Gait Training: Physical Therapy to Improve Walking
Introduction
Gait training is a physical therapy method that enhances walking patterns and mobility. It is frequently used to assist persons who are recovering from injuries or surgeries, or who have disorders that limit their ability to walk.
Your physical therapist will design a series of exercises called gait training to improve your walking. Enhancing range of motion in your lower limb joints, enhancing strength and balance, and simulating the repetitive action of your legs during walking are all goals of the exercises.
Gait training activities aim to improve a person’s walking pattern, thereby restoring a normal, efficient gait. Developing balance and strength enhances mobility and minimizes the danger of falling. This is critical for increasing quality of life and promoting independence in mobility. Increasing mobility through expert gait retraining is critical for patients recovering from knee dislocations or other injuries. This comprehensive handbook allows people to walk with confidence and comfort. Expertly designed gait training activities improve your walking pattern while also increasing your balance and stability.
Any imbalances or anomalies must be addressed to restore mobility, avoid falls, and avoid injuries. You can rediscover the joy of pain-free, efficient walking with the help of healthcare specialists, which will help you manage and improve your everyday activities. Invest in your health to open the door to a more independent and active life.
What is Gait Training?
Gait training aims to improve a person’s walking pattern and restore a normal, efficient gait. It improves balance and strength, resulting in increased mobility and reduced chance of falling. This is critical for increasing quality of life and allowing for independence in mobility.
For patients suffering from injuries such as knee dislocations, it is crucial to improve mobility through professional gait retraining. People are given the confidence and comfort to stroll with this extensive guidance. Skillfully crafted gait training routines enhance your gait, improving stability and balance.
The following common forms of gait impairments may be needed for gait training:
- Trendelenburg walking gait
- high steppage gait
- Spastic gait
- Antalgic gait (abnormal gait caused by pain)
Training your gait can be helpful to:
- Strengthen your joints and muscles.
- Improve your posture and balance.
- Increase your endurance level.
- Enhance your muscle memory.
- Retrain your legs to perform motions repeatedly.
- Lessen the chance of falls while gaining more mobility.
Who would benefit from Gait Training?
If you’ve lost your ability to walk as a result of an injury, illness, or another health problem, your doctor may recommend gait training for you. For instance, the following circumstances may make it difficult to walk:
- Spinal cord injury.
- Possible injuries include broken legs, pelvis
- Joint replacements.
- Lower limb amputations
- Stroke or neurological disorders
- Muscular dystrophy or musculoskeletal disorders
Treatment for abnormal gait may be necessary for children with neurological disorders, musculoskeletal issues, or brain injury. Gait treatment may be advised by their doctors either before or after they learn to walk.
The Benefits of Gait Training
Gait retraining is required to address inappropriate walking patterns, and reduce the possibility of falls while enhancing mobility. It’s crucial to ensure a safe and effective return to regular walking for those who are healing from injuries.
Increasing Mobility
Regaining independence and a higher quality of life requires increased mobility, which can be achieved through specific exercises, physical therapy, and gait training. People can improve their range of motion, feel less pain, and be able to carry out everyday tasks with confidence and efficiency again.
Managing and Reducing Pain
Pain management techniques, exercise, and good posture all contribute to pain prevention and relief by easing suffering, improving overall health, and facilitating a person’s quicker return to normal activities.
Handling Conditions and Disorders of the Gait
Physical therapy, gait retraining, and customized therapies can assist people with gait disorders and diseases manage their symptoms, feeling less uncomfortable, and restoring confidence in their ability to walk.
Enhancing Stability and Balance
Targeting core strength and proprioception, balance training exercises, and therapies assist people in regaining their equilibrium and self-assurance in everyday tasks. Better quality of life and increased mobility freedom are some benefits of this.
Promoting Neurological Recovery
To assist regain lost sensory and motor abilities, rehabilitation is essential. This includes neuromuscular reeducation and focused activities. For those with neurological involvement, promoting nerve regeneration and enhancing muscular control improves mobility and quality of life, resulting in a more thorough rehabilitation process.
Encouraging Prolonged Joint Health
Discomfort, joint wear, and overuse issues can be prevented by minimizing walking abnormalities and preserving ideal biomechanics. This all-encompassing strategy, which incorporates proprioception training, posture correction, and exercises, promotes sustained joint function, speeds up healing, reduces the risk of more knee dislocations, and improves general health in the process.
How Physical Therapists Identify Gait Problems and Develop Effective Approaches
- When evaluating a patient’s gait, physical therapists watch how they walk and search for abnormalities in posture, foot placement, and stride length. They might record specifics about movement via video analysis.
- To determine the root causes, therapists assess joint mobility, muscular strength, and flexibility through manual examination.
- They create specialized treatments based on these results, including workouts and gait retraining methods to deal with particular problems.
- To improve the general effectiveness and quality of walking, these may include proprioceptive training, strength training, and balancing activities.
Methods of Gait Training
The goals of several gait training methods vary from one another. Physical therapists lead these techniques, which could include:
Gait Analysis
Understanding a patient’s gait pattern is essential for physical therapists to identify any abnormalities or disorders that may exacerbate gait problems. Once these difficulties are recognized, targeted treatments can be developed to successfully address them.
Biofeedback and Suggestions
These methods assist people in becoming more conscious of their gait by utilizing sensory information and real-time data. With the use of biofeedback systems, patients can make deliberate changes for a more effective and balanced gait by receiving immediate feedback on their weight distribution and stride length.
Equilibrium Exercises
These exercises are vital for increasing walking stability, which is necessary for avoiding falls and guaranteeing secure and assured mobility. Exercises for balance improve proprioception and strengthen the core muscles, which improve gait control.
Exercise on a Treadmill
It enables patients to practice walking in a supervised environment, which facilitates real-time gait analysis and adjustment by therapists. Better walking habits and greater cardiovascular fitness may result from this.
Analyzing Efficient Techniques for Gait Training
A range of exercises and activities known as “Gait Training” are used with patients to help them restore their ability to walk and increase their general mobility. When we get into the details, we’ll look at a variety of successful gait training techniques that address diverse requirements and the scientific underpinnings of their effectiveness.
Personalizing Your Gait Training Course
Customization is essential to meeting each person’s particular demands and obstacles. Tailored regimens can target certain deficiencies, such as proprioceptive impairments, joint restrictions, or muscle imbalances. A more successful and individualized gait training program is possible when factors like joint limits, muscular weakness, or aberrant gait are taken into account. This enables focused workouts and treatments to address particular issues.
Moving Gradually Toward a Better Gait
This method gradually increases the level of difficulty, duration, and intensity of walking tasks and exercises. It makes sure that patients increase their gait gradually without using too much physical force. Better gait quality and general mobility occur from individuals taking on increasingly difficult gait-related tasks as their strength, stability, and confidence grow. This is especially true for people recuperating from knee dislocations or other diseases that influence their walking patterns.
Keeping an Eye on Your Gait Training Progress
Measuring improvements in variables such as gait symmetry, balance, and stride length allows patients and therapists to modify the training strategy accordingly. This data-driven strategy guarantees that the gait training program stays efficient and customized to each person’s needs, allowing for improved results and assisting people in regaining confidence in their walking abilities, especially following hip or knee injuries.
Using Assistive Technology to Improve Gait
It can be advantageous to use assistive devices to improve one’s gait, particularly for those who are less mobile or are in the early phases of gait training. Canes, walkers, and orthotic aids are examples of equipment that offer extra support and help with balance and stability during a patient’s progression. With time, the patient may become less dependent on these devices and eventually walk alone.
Participating in Group Exercises to Gain Motivation
You may encourage cooperation and encouragement by exchanging experiences, challenges, and achievements with people who are going through similar things, much as participating in group gait training sessions acts as inspiration as well as guidance during rehabilitation. In particular, for individuals recuperating from knee dislocations or other injuries, group dynamics and friendly competition can enhance morale, making the gait training trip more engaging and pleasurable and ultimately assisting advancement.
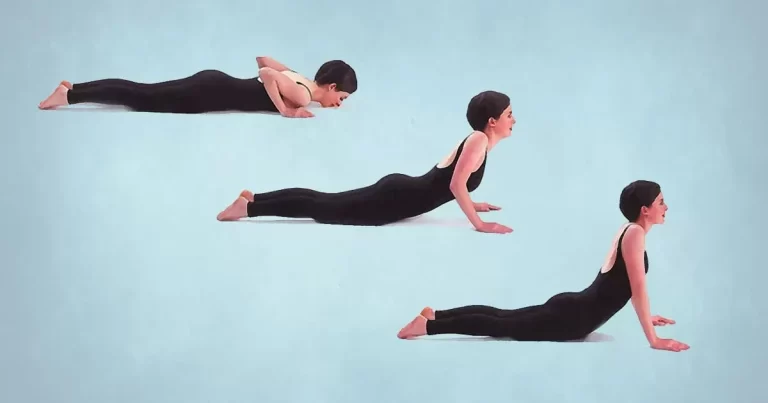
Basic Gait Training Exercises to Improve Mobility
Gait training comprises strength and flexibility exercises, while also improving balance and numerous additional skills. These exercises improve overall walking patterns, promote mobility, and address irregularities in gait.
Strength and stability Exercises
Strength and stability exercises, which focus on core muscle groups and strengthen joint stability, are especially beneficial for those recovering from knee dislocations or related injuries. They minimize the possibility of falling, enhance balance, and encourage a more intentional and effective walking gait.
Range of Motion and Flexibility Exercises
To promote a more comfortable and natural gait, range-of-motion and flexibility exercises are concentrated on increasing joint mobility while lowering stiffness. Increased flexibility helps people move pain-free and correct anomalies in their gait, allowing them to walk more comfortably and effectively. This is especially beneficial when recovering from knee dislocations or other diseases that impair mobility.
Balance and Coordination Exercises
Exercises for balance and coordination focus on enhancing proprioception, muscle control, and equilibrium all of which are critical for avoiding falls and guaranteeing a secure, confident gait. These exercises are essential for improving general mobility, healing after knee dislocations or associated injuries, and lowering the chance of gait-related problems.
Practical Walking Exercises
Practical walking drills are crucial for gait training because they help people restore their ability to walk easily and confidently by focusing on real-world applications of walking that replicate everyday activities. Especially following knee dislocations or associated injuries, they help patients traverse daily chores with stability and a lower chance of discomfort by enhancing gait efficiency and reinforcing normal walking patterns.
Suggestions for Efficient Gait Training
Efficient gait training can improve overall mobility and well-being, minimize falls, and maximize rehabilitation success.
Selecting the Correct Footwear for Ideal Gait
The correct arch support, cushioning, and stability can be achieved by choosing the appropriate shoes. They need to fit properly, taking into account the need for any orthotic devices. Wearing the proper footwear promotes healthy and effective walking patterns by lowering the risk of discomfort and irregularities in gait.
Keep a Regular Speed and Rhythm
Maintaining a constant speed while walking lowers the danger of overstretching muscles and minimizes energy expenditure. Additionally, it facilitates a more pleasant and seamless walking experience. Predictable and controlled movements are made possible by a consistent rhythm, which promotes healing and reduces excessive strain on the muscles and joints.
Improving Alignment and Posture During Walking
Good posture minimizes discomfort and encourages a natural gait by easing the pressure on the musculoskeletal system. Alignment of the head, shoulders, hips, and feet should be the main focus to achieve effective and harmonious movement. This is particularly important for those healing from any kind of injury since it promotes joint stability and lowers the possibility of recurring problems, which makes the healing process go more smoothly and successfully.
Reduce Discomfort and Tiredness
It’s crucial to progress gradually, wear appropriate footwear, and take enough breaks. Exercises for strengthening and stretching the muscles correct imbalances that frequently cause pain. Keeping adequate nourishment and hydration also helps to sustain energy levels. Reducing pain and weariness makes it possible for people to continue their gait training program, which eventually improves mobility and gives better results.
Summary
Training your gait might be challenging. Walking or learning to walk again after prolonged immobility can be physically and mentally exhausting. Share concerns with your medical professional or physical therapist. Inquire about their long-term prognosis, gait training program, and particular ailment.
FAQs
What exactly is gait training, and what makes it crucial?
Gait training is a therapeutic practice that enhances walking patterns. It is essential for movement, balance, and avoiding falls after an injury.
How long does it usually take to show improvement in gait through training?
Depending on the individual and their condition, gait improvement might take anywhere from a few weeks to many months.
Are there any workouts or strategies that are appropriate for diverse gait problems?
Indeed, particular workouts and methods are designed to target individual problems for more successful rehabilitation. These methods address various gait abnormalities.
Can people of different ages and fitness levels benefit from gait training?
Because it can be tailored to meet different demands and conditions, gait training is beneficial for people of all ages and fitness levels.
What advantages does gait training give?
Gait training has various advantages such as retraining the legs and fostering muscle memory.
Strengthening the affected joints and muscles.
Enhancing equilibrium.
Enhancing alignment.
Enhancing endurance.
Boosting movement.
Lowering the risk of falls.
What does a gait training example look like?
When exercising, such as walking on a treadmill, you can wear a harness. In addition, your therapist might advise you to practice sitting, standing, stepping over objects, and elevating your legs, among other exercises.
How does a gait trainer help people?
Similar to walkers, gait trainers are assistive technology that can help kids who might not be able to stand or walk on their own. By doing this, kids can learn to walk independently and explore their surroundings without needing assistance from an adult.
References
- Pt, B. S. (2022, March 14). Gait Training Exercises In Physical Therapy. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/gait-training-in-physical-therapy-5069884
- Gabbey, A. E. (2017, March 21). Gait Training. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/gait-training#process
- Cscs, A. T. P. D. N. (2022, December 30). Gait Training Exercises for Stroke Patients: How to Improve Your Walk. Flint Rehab. https://www.flintrehab.com/gait-training-exercises/






3 Comments