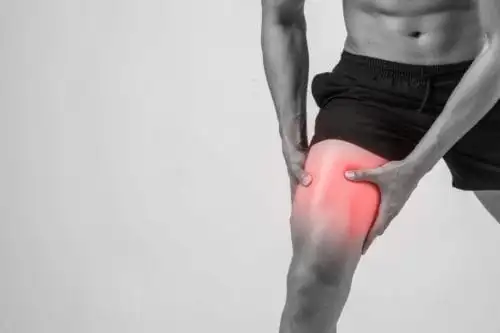
Muscle Pain In Leg
Muscle pain in the leg, also known as myalgia, is a common issue that can result from various causes such as overuse, muscle strain, dehydration, or minor injuries. It may also be linked to underlying conditions like poor circulation, nerve issues, or nutritional deficiencies.
The pain can range from mild discomfort to sharp or throbbing sensations, often affecting mobility. Identifying the cause is key to effective treatment, which may involve rest, stretching, hydration, or medical evaluation for persistent or severe cases.
What is a Muscle Pain In the Legs?
- Leg pain is the most common because the leg bears the weight of the entire body during daily activities like standing for extended periods, walking, climbing stairs, playing sports continuously, or working too much.
- There are numerous reasons for this pain, including musculoskeletal issues and trauma.
- Numbing, radiating, burning, and tingling sensations in the painful area are the causes of this pain.
- A variety of diagnostic tests are used to diagnose this pain.
- Pain medicine, physical therapy, and the RICE principle are the main methods used to relieve this pain.
What causes Muscle pain in the leg?
Traumatic causes:
- Musculoskeletal, neurological, and vascular causes of leg pain include sports injuries; other causes include blood vessels, muscles, nerves, soft tissues, bones, and joints; repetitive sports, such as running, can result in shin splints and stress fractures; and occasionally, leg pain is a sign of serious vascular issues.
Musculoskeletal causes:
- The musculoskeletal causes include arthritis, an inflammatory illness affecting the hip, knee, and ankle joints, and crepitus, identified by a popping and cracking sound in the knee joint.
- If a fall causes a muscle, tendinitis, or ligament to become strained, as well as any pain that stems from musculoskeletal issues.
- The musculoskeletal system is also responsible for stress fractures, compartment syndrome, and night cramps.
Vascular Causes:
- Neurological pain is constant, even at night and while you’re sleeping, and can be caused by neuropathy or nerve pain, sciatic nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome, a disease in which the legs twitch uncontrollably.
Neurological causes:
- Neurological causes include sciatic nerve pain, neuropathy or nerve damage, and restless legs syndrome, in which the legs twitch uncontrollably. Neurological pain is always present, even at night and while sleeping.
Leg cramps & Charley horses:
- This illness is characterized by brief pain episodes that last for a few minutes.
- This also usually happens when the calf muscles at the rear of the lower leg tense and spasm.
- At night, cramps are more likely to develop.
- One in three adults over 60 get night cramps, and 40% have more than three episodes per week.
Peripheral artery disease:
- Leg pain caused by inadequate circulation is the result of this ailment.
Intermittent claudication:
- occurs as a result of the leg muscles’ blood supply becoming too limited.
- It is administered because pain is caused by a shortage of oxygen and nutrients.
DVT = deep vein thrombosis:
- This is a form of leg pain that, if left untreated, can develop into a blood clot on the lung.
- This ailment describes a blood clot in the leg’s deep veins.
- After a prolonged period of sitting, such as on a long-distance flight, it may emerge.
- Running and jogging produce recurrent impact pressures that put too much strain on the muscles and tendons.
- Shin splints are caused by extreme, localized muscular soreness.
- The shin bone is frequently the site of bone pain.
Fractures & stress fractures:
- Applying excessive pressure to a bone that has been affected by a fall might lead to fractures.
- Some fractures have significant bruising, swelling, and deformity and are readily and instantly noticeable.
- Usually, this illness requires immediate medical intervention.
- Small fractures known as stress fractures are caused by repetitive strains that athletes experience, frequently when their level of exercise increases too quickly.
Popliteus tendinitis:
- is caused by knee soreness when running downhill.
- The popliteus tendon, which is crucial for knee stability, becomes inflamed in this syndrome.
Strain & sprains:
- Strains and strains are caused by acute trauma.
- The term “sprain” describes tearing and stretching.
- A strain indicates a muscular or tendon pain.
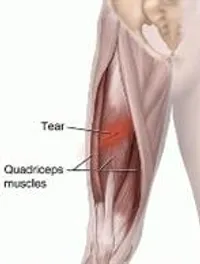
- Running causes this pain, and a hamstring strain can cause severe pain in the back of the thigh muscle, but it generally results from a partial tear.
- The most common causes of sprains and strains are insufficient overstretching, flexibility training, and failing to warm up before an activity.& continue exercising even after the pain has occurred.
Compartment syndrome:
- When leg pain occurs, it causes swelling and dangerously high muscle pressure, which can result in both acute and chronic compartment syndrome.
- It is caused by significant bruising and a fracture.
- The swelling causes pressure to build up until the muscular tissue’s blood supply is severed, which deprives the muscles of oxygen and nutrition.
- Given the pain, this pain is rather intense.
- In severe situations, numbness and paralysis occur after the first agony.
Sciatic nerve pain:
- It happens when a nerve, usually in the spine, is compressed, causing pain that travels from the hip joint to the foot.
- It occurs when a herniated disk and a pinched nerve cause a muscle spasm.
Ovarian cancer:
- Additionally, this ailment causes leg pain and swelling.
Symptoms of Muscle pain in the leg?
- You get cramping pain in your muscles when you strain yourself and exercise.
- You experience pain in your calves, thighs, feet, and buttocks.
- You have agony when you walk and climb stairs.
- Additionally, note any swelling in the painful location.
- In the painful location, you experience tightness and spasms.
- Additionally, the patient exhibits trigger points and tenderness in the location of muscular soreness.
- Additionally, you may have a burning feeling where the pain is.
- You can also feel the leg’s frailty.
How can muscle pain in the leg be diagnosed?
- Contacting a doctor is necessary in certain serious situations.
- When you see a doctor, they evaluate to determine the cause of your leg pain.
- The initial physician inquires about the patient’s medical history and attempts to determine the reasons for the pain.
- Next, note the muscle soreness and any swelling or redness.
- A portion of the palpation detects muscle pain, including swelling and spasms.
- Part of the evaluation looks at the range of motion and strength of the leg pain.
- Following the diagnosis, the doctor recommended appropriate leg treatment.
What is the treatment for the leg pain?
The diagnosis of leg pain, including its etiology and related symptoms, is the primary step in treating it. The most often used therapeutic approaches are physical therapy combined with exercise and pain medication based on the RICE Principle.
When the pain first started, the doctor gave you advice on how to relieve muscle pain using the RICE method.
- R- Rest: To avoid more pain and to give the body time to heal and lessen swelling, the doctor recommends a few days of rest.
- I- Ice: It helps you reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. It is administered to the area of pain for up to 20 minutes while wrapped in a cloth rather than directly on the skin. You may also use frozen peas and an ice pack to assist reduce swelling.
- Compression: To lessen pain and swelling, apply an elastic bandage, but don’t wrap it too tightly.
- Elevation: Lift the wounded leg above the level of the heart so that gravity assists with the drainage, which helps you lessen the swelling & pain.
Pain medication:
- The majority of the medications your doctor gave to you are painkillers, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs).
- To relieve pain and swelling, you can also apply a pain-relieving gel or spray to the affected area.
- However, see a doctor if the pain does not go away after more than 72 hours.
Cold / Heat therapy:
- You can also apply a hot or cold pack to the affected area for 20 minutes if you have leg muscle pain accompanied by edema and spasms.
- How is leg pain treated with physical therapy?
- The physical therapy treatment involves massage, electrotherapy, stretching exercise & strengthening exercises.
Massage:
- It is recommended to massage the trigger points and tender points to relieve the pain and swelling.
- Oil and powder are used to apply this massage for five minutes.
- Additionally, the massager applies this massage.
Electrotherapy treatment:
- SWD, TENS, IFT, US, and deep heating therapy are all incorporated into the electrotherapy treatment to relieve pain and edema.
- To alleviate the tender points and swellings, the therapist employed US = ultrasound on the painful area for five minutes.
- To lessen leg muscular soreness Physical therapists apply transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) machines, short wave diathermy (SWD), and interferential treatment (IFT) to the pain location for ten minutes.
Stretching exercise:
- Calf Stretch
- Shin Stretch
- Hamstring Stretch
- Quadriceps Stretch
- Inner & Outer Legs Stretch
Calf Stretch:

- The patient sits on the ground with her legs extended straight in front of her.
- Wrap the balls of the feet with a large towel and a yoga strap.
- Surely Pull the towel and strap slowly until the toes begin pointing toward the torso while maintaining a straight back and knee joint.
- The patient holds the stretch for 30 seconds and then releases it while breathing properly.
- This stretching is done three times in a row, three times a day.
Shin Stretch:
- With the tops of their feet on the ground, the patient is kneeling on the ground and pointing their toes.
- Sit back on the heels gently until the shins start to stretch a little.
- After 30 seconds of holding this stretching position, take a break.
- This stretching is done three times in a row, three times a day.
Hamstring Stretch:

- The patient has both legs extended straight out in front of the body while seated on the ground.
- Maintain a long back and an open chest by bending at the waist.
- Sliding your hands from the floor toward your feet, extend your body forward.
- For 30 seconds, hold this stretching position.
- This stretching is done three times in a row, three times a day.
Quadriceps Stretch:
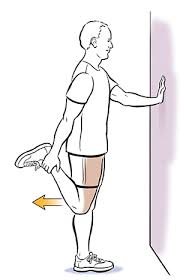
- To maintain balance, the patient is held onto a chair and a wall. Standing on one leg, the patient raises the other leg off the ground, bends at the knee, and pulls the foot up near the buttock.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds, then repeat the stretch on the other leg three times at a time, three times a day.
Inner & Outer Legs Stretch:
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart and face forward to begin.
- To lunge to the left, try stepping out while bending your knee joint to 90 degrees without letting it pass your toes. then straighten the right leg and lower into the left side.
- Place your hands on your left leg while maintaining a straight back, and hold the position for 30 seconds.
- After that, straighten up from standing.
- On the other side, repeat this stretching.
- This stretching is done three times in a row, three times a day.
Ankle Pumps:
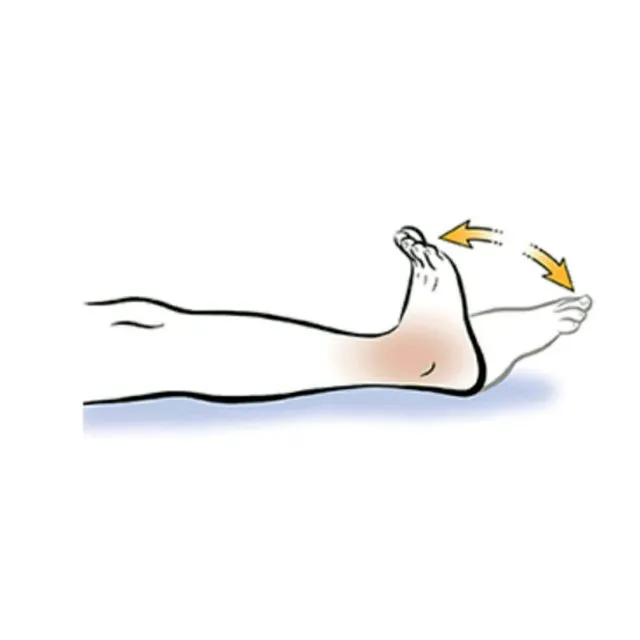
- On the floor, the patient is sitting and recumbent with both legs outstretched.
- You can perform this exercise anywhere, including at the office, while seated in a chair.
- Next, point the toes away from you and pull them toward you.
- Pull and push the toes as far as you can in each direction.
- After that, do this exercise ten times.
- Regularly perform this workout two to three times a day.
Straight leg raises:
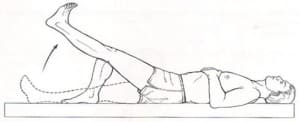
- With one leg bent and the other straight out in front of the body, the patient is lying on the floor.
- Then Stretch your quadriceps, straighten your leg, and then slowly raise it off the ground until it is as high as your bent knee joint.
- Return to the beginning position after holding this exercise for ten seconds.
- Perform this exercise two or three times, doing ten repetitions for each leg.
Summary
There are numerous reasons for leg pain, and the symptoms frequently coexist. The person should get in touch with a doctor if they continue, get worse, or make living difficult.
Depending on what is causing the leg pain, a person can obtain treatment. By stretching, massaging, and drinking plenty of water, they can also take care of it at home. Physicians currently use the PEACE and LOVE treatment to treat sports pain.
FAQs
What deficiency results in nighttime leg pain?
Leg cramps are known to be caused by carnitine deficiency, which can occasionally be seen in individuals taking specific drugs, such as antibiotics that include pivalate.
Which vitamin helps with pain in the legs?
Our findings showed that daily vitamin K2 administration reduces the incidence, duration, and intensity of muscular cramps in older adults with NLCs.
What beverage helps with leg pain?
Compared to commercial sports drinks, coconut water has a higher potassium content. Coconut water may help avoid leg cramps caused by activity and perspiration since insufficient potassium is linked to leg cramps. According to research, consuming coconut water before working out can help your muscles get more potassium.
What is the best way to treat leg pain at home?
Treatment and Care
The RICE method can be used if your leg pain is modest, such as from muscular cramps or overuse pain. RICE is an acronym for: R— Rest: Give your leg as much rest as you can. I — Ice: For 15 minutes at a time, apply ice to the sore spot.
I have leg pain; should I consult a physical therapist?
So, how can you determine if seeking treatment from a physical therapist for leg pain is worthwhile? Constant Pain, or Almost Constant Pain After the first few days, if your legs hurt constantly, or perhaps most of the time, you’ll probably require a physical therapist’s assistance to heal.
For leg pain, which workout is best?
The Greatest Leg Pain Relief Stretches and Exercises
Hamstring Stretches: The back of the upper leg contains the hamstring muscles.
Stretch your calves by standing arm’s length away from a wall.
Hip Flexor Stretches: Maintain a straight back while sitting on the floor.
Leg pain is caused by this deficiency?
Thiamine, or vitamin B1,
If you run and eat a low-calorie diet, you may be at risk for vitamin B1 deficiency. Muscle cramps, exhaustion, and strange sensations in your legs and feet are all symptoms of a vitamin B1 shortage.
How can I get rid of leg muscle aches the quickest?
When an accident causes sudden pain, apply the RICER method:
Don’t move your leg while you rest.
Ice: apply a bag of frozen peas or an icepack to the aching spot for 15 to 20 minutes at a time.
Compression: securely bandage the affected area.
Maintain your leg above your hip for elevation.
Referral: have your physician examine your pain.
What causes leg pain primarily?
There are numerous potential causes for leg pain. The majority of leg pain is caused by overuse or wear and tear. pain or illnesses affecting the joints, bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, or other soft tissues may also be the cause. Issues with your lower spine may be the cause of certain types of leg pain.
Can leg pain be resolved with physical therapy?
For the best short- and long-term outcomes, it is critical to get physical therapy treatment as soon as feasible. To bring you back to sports and daily activities as soon as possible, physical therapy treatment will lessen pain and swelling, encourage healing, and increase muscular strength and flexibility.
Which vitamin is excellent for leg pain?
Our findings showed that daily vitamin K2 administration reduces the incidence, duration, and intensity of muscular cramps in older adults with NLCs.
Does walking help with muscle soreness in the legs?
According to Dr. Knepper, walking promotes the enlargement of the legs’ tiny arteries, which raises blood flow. He advises, “Remember that any pain you may experience while walking is not resulting in additional harm.” You can start a basic walking regimen to start improving the health of your legs if your doctor gives the go-ahead.
How does relaxation alleviate leg muscle pain?
Claudication is the term for oxygen-deficient muscle pain that is caused by activity and goes away with rest.
What is the most effective way to alleviate muscle soreness in the legs?
Take these actions first if you have leg pain from cramping or overuse:
Get as much rest as you can.
Raise your leg.
Use ice for a maximum of fifteen minutes.
Stretch and massage the muscles that are cramping gently.
Use over-the-counter pain relievers such ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Can physical therapy help with leg pain?
Lower leg pain that has been referred can typically be resolved in a few months of physical therapy; however, if the issue has persisted for a long time, more intensive care may be required to address it.
References
- Dhameliya, N. (2022, May 13). Muscle pain in leg: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment & Exercise – Samarpan. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/muscle-pain-in-leg-treatment/
- Felman, A. (2023, January 10). What to know about leg pain. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/241968