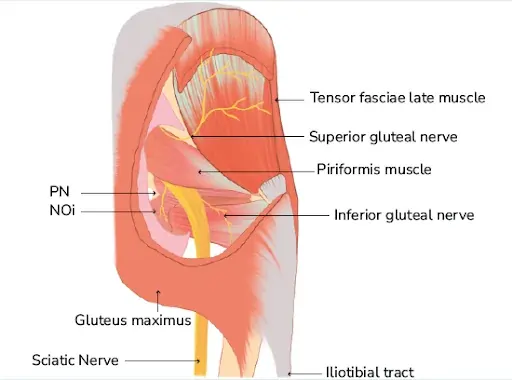
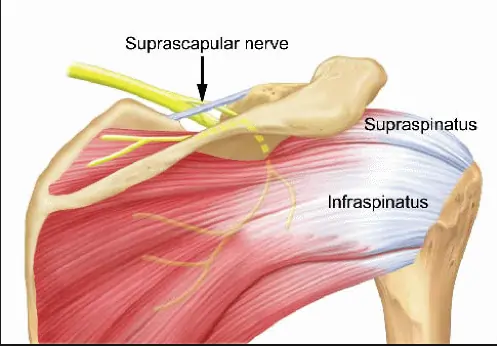
Long Thoracic Nerve
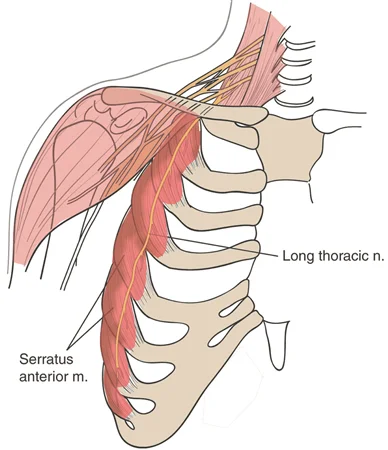
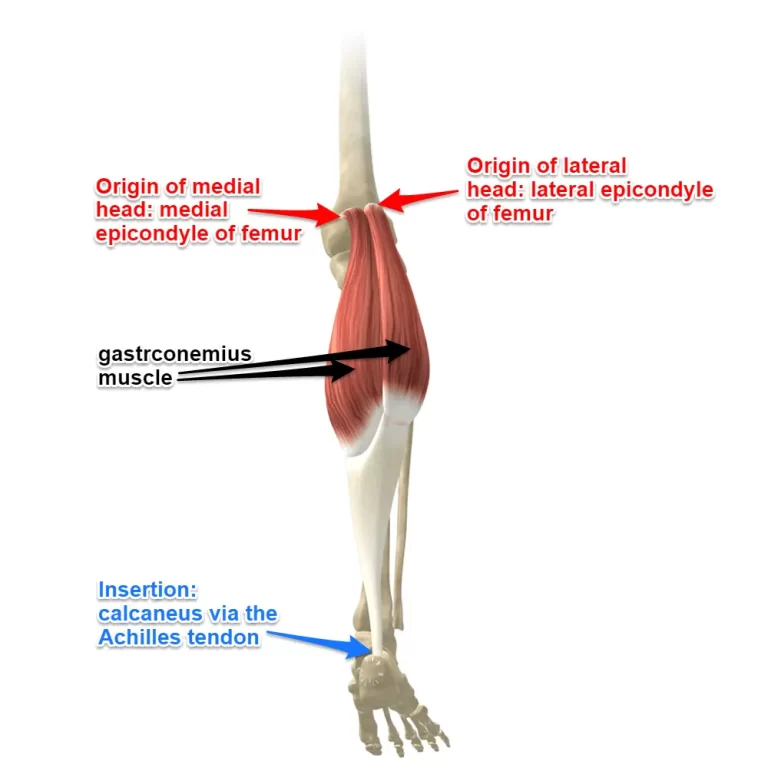
Introduction The long thoracic nerve arises from the C5-C7 nerve roots and innervates the serratus anterior muscle. It plays a crucial role in scapular stability, preventing winging of the shoulder blade. Injury to this nerve can result in scapular winging, weakness in shoulder protraction, and difficulty in overhead movements. The serratus anterior muscle, one of…