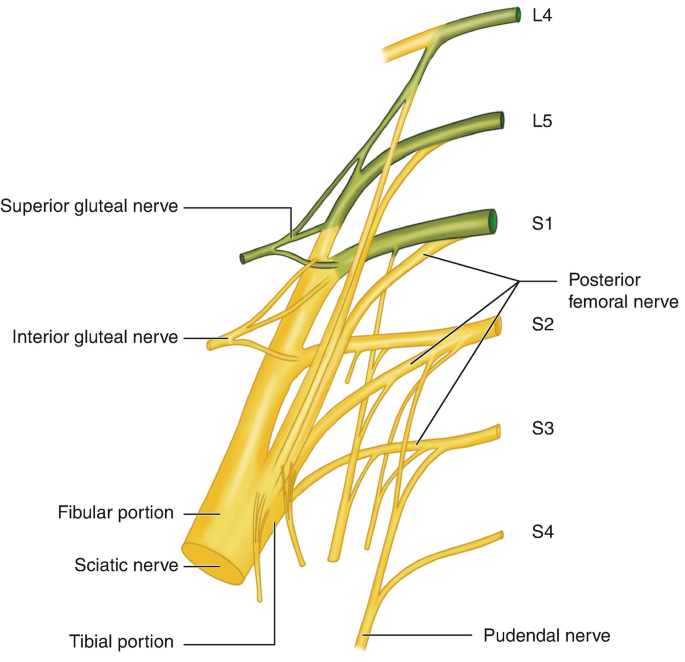
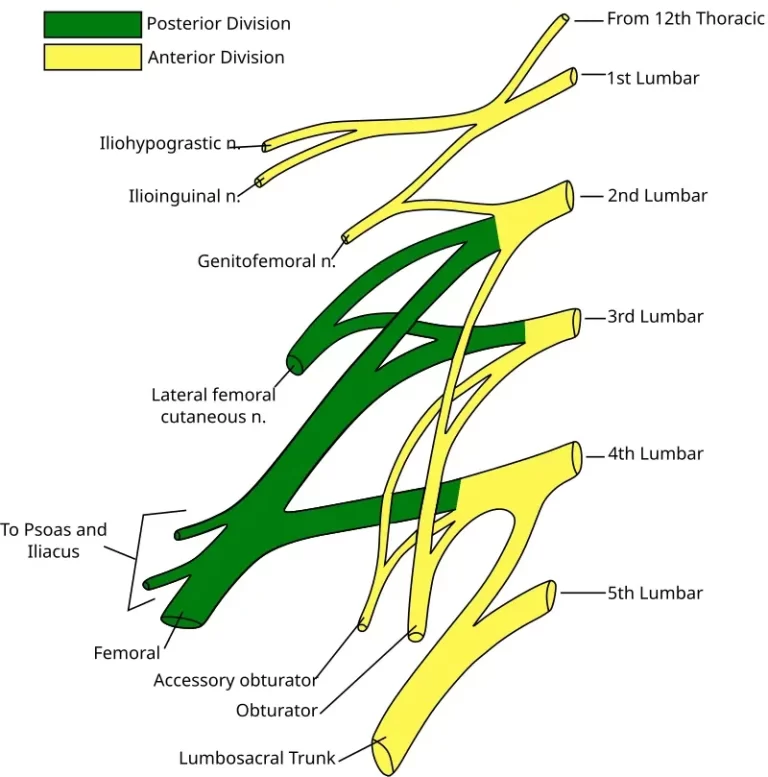
Iliohypogastric nerve
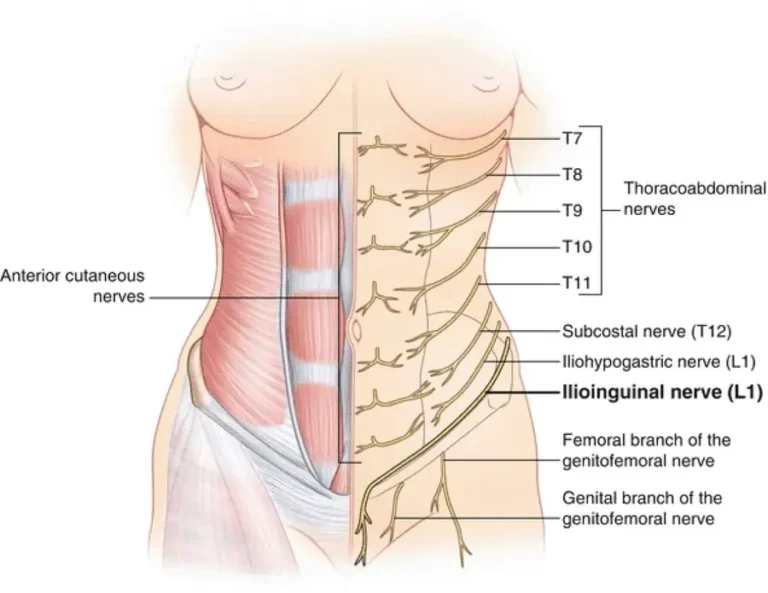
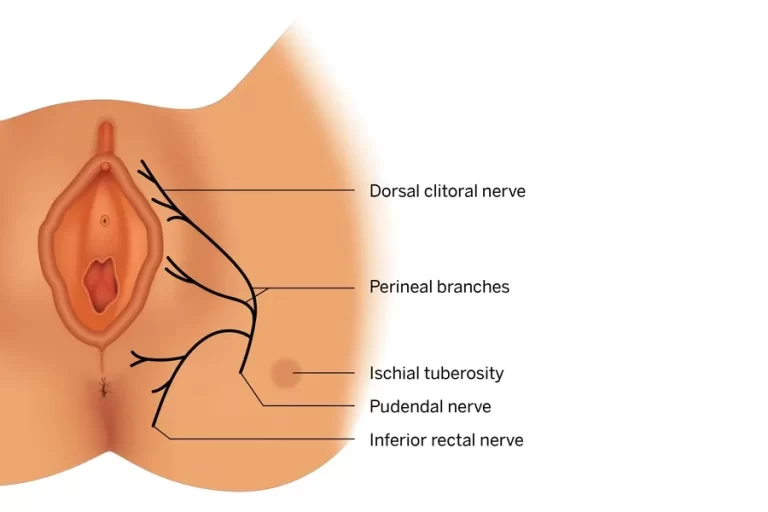
Introduction The iliohypogastric nerve is a branch of the lumbar plexus, originating mainly from the L1 spinal nerve. It provides motor innervation to the lower abdominal muscles (such as the internal oblique and transversus abdominis) and sensory innervation to the skin over the lower abdomen and upper hip (gluteal) region. It plays a role in abdominal wall…