can lead to several stress points forming in your discs, lumbar facets, and muscles. When the offending posture is corrected, these stresses may subside, but they may also persist and gradually deteriorate the impacted structure. Long-term hunching when sitting or standing can lead to blood flow problems in your abdominal, back, and core muscles as well as gradual stiffness and weakening in your lower back and trunk muscles. The spine flexes slightly forward when sitting unaided. Disc herniation may result from the forward-bent posture’s gradual loading of the lower spinal discs.
Your lumbar disc may herniate as a result of improper lifting technique, which might lead to lower back pain and/or spread pain down your leg via a neighboring spinal nerve. Your hipsterism and lower back may stretch (bend backward) excessively while you work on a laptop or read while resting on your stomach, which will change the way the lower lumbar spinal curvature functions.
Maintaining proper posture usually requires less work than incorrect posture.
Symptoms of Poor posture:
- A kind of muscular ache that feels acute, scorching, or shooting is called back pain.
- The Price of Bad Posture on Health
- If you need a little extra incentive to correct your posture while sitting and standing all day, consider the possible health risks associated with poor posture. The deformation of the spine’s natural curvature has the most effect on health. There are three naturally occurring curvatures in your spine that support the rest of your body; they don’t have to be straight. Your spine changes during a squat, putting strain on your vertebral joints. Pain in the shoulders and lower back that is easily felt might be caused by poor posture. This can lead to muscular imbalances, which can cause pain in other parts of your body as well.
- Moreover, bad posture and persistent pain might result in internal issues that impact the cardiovascular and digestive systems. because of the unusual manner in which they grasp the intestines. This may hinder your body’s ability to break down food properly, which may result in gas and other pain. Additionally, it restricts circulation, which greatly impedes the body’s ability to mend damage on its own. Poor posture might make you look unprofessional to others. Crouching might make you appear shy, whereas standing straight up conveys confidence and ease.
The Drawbacks of Spending the Entire Day Seated
The National Health Service (NHS) recommends that individuals aged 19 to 16 engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-to-intense physical activity or 75 minutes of intense physical activity every week. Long periods of sitting, especially if you’re sitting poorly, can cause pain in your lower back. However, that’s no longer the only factor. An analysis published in The American Journal of Preventive Drugs revealed that higher levels of daily sitting are associated with an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease in addition to poor posture. depressed attitude ongoing pain.
Risk Factors
Pain in the back can affect individuals of any age, including younger ones. The following factors may make you more susceptible to back pain as you age. As you age, back pain becomes more frequent, beginning in your 20s or 40s. insufficient exercise. Back pain can also be caused by weak muscles in the back and abdomen. surplus weight. Being overweight puts undue strain on your back issues. careless lifting. Pain in the back might result from using your lower back as opposed to your legs. psychological state. smoking. Smokers’ back pain is more severe. This could be the case because smoking aggravates coughing, which raises the risk of a herniated slice.
How can posture affect our health?
Your health may suffer if you have poor posture. Slumping or hunching over the can:
- Your musculoskeletal system is incorrect.
- Wear away at your spine, increasing its softness and susceptibility to damage
- Reduce your capacity for flexibility
- impact the degree of joint mobility
- Make your food more difficult to digest
- Make breathing more difficult
What good posture means
Maintaining good posture entails the following:
- chin in line with the floor, shoulders evenly spaced (you may do this by rolling your shoulders up, back, and down).
- neutral spine (avoid flexing or arching to accentuate your lower back’s curvature)
How good posture helps
You benefit from proper posture in the following ways:
maintains the right position of bones and joints to enable the effective usage of muscles
reduces the deterioration of joint surfaces, including the knee, to help delay the development of arthritis
reduces the stress on the spine’s ligaments and keeps the spine from growing stuck in unnatural positions
prevents aches in the muscles and back.
Correct Positions while doing daily activities
- Sitting in the right position is essential for maintaining a healthy posture. To do this, just adhere to the simple sitting positions. These suggestions are generally beneficial when utilizing a backrest.
- Your rear end should be in contact with your buttocks.
- Ten degrees is the minor release of position. This is a sensible way to sit.
- Balance your weight equally across both hips.
- Make sure your knees are bent straight. (If needed, use a stool or foot support.) Avoid crossing your legs.
- Don’t take your feet off the ground.
- Straightening your legs will help you stand. Perform ten standing backbends to immediately extend your back.
You should abide by these guidelines when operating a vehicle.
- At the back, place a lumbar roll.
When lifting objects:
- If you must lift something, avoid attempting to lift something uncomfortable or weighing more than thirty pounds.
- Avoid bending at the waist while keeping your knees straight.
- Lift the thing with your leg muscles while contracting your tummy muscles. Make sure to straighten your knees steadily.
- Maintain a straight posture without bending. When lifting something, always place your feet in front.
- To hold an object near to your body when raising it off a table, move it to the edge of the surface. To get near to the thing, bend your knees. Lift the thing with your legs and raise it to a standing posture.
- Avert lifting bulky items higher than your waist.
- Maintain the contraction of your abdominal muscles. Move carefully and in modest steps.
- Place your feet where you lifted them, contract your abdominal muscles, and bend your knees and hips to drop the object.
The ideal sleeping position to remember in order to prevent bad posture.
- The cushion should always be beneath your head, not your shoulders, and the right thickness to let your head rest in a natural position when you are lying down.
- Choose a box spring set and mattress that are firm and do not droop. If required, you can even temporarily set the mattress on the floor. Switching to a hard surface while you’ve always slept on a soft one might hurt more.
- To improve your comfort level at night, consider employing a lumbar support. You might find it useful to wrap a towel or rolled sheet around your waist.
- Turn onto your side, lift both knees and swing your legs along the bed’s edge to stand up from a laying posture.
- Most people who suffer back pain as a result of incorrect or improper posture can benefit from these guidelines.
How to Correct Poor Posture?
These might be as simple as providing extra support to your chair or as complex as altering your exercise routine. A poor posture can be corrected in a variety of ways.
Strengthen your Back and Core
People often have bad posture because their torso muscles are weak. This is one of the reasons why people do this in the first place. Increasing the strength of the muscles in this area of your body will make it much easier to keep your lower back extremely straight. There are a few ways you may go about accomplishing this. While lifting little weights may be very helpful for building up energy, make sure to stretch your muscles after lifting to prevent tenseness.
Exercises like yoga and pilates are excellent for building energy and controlling this region. While yoga poses are great for stretching muscles and increasing their mobility, Pilates places more emphasis on firming the muscles. suppose you were unable to attend a lesson. You may look up sports activities on the internet to give it a try.
Exercises for a good posture
- Child’s pose:
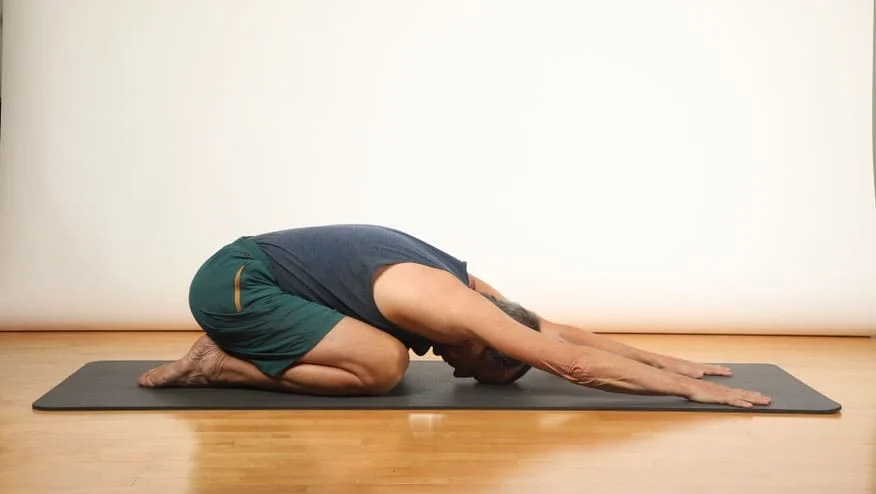

Your neck and lower back will feel less tense when you adopt the child’s stance.
To do this:
- With your knees together, your big toes touching, and your heels spread apart, take a seat on your shin bones.
- Put your hips back where your feet are. If your thighs aren’t going all the way down, use a folded blanket or pillow to support them.
- Take a deep breath through your waist and the back of your ribs.
- Hold this stance for five minutes, relaxing and breathing deeply the entire time.
- Forward fold:
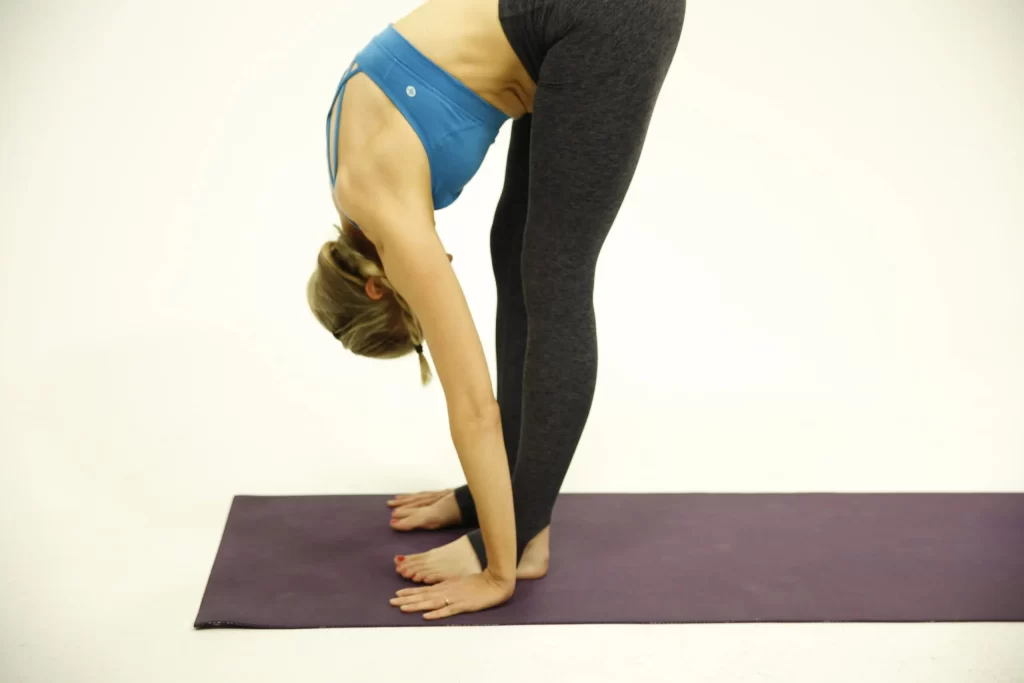

This standing stretch will release tension in your hamstrings, glutes, and spine. It extends your legs and hips as well. You should feel your entire back side stretching and opening up as you perform this stretch.
To do this:
- While standing, place your big toes together and slightly apart.
- Bring your hands to your hips and bend forward at the waist.
- Your hands can either fall to the ground or be placed on a block. Go as far as you can and don’t worry if your hands don’t contact the earth.
- Let your spine stretch, relax the joints in your hips, and softly bend your knees.
- Cat cow:
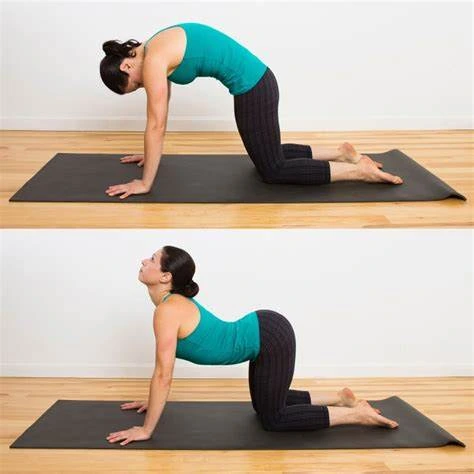

In addition, it releases stress from your chest, shoulders, and neck and promotes blood circulation.
To do this:
- Take a position on your hands and knees, evenly dispersing your weight over the four spots.
- Breathe in to gaze up, lowering your belly to the floor and extending your spine.
- Maintain this motion for a minimum of 60 seconds.
- Standing cat-cow:
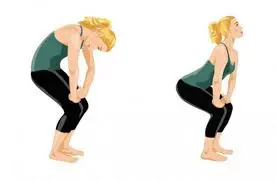
Stretching your glutes, hips, and back while standing will assist release stiffness in these areas.
To do this:
- Next, raise your chest, tilt your head forward, and flex your spine in the opposite direction.
- For five breaths at a time, hold each posture.
- Keep doing this for a few minutes.
- Chest opener:
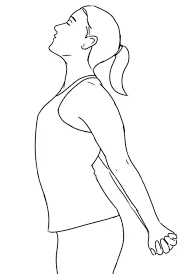
Your chest may be opened and stretched with this workout. This is particularly helpful if you sit for the majority of the day since this might cause your chest to inwards expand.
To do this:
- Standing, position your feet hip-width apart.
- With your arms folded behind you, make a fist with your fingers and press your palms together.
- If your hands cannot reach each other, grab a towel.
- Maintain a straight head, neck, and spine while looking directly ahead.
- Inhale, then lower your hands to the floor and lift your chest to the ceiling.
- Take deep breaths and hold this stance for five breaths.
- Breathe deeply a few times, then let go and unwind.
- Do this at least ten times.
- Plank

Benefits: This exercise helps strengthen the muscles in your shoulders, upper back, glutes, and abdomen.
To do this:
- Place your face down on a yoga mat or other soft, comfy surface.
- Maintaining a straight body line from your head to your ankles, push yourself up onto your toes and palms. Try beginning with a low plank exercise if this is too strenuous. Simply elevate yourself onto your forearms rather than fully straightening your arms.
- Maintain this stance while bracing your glutes and stomach.
- For at least thirty seconds, hold.
- High plank:
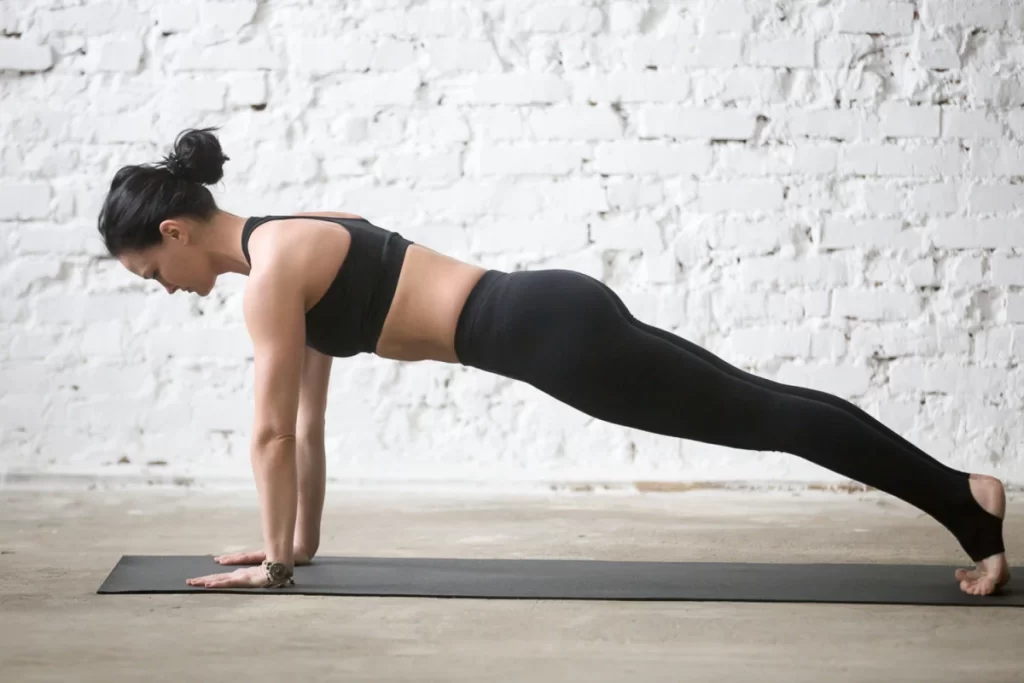

The high plank posture strengthens your shoulders, hamstrings, and glutes while reducing stiffness and soreness throughout your entire body. Additionally, it strengthens your back and core, which are crucial for proper posture, and helps you establish balance.
To do this:
- While engaging your arm, leg, and abdominal muscles, keep your back upright.
- Stretch the back of your neck, soften your throat, and cast your gaze downward.
- Recall to maintain an open chest and back shoulders.
- Side plank:

To keep your legs and spine in their neutral posture, you can perform a side plank. This energetic stance strengthens your glutes and side muscles.
To do this:
- Raise your left hand to a high plank posture and place it slightly in the center.
- Put your right hand on your hip or raise it to the sky.
- Hold this posture by contracting your side body, glutes, and abdominals.
- Look up at your hand or directly ahead of you.
- Maintain this position for a maximum of thirty seconds.
- Continue on the other side.
- Downward-facing dog:

You may utilize this forward bend as a resting position to help you find equilibrium in your body. The downward-facing dog stance strengthens and aligns your back muscles while also assisting with back pain relief. Regular practice helps to correct posture.
To do this:
- Either bury your chin completely into your chest or keep your ears in line with your upper arms.
- Firmly press onto your hands while maintaining a slightly raised heel.
- Pigeon pose:

This opens your hips and tones your glutes, hamstrings, and spine. Additionally beneficial for stretching your quadriceps and sciatic nerve is the pigeon stance.
To do this:
- Place your right shin’s outside down on the ground.
- With your arms out in front of you, slowly lower your body until it rests on your inner right thigh.
- Thoracic spine rotation:
This exercise improves stability and mobility while releasing back pain and tension.
To do this:
- Return to the initial position after release.
- Do this five to ten times over.
- Continue on the other side.
Glute squeezes:
Additionally, it enhances pelvic and hip position and function, which promotes improved posture.
To do this:
- A foot should separate your feet from your hips.
- With your hands facing downward, place your arms at your sides.
- After ten seconds of holding this posture, shift them farther apart from your hips.
- Keep doing this for a minute.
- Perform this exercise many times daily.
- Isometric rows:
Excessive sitting still can cause pain and stiffness, which can be eased with this exercise. You may strengthen your shoulders, arms, and back using isometric pulls, which will help you keep proper posture.
To do this:
- Occupy a chair with a cushioned back.
- Take deep breaths and maintain this posture for ten seconds.
- For a minute, keep doing this.
- Glute bridge
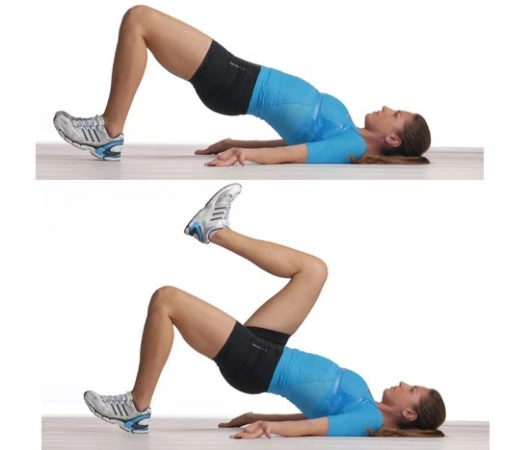

Benefits: You may develop your glute muscles and core muscles by performing glute bridge exercises.
To do this:
- Spread your feet apart a little.
- pause for a little moment before returning to the initial position.
- As your core strength increases, try working up to three sets.
Kneeling hip flexor stretch
- Make sure your right knee is precisely over your right ankle as you crouch on your left knee.
- As you assume a forward flexion posture, make sure your back and pelvis are firm. The inner thigh and hip flexor muscles ought to be stretched.
- To lengthen the remaining hip flexor muscles, switch sides and carry out the same motions.
Regularly see a chiropractor and physical Therapist
Making an appointment with a chiropractor or physical therapist is another simple method to ease back pain. But if the chine has moved, chiropractors utilize adjustments to put the spine back in its proper position. These modifications will not only aid with chronic pain relief, but they will also make it much simpler to keep proper posture going forward. It may help you make good adjustments by assessing your food, exercise routine, sleep patterns, and other health-related aspects, in addition to offering stretches and exercises to assist in correcting your bad posture.
Buy a mattress and a useful desk chair.
If your chair is uncomfortable and doesn’t maintain your back’s natural curvature, it can significantly affect your posture if you spend a lot of time sitting at your desk. As a consequence, it’s simple to slump into a squat. Rather than forcing yourself to sit upright, choose a desk chair whose high back conforms to the curve of your spine. In order to maintain the comfort and support of your muscles, they should also be composed of lightweight, supporting materials.
Additionally, a supportive mattress is required. A supportive memory foam mattress that maintains the body’s curves without drooping is ideal for a mattress. If you do not want to spend money on a new mattress, you may also purchase an inexpensive mattress topper for additional bed support. For additional bed support, you may also purchase an inexpensive mattress topper.
Consider your partnership carefully.
If you have never done this before, it may take some getting used to, but after a little practice, it will come naturally to you. Wearing a colorful bracelet or ring that encourages proper posture could be a wonderful idea.
It could need some getting used to, but eventually, you’ll learn to embrace this position on autopilot. Nevertheless, if you’re still experiencing problems with keeping proper posture, consult a physician or chiropractor.
How do you prevent Poor posture?
Back pain may indicate a more serious health issue. You may relieve back pain or keep it from coming back by understanding and using good body mechanics to enhance your physical state.
To maintain a robust and healthy back Work out. Frequent low-impact aerobic exercise can help improve muscle function and build back strength and endurance without straining or shaking your back.
Swimming and walking are excellent choices. Consult your physician about possible courses of action. Exercises that strengthen your abdominal and back muscles assist your muscle’s function as a natural corset for your spine. Sustain a healthy weight.
Carrying too much weight strains the back muscles. Pruning, however, might aid if you’re overweight to avoid back strain. Give up smoking. Given that the risk rises with daily cigarette consumption, quitting should help lower the risk. keep away from actions that might strain or distort your back muscles.
Preserve a neutral pelvic position. If you must stand for extended amounts of time, elevate one foot on a low footstool to relieve some of the strain on your lower back. Switch up your foot placement. Good posture helps ease the strain on the muscles in the back. Take a smart seat. Select a chair that has armrests, lumbar support, and swivel support. You may support keeping your back in a natural curvature by placing a cushion or dry cloth on it. Every thirty minutes at the absolute least, shift positions often.
Lift carefully
Maintaining a straight back and bending your knees, crouch down in front of the heavy item and raise it off the ground. To stand up, straighten your legs and grab the item at your chest.
When lifting lighter things, elevate one leg rearward for counterbalance, bend down at the hips (keeping your back straight), and grab hold of a table or counter with one hand. Lift the thing with your other hand. The golfer’s lift is a method that is particularly helpful for repetitive lifting tasks.
Astute Selection. Try to avoid lifting heavy items as much as you can, and if you must, utilize your leg strength to lift them. Bend your knees without twisting while maintaining a straight back. Maintain your weight near your body. Find a lifting companion, though, if the thing is heavy or awkward.
FAQs
How can I correct my poor posture?
Continue to move. While any sort of exercise can help with posture, several exercises are particularly beneficial. These consist of body-awareness-focused classes like tai chi and yoga. Exercises that strengthen your core, or the muscles in your back, belly, and pelvis, are also a smart option.
Is it better for posture to lie in bed?
It could be most pleasant for those with neck or back pain, particularly lower back pain.
How can I adjust my posture?
Maintain a straight posture, towering stature, and back shoulders.
Make sure your head and body are at the same level.
Draw in your lower body.
Maintain a shoulder-width gap between your feet.
Keep your knees apart.
Which example of a posture will you give?
An asymmetrical or non-neutral bodily position is referred to as bad posture or poor posture. For instance, having a lordosis, or an unusually wide curvature in the back, is seen as bad posture.
Which postural issues are most prevalent?
Typical postural issues
Head forward. Your head should be positioned with your ears in front of your body’s perpendicular midline when you have a forward head posture.
kyphosis. The term “kyphosis” describes an atypical curvature of the thoracic spine, which is the region of your upper back where your shoulders are rounded forward.
Back off.
rounded back.
What symptoms indicate poor posture?
broad shoulders.
Potbelly.
bending the knees when moving or standing.
back pain.
Aches and pains throughout the body.
muscle fatigue.
pain.
What does poor posture look like?
Instances of Poor Back Support and Posture:
slumping, hunching forward at the shoulders.
Lordosis: An excessively wide inward bend in the lower back, commonly referred to as “swayback”
putting a lot of weight on one side of the body.
holding a phone receiver between the shoulder and neck.
Why does poor posture occur?
Bad habits like slouching and inactivity contribute to muscular stress and exhaustion as we age, which in turn results in poor posture.
Is poor posture everlasting?
Although it will need daily effort, there are things you can do to help your posture. Your ability to sit or stand with proper posture may be affected by certain muscle groups, so you should concentrate on stretching and strengthening those areas
How much of an issue is poor posture?
Back, shoulder, and neck pain are frequently caused by holding your body incorrectly and moving in bad ways. Approximately 1 in 4 individuals in the United States have back pain at least one day every three months. Your flexibility, balance, and joint mobility can all be negatively impacted by poor posture.
Is it possible to correct poor posture?
The muscles in the upper back, chest, and core need to be strengthened and stretched in order to correct bad posture. Scapula squeezes, which include pressing your shoulder blades together for 30 seconds at a time, and rows, which involve pulling back your elbows with a resistance band like you’re rowing, are two exercises that strengthen your shoulders.
Does poor posture have a cure?
Poor or misaligned posture is widespread. It may have an impact on your general well-being, self-esteem, and looks. The good news is that you may use posture aids if needed and exercises to help you achieve better posture.
How can I position myself properly at home?
This will help you with your posture and allow your body to return to its normal resting position.
References
- Patel, D. (2022e, September 27). Poor Posture – Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/poor-posture/
- Dhameliya, N. (2022c, June 21). How to Improve Poor Posture – Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/how-to-poor-posture/




9 Comments