Ankle Mobility Test
Introduction:
The range of motion and flexibility of your ankle joint are evaluated by an ankle mobility test, which is essential for healthy walking, running, squatting, and lower-body function in general.
I frequently see patients with stiff ankles, particularly those that affect their ability to dorsiflex, or raise their foot. Inadequate ankle mobility is a significant cause of problems that extend up the kinetic chain, causing problems at the knee, hip, and lower back in addition to the ankle.
When the ankle is immobile, other joints overcompensate, which accelerates wear and tear. Using a protractor while lying down, you should have at least 10 to 15 degrees of dorsiflexion.
Numerous factors, including tight calf muscles, restricted ankle joint mobility, bone abnormalities, or inadequate muscular control, might contribute to stiff ankles. It might be time to have your ankle examined by a specialist to determine how you can increase your mobility and alleviate symptoms if you have a chronic ankle or knee problem, and discover that your ankle lacks dorsiflexion movement.
Purpose of Ankle Mobility Test:
Assessing your ankle joint’s range of motion, especially its ability to dorsiflex or flex upward toward the shin, is the goal of the ankle mobility test. For routine motions like walking, sprinting, squatting, and leaping, this motion is essential.
- Evaluate your range of motion.
- Identify Any Mobility Restrictions.
- Avoid getting injured.
- Improve the quality of movement.
- Track Training or Rehab Progress.
Technique of Ankle Mobility Test:
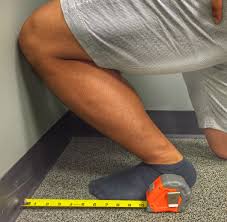
It is necessary to conduct this test against a wall. You’ll need a normal tape measure (cm). Participants are instructed to position their foot so that, on the floor tape measure, an imagined line drawn across the big toe and heel lines up. In addition, a vertical line aligned with the tape measure is drawn on the wall. Plunging forward till the participant’s knee reaches the wall (vertical line) is the directive.
It is necessary for the heel to always be in contact with the ground. The heel stays in contact with the floor, but the foot is shifted away from the wall until the knee can only touch the wall slightly. Participants are permitted to grasp onto the wall for support, and the leg that is not being tested may rest on the floor. The greatest distance between the big toe’s tip and the wall is noted. Ankle dorsiflexion is measured in centimeters (cm), where one centimeter is equivalent to roughly 3.6°.
Evidence of Ankle Mobility Test:
For the weight-bearing lunge test, the inter-rater reliability for the distance measured was R = 0.99 (95% CL: 0.97 – 0.99). Additionally, the measurement had great intra-rater reliability (ICC between 0.98 and 0.99).
Additionally, there is compelling evidence that the weight-bearing lunge test has good intra-rater reliability (ICC = 0.65 – 0.99), as well as inter-rater reliability (ICC = 0.80 – 0.99), according to a recent systematic review on the test’s reliability.
The important role of proper ankle mobility:
We discussed that you may struggle to complete a squat without falling backwards, but the main problem is that it might cause injury. As an athlete, you may be taught to stay alert for extended periods. Tennis players, for instance, are taught to be alert and keep their feet moving to respond more quickly.
Some track athletes and cross-country runners run on their toes. The majority of people struggle with this assignment; however, other people don’t. It’s only a matter of stance. This will result in stiffness in the calf and soleus muscles and force the ankle into a plantarflexion resting position.
This is a problem because when you run, leap, or plant, your body won’t be able to absorb the tension or shock that the ground causes if your ankle joint doesn’t have enough dorsiflexion. Remember that landing, cutting, and planting can create forces that are 4–11 times your body weight (CES Corrective Exercise Specialist NASM Textbook).
Smaller constructions experience shock if pressures or forces are not distributed across the body and many joints. These tiny structures will get inflamed or break because they lack a base to support that weight.
Conclusion:
The ankle mobility test is a straightforward yet effective method for evaluating the range of motion of your ankle joint, particularly in dorsiflexion. For optimal lower-body function, including walking, squatting, and running, ankle mobility is crucial.
Your chances of getting hurt or having trouble moving efficiently may be increased if your results indicate reduced mobility. Frequent testing can help you prevent imbalances, improve ankle function, and perform better in everyday activities and sports when paired with specific stretches and mobility exercises.
FAQs
How can ankle mobility be improved?
Exercises that increase the ankle joint’s range of motion and flexibility should be the main focus of any ankle mobility improvement program. These workouts focus on dorsiflexion and plantar flexion and involve calf stretches and ankle circles. Stability and mobility can also be improved by strengthening exercises like toe lifts and heel walks.
Why do ankles become immobile?
Tight lower-leg tissues, such as the Achilles tendon or the calf muscles that move your ankle, are most frequently the cause of decreased ankle mobility.
What are some ways to improve ankle mobility?
Ankle Circles
Underneath the front ankle, place a folded towel. Alternate between clockwise and counterclockwise rotations with your front foot. Make sure you only move your foot and not your leg. For a total of 40 seconds, repeat three times on each foot.
What is the ankle mobility surgery?
A minimally invasive, successful procedure for treating a variety of ailments is ankle arthroscopy, which includes: Unstable: It may be difficult to stand or move firmly if you have a bone abnormality inside your ankle joint. What is causing your unsteadiness during an arthroscopy can be identified and fixed by your surgeon.
Ankle mobility: what is it?
Ankle mobility: what is it? The flexibility of the ankle joint and the muscles and tendons that surround it is referred to as ankle mobility. Your range of motion during activities is increased when your ankle is flexible.
How can one determine whether ankle mobility is poor?
Let’s do a brief evaluation: Place your toes six inches from the wall while kneeling. Try to touch your knee to the wall while leaning forward so that your heel does not lift off the floor. You may have limited ankle mobility if your knee is unable to reach the wall.
How can ankle mobility be tested?
Use a Seated Heel Sit to rapidly check for ankle plantarflexion mobility. You may have limited ankle plantar flexion if you are unable to reduce the space between your ankles and the floor. With little difficulty, you should be able to sit with your torso upright and your glutes resting on your heels.
What signs of limited ankle mobility are present?
A chronic sense of instability, a feeling that the ankle is going to give way, and trouble keeping balance are just a few of the symptoms that people with weak ankles may have. Additionally, some people may experience frequent flare-ups of ankle pain and edema, particularly following physical activity.
References:
- Carreon, J., & Carreon, J. (2022, January 13). Knee to Wall test – Washington Athletic Club. Washington Athletic Club. https://www.wac.net/wac-wire/knee-to-wall-test/
- Knee to wall Test (Ankle mobility). (n.d.). https://sportsphysio.ie/test/knee-to-wall-test-ankle-mobility-3650.html
- Knee To Wall Ankle Dorsiflexion Assessment – [P]rehab. (2023, October 18). [P]Rehab. https://library.theprehabguys.com/vimeo-video/knee-to-wall-ankle-dorsiflexion-assessment/