What Is The Difference Between Bone Pain and Nerve Pain?
Bone pain and nerve pain differ in their causes, sensations, and characteristics. Bone pain is usually deep, aching, or throbbing and is often linked to fractures, infections, arthritis, or cancer. It worsens with movement or pressure.
Nerve pain (neuropathic pain) is typically sharp, burning, tingling, or shooting and results from nerve damage or compression, as seen in conditions like sciatica, diabetic neuropathy, or carpal tunnel syndrome. Unlike bone pain, nerve pain can occur spontaneously, radiate along nerve pathways, and may be accompanied by numbness or weakness.
What is Nerve Pain?
Neuropathic pain, another name for nerve pain, is a stinging, burning, or tingling sensation that can feel like electric shocks. When nerves are injured or inflamed, they send conflicting messages to the brain, causing nerve pain, as opposed to muscle or bone pain, which is more annoying because it doesn’t necessarily have a visible injury.
It may be nerve pain if you have ever had strange sensations in your hands or feet, such as pins and needles or a scorching, numb feeling. The causes of nerve pain, symptoms to watch out for, and treatment choices will be covered in more detail in the sections that follow. Read on to find out more.
Numerous drugs and implanted technologies, such as spinal cord stimulators, are frequently used to treat nerve pain. Signals are sent to and received from the brain via nerves. The signals that the routes transmit may be absent if they are damaged. Additionally, a stroke or harm to the central nervous system may cause it. Nerve pain can occasionally be caused by a faulty neural system rather than painful stimuli. People who experience nerve pain frequently compare it to a burning sensation or an electric shock.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is a common treatment for nerve pain. The way nerve pain drugs function is by reducing the excitability of the nerves. Additionally, acupuncture and physical therapy could be recommended.
What is Bone Pain?
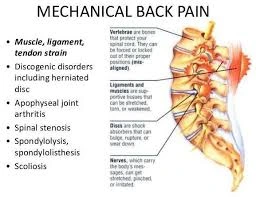
A deep, throbbing pain that frequently feels worse than joint or muscle pain is called bone pain. Bone pain is typically more persistent than other forms of pain and is frequently associated with significant illnesses. Any age can be affected, and it can happen when bones are damaged or weakened. To receive the proper care and comfort, it is crucial to comprehend the distinctions between bone pain and other forms of pain.
This pain can be either acute (short-lived) or chronic (long-lasting), and it can range in intensity from mild to severe. A bone fracture, ligament sprain, or muscle strain are the results of injury. Excessive force applied to a bone, as in a fall or auto accident, can result in fractures. Overstretching or tearing of the ligaments and muscles supporting a joint can result in sprains and strains. Swelling, bruising, and trouble moving the injured limb may accompany the pain, which is typically localized to the site of the injury.
Diseases such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis can all lead to pain in the bones. Osteoarthritis is a condition in which the cartilage which is located between joints that cushions the joints wears away, leading to Joint pain with stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Osteomyelitis is one infection that can cause bone pain. A bone infection known as osteomyelitis can be caused by either bacteria or fungi. Fever, exhaustion, and redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area are all possible symptoms of this infection. Benign bone tumors do not spread to other parts of the body but can cause pain as they grow and press on surrounding tissues. For instance, menopausal women may have bone pain because their estrogen levels are dropping, which can cause bone loss.
A number of factors, including disease, trauma, and other underlying health conditions, can cause bone pain. For an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan, it is imperative that you see a doctor if you are experiencing bone pain. Medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in certain cases, surgery are among potential treatments. Finding the cause of your bone pain and getting the appropriate treatment will help you manage your pain and improve your quality of life.
What Causes Nerve Pain?
When the nerves that transmit signals to the brain are injured or malfunction, it can result in nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain. Diabetes is another key cause, as elevated blood sugar over time can injure nerves, particularly in the hands and feet, producing diabetic neuropathy.
In addition to disorders like multiple sclerosis or HIV that can cause nerve damage, infections like shingles can cause inflammation of the nerves, which can cause an intense, searing sensation. Furthermore, chronic alcohol misuse may be a factor in the decline of nerve function. Effective treatment and pain alleviation depend on identifying the underlying source of the pain, which varies.
“You need a very discerning physician to do a good physical exam to figure out the cause because there are so many orthopaedic conditions that overlap between pain originating from problems with tendons, muscles, joints, and nerves.
Joint pain, such as that caused by arthritis, will feel more like stiffness when you rise up after sitting. Pushing on the damaged area will cause soreness if you have tendon pain.
What Causes Bone Pain?
Numerous reasons, many of which are severe and necessitate medical attention, can cause bone pain. Sharp, localized pain is caused when a bone breaks because it affects the surrounding tissues and nerves. Other factors include osteoporosis, a disorder that makes bones weak and brittle and raises the risk of fractures.
Osteomyelitis is one infection that can cause excruciating pain by inflaming the bone and surrounding tissues. In more severe situations, bone pain may be associated with cancers that have spread to the bones or bone cancer itself, which results in excruciating pain that is difficult to relieve.
Symptoms of Nerve Pain:
Muscle or bone pain is frequently very different from nerve pain, which has its own distinct set of symptoms. The following are typical indicators:
- Burning or tingling: A typical sensation in the hands or feet that resembles pins and needles.
- When the diseased area is touched or moved, electric shock pain a sudden, sharp, shooting pain often results.
- Numbness: You may experience a loss of feeling in particular body parts.
- Hypersensitivity: Pain can arise from even the smallest contact, such as your clothing rubbing against your skin.
- Muscular weakness: Nerve pain can occasionally result in issues with coordination or muscular weakness.
If any of these symptoms seem familiar to you, nerve pain is probably the cause. To learn more about possible treatments for these unpleasant feelings, continue reading.
Symptoms of Bone Pain:
- Deep, aching pain
- Localized pain
- Getting worse with movement
- Swelling or tenderness
- Chronic pain
Treatment Options for Nerve Pain:
It ta:kes more than just resting or applying ice to the affected area to treat nerve pain. The following are a few of the best available treatments:
- Medication: To assist treat nerve pain, doctors frequently prescribe antidepressants or anticonvulsants.
- Physical treatment: Tailored physical treatment can increase mobility and lessen nerve compression. Mary Thomas P.T. and other professionals at Innovative Therapy PC develop personalized plans to reduce nerve pressure and enhance function.
- Injections: For severe nerve pain, steroid injections or nerve blocks may provide more immediate relief.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Nerve pain can be lessened by controlling blood sugar levels (for diabetic individuals) or by include mild activity, such as swimming.
Treatment Options for Bone Pain:
By using drugs like bisphosphonates and altering one’s lifestyle to include more calcium and vitamin D, osteoporosis treatments aim to strengthen bones. Antibiotics and perhaps surgery are needed to eradicate infections like osteomyelitis. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery to remove the malignant growth are possible therapies for more severe illnesses like bone cancer.
Recovery from bone pain can also be greatly aided by physical therapy, particularly following surgery or a fracture. Our staff at Innovative Therapy PC strives to lessen pain while restoring strength and mobility. Please contact us for a customized recovery plan if bone pain is interfering with your day-to-day activities.
FAQs
Who is the best physician for nerve pain?
A neurologist should be consulted right away for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan if you have persistent nerve pain that won’t go away and is beginning to interfere with your everyday activities.
What is the most recent nerve pain treatment?
The medications, called peripheral sodium channel blockers, would give physicians a new treatment option for the millions of Americans who suffer from neuropathy, or nerve pain, for the first time in more than 40 years.
What differentiates acute pain from nerve pain?
Usually restricted to a single location, such as the neck, shoulders, or back, muscular pain is sometimes caused by strain, misuse, or injury. However, nerve pain usually spreads along the injured nerve’s route.
How can bone pain be prevented?
Acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen are examples of over-the-counter pain medicines that may provide you with short-term relief from bone pain. Usually, oral or intravenous antibiotics are needed to treat osteomyelitis. The management of pain associated with cancer can be quite complicated.
What instantly relieves nerve pain?
Nerve pain can be treated in a number of ways, such as using drugs, physical therapy, and relaxation methods.
What is mistaken as pain in the nerves?
Because neuropathy and radiculopathy share symptoms including pain, weakness, tingling, and numbness, they are frequently confused.
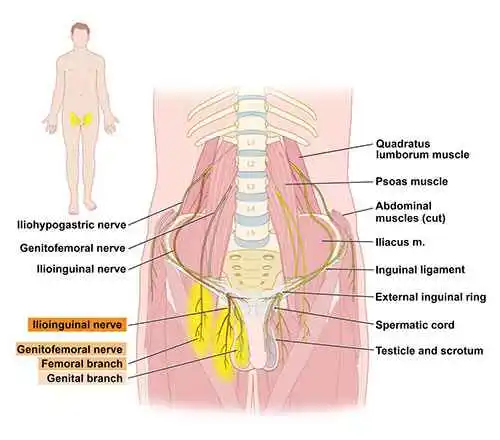
Why do bones and nerves pain?
Nerve root pain can be caused by the following:
arthritis. spurs of bone. inflammatory condition. spinal stenosis and other degenerative spinal disorders.
How can bone pain differentiate from nerve pain?
It is more akin to a stinging, burning, or tingling sensation that could feel like electric shocks than a simple ache or soreness. Nerve pain is more annoying since, unlike muscle or bone pain, it doesn’t necessarily have an obvious injury.
References
- MaryT. (2024b, October 24). Bone Pain Vs Muscle Pain Vs Nerve Pain – Spot & Heal Faster. Innovative Therapy PC. https://innovativetherapypc.com/bone-pain-vs-muscle-pain-vs-nerve-pain/
- Patel, D. (2023a, February 10). What is the difference between bone pain and muscle pain? Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/difference-between-bone-pain-and-muscle-pain/
- SaaolOrtho Blogs. (2024, January 16). Understand the differences between bone and muscle pain. https://www.saaolorthocare.com/blog/understand-the-differences-between-bone-and-muscle-pain/