Vastus Intermedius Muscle
Introduction
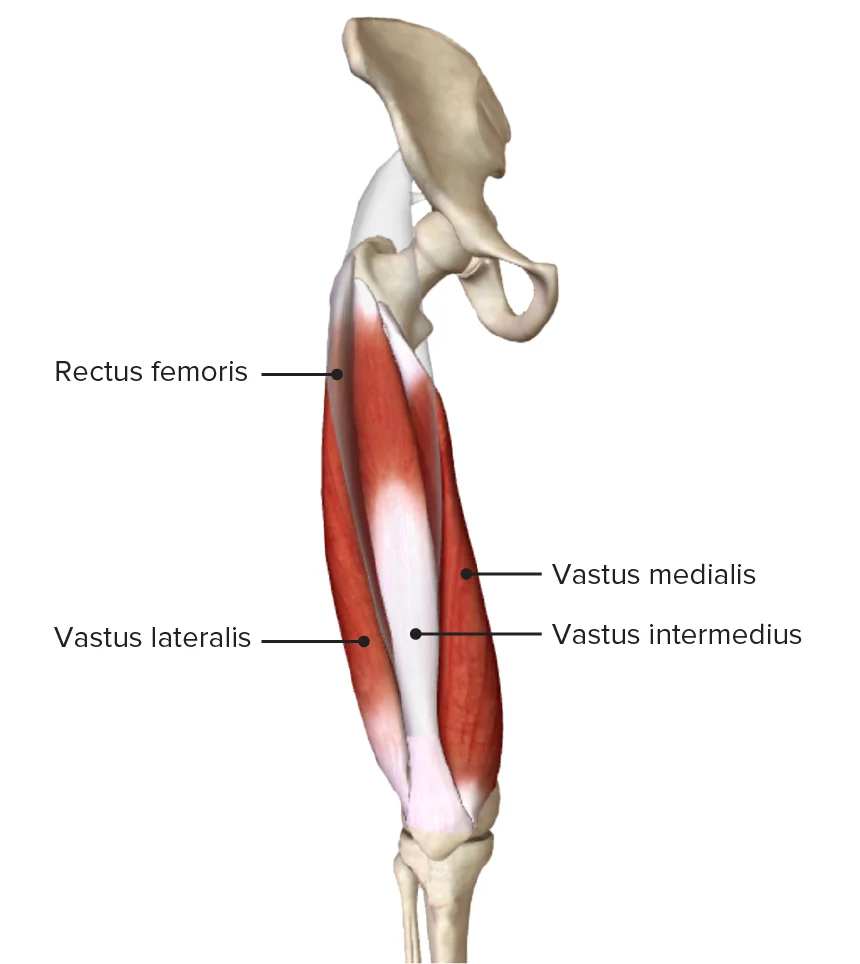
The Vastus Intermedius is one of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris group in the anterior thigh. Located deep between the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis, it lies beneath the rectus femoris and plays a crucial role in knee extension.
As a key component of the quadriceps, the vastus intermedius contributes to movements such as walking, running, and jumping by helping to straighten the leg at the knee joint. Its function is essential for lower limb stability and strength, making it an important muscle for both daily activities and athletic performance.
Origin
The Vastus Intermedius originates from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the proximal two-thirds of the femoral shaft, specifically along the upper portion of the femur’s anterior and lateral aspects. It also arises from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum.
Insertion
The Vastus Intermedius inserts into the tibial tuberosity via the quadriceps tendon, patella, and patellar ligament. Specifically, its fibers merge with the deep portion of the quadriceps tendon, which attaches to the superior border of the patella.
Innervation
Neural impulses coursing through the femoral nerve, specifically from lumbar nerve roots L2, L3, and L4, animate the Vastus Intermedius muscle.
Blood supply
This muscle is supplied by the lateral circumferential femoral artery’s descending branch.
Lymphatic drainage
The vastus intermedius, a quadriceps muscle in the thigh, primarily drains its lymph into the inguinal lymph nodes. Lymphatic vessels accompanying the major blood vessels of the thigh facilitate this drainage. Ultimately, lymph from this region converges into the common iliac lymph nodes, reflecting the general drainage pattern of thigh muscles towards the inguinal lymph node chain.
Functions
Extension of knee
The quadriceps muscle group, comprised of the vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, and rectus femoris, plays a crucial role in extending the knee.
Exercises
Stretching Exercises of Vastus Inter-medius
Standing Quadriceps Stretch:
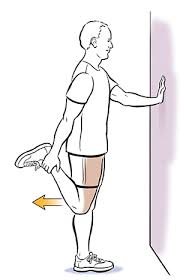
- Stand upright, using a wall or chair for balance.
- Flex one knee, drawing your heel towards your buttocks.
- Gently grasp your ankle or foot with the same side hand.
- Pull your heel gently in the direction of your buttocks until the front of your thigh feels stretched.
- Maintain this position for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs.
Kneeling Quadriceps Stretch:
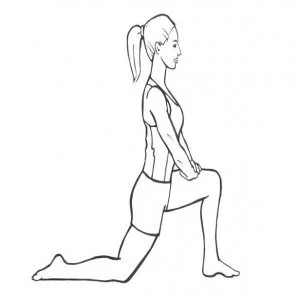
- Begin by kneeling on the floor. Bend one knee to a 90-degree angle, placing the other foot flat on the ground in front of you.
- Gently lean forward, placing your hands on the ground for support.
- Transfer your weight to the front foot.
- You should feel a comfortable stretch in the quadriceps muscle of the back leg.
- Hold this position for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat.
Lying Quadriceps Stretch:
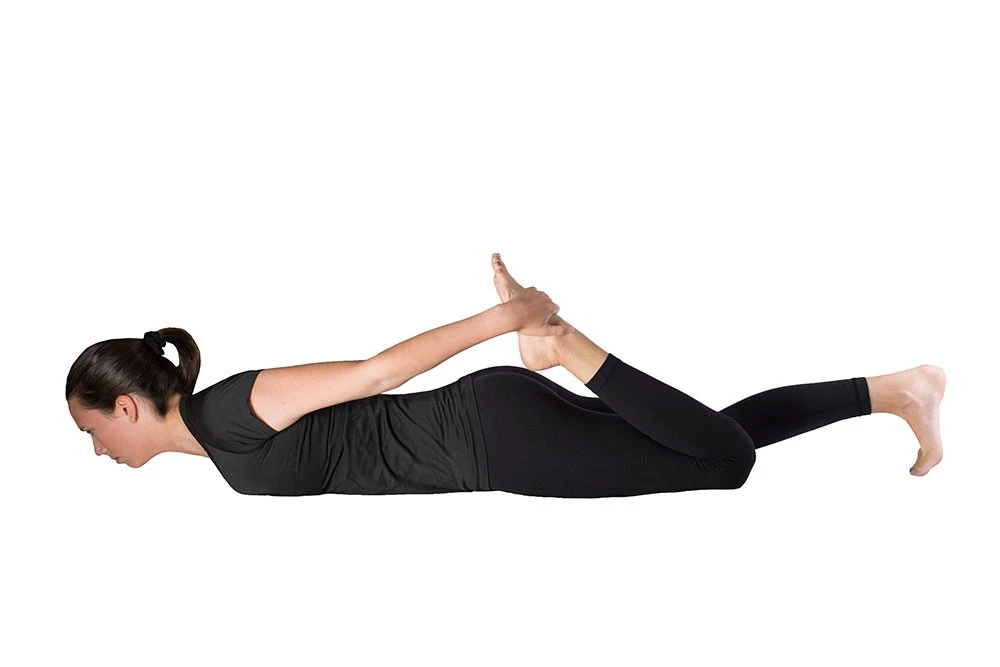

- Lie on your side, bottom leg bent, top leg extended.
- Bend your top knee and grasp your ankle or foot.
- Gently pull your foot towards your buttocks, stretching your thigh.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch foots.
Strengthening Exercises
- Leg Extensions:
- With the seat and weight properly adjusted, sit on a leg extension machine.
- Squeeze your quads at the peak of the exercise as you extend your legs against the machine’s resistance.
- Push off with your front foot to go back to the starting position.
2. Squats:
- Place your toes slightly out and your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Maintaining a straight back and an active core, lower your body as though you were reclining on a chair.
- To go back to the beginning position, push through your heels.

Among the variations are:
3. Lunges:
- Bend both knees to a 90-degree angle and take a single stride forward.
- Use your front foot to push off the ground and return to the starting position.
- Do the same with the opposite leg.
- Variations include:

- Walking lunges: Make a walking motion by stepping forward with one leg first, then the other.

2. Reverse lunges: Step backward with one leg to do a reverse lunge.
3. Bulgarian split squats: Put one foot on a chair or bench behind you to perform Bulgarian split squats.

4. Leg Press:
- Adjust the weight on a leg press machine while seated.
- Stretching your legs can help you push the weight away from you.
- Return to the starting position gradually.

5. Step-Ups:
- Use one foot to ascend onto a platform or step, then raise the other foot to join it.
- Take one foot and then the other to step back down.

Vastus Intermedius Muscle Pain
Vastus intermedius muscle pain can arise from various factors, including:
- Referred pain: Pain felt in the vastus intermedius may originate from another area, such as the lower back.
- Muscle strain: Overexertion or sudden injury can lead to muscle strain, a common cause of vastus intermedius pain.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendon connecting the vastus intermedius muscle to the kneecap can cause pain.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac cushioning the joint, can also lead to pain.
- Nerve entrapment: Compression or pinching of a nerve can cause pain and numbness in the affected area.
Treatment for Vastus intermedius muscle pain:
- Reducing swelling by icing the afflicted region.
- Compression to provide support to the afflicted area.
- For reduction of swelling you can elevate the limb which is affected.
- NSAIDs, or anti-inflammatory drugs, are used to lessen pain and swelling.
- Passive range of motion exercises are a possible treatment.
FAQs
What is the cause of Vastus Intermedius muscle pain?
Vastus intermedius pain is frequently caused by muscle strain, often resulting from sudden, forceful eccentric contractions. Overuse, overstretching, or muscle fatigue can also lead to pain in this area.
How is a vastus intermedius injury treated?
The treatment for a vastus intermedius injury will depend on the severity of the injury. Mild injuries may heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). More severe injuries may require physical therapy or even surgery.In the early phases of acute injury, NSAIDs are frequently recommended. Oral steroids or muscle relaxants may be used in severe instances involving several joint areas. Treatment methods may include steroid injections, botox, or trigger point injections.
What does the vastus intermedius do?
The main function of the vastus intermedius is to extend your knee joint, which means straightening your leg. It also helps with other movements like walking, running, and squatting.
How long does it take to recover from vastus intermedius?
You won’t be able to play after experiencing an abrupt, severe ache. You may get slight bruising or some swelling, and you frequently experience knee pain when walking and bending. It will take four to six weeks to fully recover, and in order to restore your full function, you will need appropriate therapy.
How can the vastus intermedius be strengthened?
Step Ups
Goblet Squat
Pulse Squat
How is a strain of the vastus intermedius treated?
By adhering to the RICE concept (rest, ice, compression, and elevation), the goal of acute phase therapy for quadriceps strains is to reduce bleeding into the muscles. Resting the muscle stops the initial injury from getting worse.
References:
- Vastus intermedius muscle. (2024, July 29). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vastus_intermedius_muscle
- Valand, B. (2022, September 23). Vastus intermedialis muscle Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercises. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/vastus-intermedialis-muscle-anatomy/
- Vastus Intermedius, Physio pedia , https://www.physio-pedia.com/Vastus_Intermedius