Physical Therapy In Lower Back Pain
Introduction:
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing lower back pain by reducing pain, improving mobility, and preventing recurrence. Through targeted exercises, manual therapy, posture correction, and patient education, physical therapists help individuals restore function and return to daily activities safely and effectively.
The lower lumbo-sacral region of the spine is most frequently affected by lower back pain, a painful condition.
- It becomes immobilized and too uncomfortable for anyone.
- The causes of this lower back pain include injuries, physical exertion, and some conditions.
- People of all ages might experience lower back muscle pain, however, the causes vary.
- Discomfort mediation, physical therapy, and the RICE principle all help to relieve lower back muscle pain.
- One of the most prevalent problems is lower back pain, which can be extremely uncomfortable.
Physical Therapy for Lower Back Pain:
Massage therapy:
- Massage therapy also aids in the relief of low back muscle spasms, which are typically the cause of low back pain.
- Additionally, by increasing blood flow to the lower back, this massage therapy helps damaged muscles receive oxygen and nutrients, hastening the healing process.
- Massage is given when you feel as though the pain has decreased, which is two to three days after following the RICE approach.
- Three times a day, people get massages at home.
Electrotherapy Treatment:
- Ultrasound treatment, or US.
- Five to ten minutes are spent applying this gel-assisted therapy to the sore spot.
- Short wave diathermy (SWD).
- Interferential treatment (IFT),
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Lumbar traction.
- In the clinic, the therapist applies it.
- Back stretches are performed with weights and pulleys.
- Pain can be reduced by traction, but only while it is being used.
Manual manipulation:
The physical adjustments made to the spine by a chiropractor and other medical professionals are intended to increase your range of motion and lessen pain, stiffness, and discomfort.
Best Exercises for Lower Back Pain:
Stretching exercise:
- Piriformis stretches
- Knee-to-chest stretch
- Seated spinal twist stretch
- Sphinx stretch
- Knee-to-chest stretches
- Kneeling back stretch
- Modified seated side straddle
- Lower Back Rotation Stretch.
Piriformis stretches:
 Piriformis stretches
Piriformis stretches
- This stretch is performed as a strong backside stretch that is strong.
- The stretching begins in the supine posture.
- The leg must then be positioned in a figure-four shape, crossing across onto the opposite thigh.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Knee-to-chest stretch:
 Knee-to-chest stretch
Knee-to-chest stretch
- Next, clasp your hands at the top of your shinbone behind your leg.
- Keep your hip joint from being raised, and extend your spine to your tailbone.
Sphinx stretch:
- This stretching begins in the prone posture.
- After that, elevate your head and chest by slowly contracting your thighs, buttocks, and lower back.
- The pelvis should be pressed into the ground.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Kneeling back stretch:
 Kneeling back stretch
Kneeling back stretch
- Hold this position for five seconds.
- Next, rock backward softly while bringing the buttocks as near to the heels as you can.
- Hold this position for five seconds.
- Then slowly rock back up to the beginning position.
Modified seated side straddle:
- You are seated with both legs extended out in front of your body and flat against the floor.
- Make sure your legs make a “V” shape by spacing your feet widely apart.
- Try bending your left leg or raising your left foot to contact your right knee joint while allowing it to drop away from your body.
- Next, lower the head as close to the right knee joint as you can, moving the hands toward the right ankle and shin or slowly rounding the spine.
- Spend 30 seconds in this stretching position, and then another 30 seconds relaxing.
Strengthening Exercises:
The physical therapist will prescribe strengthening exercises to relieve muscle weakness after electrotherapy and massage for two to three days to relieve muscle soreness.
This strengthening.
- Pelvic Tilts
- Cat/cow
- Bridges
- Drawing-in maneuver
- Lying lateral leg raises
- Supermans
- Partial curls
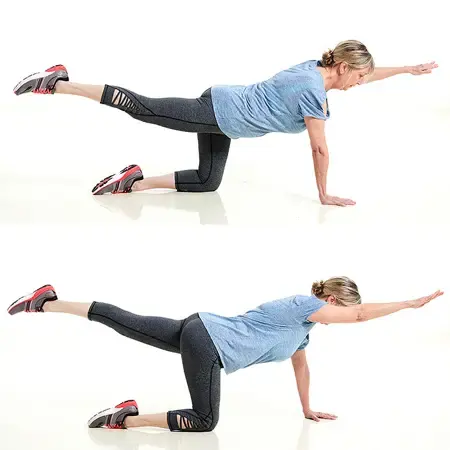
- Bird-dog
- Plank
- Side plank
- Abdominal crunches
Cat and cow pose:
 Cat and cow pose
Cat and cow pose
- When combined, these poses promote flexibility, ease neck and back stiffness, and warm up the spine. This is Cow Pose. Rounding the spine, tucking the tailbone, and pulling the chin toward the chest are the steps for Cat Pose on the exhale. People of all fitness levels will benefit from this coordinated movement with breath since it increases body awareness and encourages calm.
Bridges:
 Bridges
Bridges
- A basic exercise that improves posture and spinal flexibility, the Bridge Pose also strengthens the lower back, glutes, and core muscles. Using your glutes and thighs, raise your hips toward the ceiling while pressing through your feet as you take a breath.
Child’s pose:
 Child’s pose
Child’s pose
- The child’s position opens up your lower back more than any other workout. It’s also easy to accomplish; just sit on your heels, kneel on a mat, and lean forward with your arms out in front of you. Enjoy the relaxation that comes after placing your head on the ground.
Supermans:
 Supermans
Supermans
- Your legs are long and your arms are out in front of you as you lie on your stomach.
- To prevent straining your neck, you must keep your eyes on the floor while performing this exercise.
- At the top, hold this exercise for ten seconds.
In partial curls:
- You’re probably keeping your knee bent.
- Cross your hands across your chest after that.
- Inhale deeply.
- Try raising your shoulder joint a few inches off the ground at a time.
Plank:
 Plank
Plank
- With your elbow and shoulder joints exactly in line, you are on your stomach with your forearms against the floor.
- First, contract your gluteal and abdominal muscles.
- Avoid letting the pelvis drop toward the floor while you maintain this exercise position for 10 to 30 seconds.
- By keeping your knees on the floor and bending them slightly, you can make this exercise less difficult.
- From the knee joint to the shoulders, you need to concentrate on keeping a straight line.
Side plank:
 Side plank
Side plank
- The right arm should be positioned directly beneath the right shoulder joint, with the forearm out in front.
- The body must be kept upright.
- 30 seconds should be spent holding this workout stance.
- If you find this exercise too challenging, you should keep your lower knee on the floor and slightly bent.
How do you prevent lower back muscle pain?
- Because being overweight causes strain on the disks and vertebrae, you are keeping your weight within a healthy range.
- Always try to improve your abdominal muscles with Pilates and other programs that help you build stronger core muscles and support your spine.
- Lift anything correctly by using your legs rather than your back to prevent injury.
- You have to keep heavy objects near your body.
Conclusion:
Physical therapy is essential for managing lower back pain because it targets the underlying causes of the condition, increases range of motion, fortifies muscles, and stops recurrence.
Physical therapy not only lessens pain but also improves general function and quality of life by combining manual therapy, posture correction, focused exercises, and patient education. Long-term comfort and less reliance on drugs or invasive procedures can result from early intervention and following a customized physical therapy program.
FAQs
What is the duration required to recover from lower back pain?
The good news is that most patients heal in a week or two, and the pain normally goes away on its own. Bed rest was the standard recommendation for many years.
For low back pain, how many visits to physical therapy are necessary?
Sessions start two to three times per week for individuals with chronic or persistent back pain, and a total of eight to twelve visits are usually needed.
When should physical therapy be discontinued?
Instead, you should eventually be able to stop physical treatment. When to cease physical therapy can be determined by two indicators: Your PT objectives have been met. You’re not getting any better results.
What happens on physical therapy’s first day?
First Physical Therapy Assessment
Your physical therapist will examine you following a discussion about your issue. Your physical therapist will concentrate on assessing any impairments that might be contributing to your issue or that might be impacted by your injury.
How long does lower back pain physical therapy last?
Depending on the reason and degree of the pain, physical treatment for lower back pain usually lasts 4–12 weeks. A few weeks may be all that is needed for acute pain, but a longer course of treatment—perhaps six to eight weeks or even more—may be necessary for persistent or severe cases.
What should I wear to a session of physical therapy?
You should dress in a way that doesn’t restrict your range of motion because your physical therapist will likely ask you to perform a number of different stretches and stretches. Sportswear like yoga trousers, shorts, tank tops, and t-shirts is are great option. Avoid dress attire, jeans, and anything too tight or limiting.
Can physical therapy help with lower back pain?
Depending on what’s causing your back pain, physical therapy may be a very good option. After a session, many people report feeling pain-free immediately. When persistent back pain is an indication of a chronic medical condition, physical therapy can also help.
Which workout is most effective for lower back pain?
The “best” exercises for reducing lower back pain combine mild stretches to increase flexibility with strengthening exercises, especially for the core. The cat-cow stretch, glute bridge, and knee-to-chest stretch are a few efficient workouts.
How might lower back pain be best treated?
Physical therapy is frequently the most successful treatment for the majority of lower back pain situations. It includes a variety of stretches, exercises, and other techniques meant to improve posture, create flexibility, and strengthen the back and core muscles.
Can lower back pain be relieved by physical therapy?
Low back pain is likely to go away on its own if you have a regular exercise regimen, are in generally good physical health, and do not have pain that travels down your legs. People who are at risk of acquiring persistent low back pain are frequently encouraged to undergo physical therapy.
References
- Facos, R. D. D. P. (2022, October 4). Physical therapy for low back pain relief. Spine-health. https://www.spine-health.com/treatment/physical-therapy/physical-therapy-low-back-pain-relief
- Back exercises in 15 minutes a day. (n.d.). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/back-pain/art-20546859
- Physical therapy for lower back pain – 10 best exercises for relief. (n.d.). https://www.movementforlife.com/articles/physical-therapy-lower-back-pain-10-best-exercises-relief
- Ladva, V. (2023, February 22). Lower back pain: Cause, symptoms, treatment, exerecise. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/lower-back-pain-treatment-exercise/