Text Neck Syndrome
What is Text Neck Syndrome?
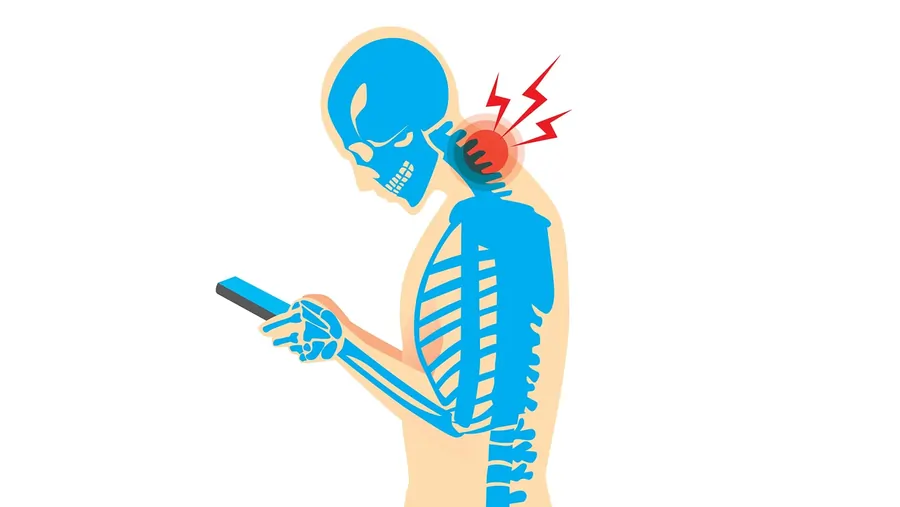
Text neck, sometimes referred to as tech neck, is a syndrome that arises from placing our heads forward, which puts continuous tension on the neck area.
Three things occur when you look down:
- Your neck extends forward.
- Your shoulders may elevate towards your ears or become rounded forward.
- The muscles in your shoulders and neck begin to tense.
Maintaining this position for extended periods might have negative effects on your cervical spine and neck in addition to your shoulder muscles and supporting ligaments.
Because you typically don’t notice the consequences of your posture until it’s too late, text neck can be very annoying. Sometimes you’re so engrossed in what you’re seeing that symptoms don’t even occur to you until much later. Regretfully, there is a cascade-like effect.
How does one develop text neck?
The tilting of the head that usually happens when staring down at a phone or tablet screen is called “text neck.”
Long-term staring down at our devices is the cause of the neck ache that results from this type of stress. Dr. Bang clarifies that while a few minutes here and there won’t make much of an impact, the length of time is what truly begins to damage your neck and spine.
he says The real issue arises when you’re scrolling on TikTok for hours at a time, even reading a lengthy email or watching something on YouTube.
What signs of text neck are present?
- The discomfort in the neck: Prolonged or irregular neck pain is one of the primary indicators of text neck. Pain can range greatly from mild discomfort to excruciating pain that is debilitating.
- Upper back pain: Pain or discomfort in the upper back that aches, especially in the area between the shoulder blades.
- Pain or discomfort in the shoulder: The forward head posture can tense and strain the shoulder muscles.
- Headaches: Issues with the neck can result in tension headaches, sometimes referred to as cervical dysplasia.
- Restricted range of motion: Turning one’s head or looking up may cause discomfort for people who have stiff necks.
- Muscle stiffness: Common symptoms include tightness and stiffness in the muscles of the upper back and neck.
- Posture changes: Weakness in the muscles and strain on the shoulders and neck can aggravate someone’s posture.
Other signs that may exist include:
- Flattening of thoracic kyphosis
- Early-onset arthritis (Cervical spondylosis)
- Spinal degeneration
- Disc compression
- Muscle weakness & tightness
- Loss of lung capacity
How to Diagnosis Text Neck Syndrome:
- Shoulders and neck are painful, either severely or sharply.
- The degree of range of motion reduction has been linked to stiffness after exercising or tightness in the shoulder and neck.
- headaches that are intermittent or persistent.
- upper limb nerve pain accompanied by tingling and insensitivity.
- eye pain.
- X-ray imaging: X-ray imaging can detect problems such as bone spurs and anomalies in the degenerative spine.
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Electromyography (EMG): A pinched nerve can be diagnosed with an EMG and nerve conduction study, which entails inserting a needle into a muscle to measure nerve signal speed.
- Blood tests: To determine whether inflammation or infection is present, a complete blood count (CBC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) test might be performed.
Treatment of Text Neck Syndrome:
When using telephones or other hand electronic devices, bear in mind the following conditions from a systematic review of Text Neck:
Refrain from overusing and take regular pauses.
refused extended periods of immobility.
Adjust the gadget so that it relieves pressure on the neck, head, and upper limbs.
Keep clear of repetitive motions like long-term talking or swiping.
Avoid holding bulky or heavy devices for extended periods in just one hand.
For people suffering with text neck, rehabilitation was proven to be quite beneficial. A 2-4 week program for rehabilitation may begin with soft tissue mobilization, Grade 1 and 2 joint mobilization, active and passive stretching of tense muscles, muscular strengthening, posture retraining, and at-home exercise regimens.
In active instances, the primary objective is pain alleviation. It is attainable through:
- a common neck activity includes extending and rotating.
- Exercises for the chin
- Heat/ice packs
- Massage
- Medication for discomfort, facet joint injections, or trigger point therapy are options in severe chronic instances.
Physiotherapy Treatment of Text Neck Syndrome:
Pain Control:
- Initially, modalities including electrical stimulation, heat therapy, cold therapy, or ultrasound may be utilized to assist reduce inflammation and pain.
- Massage and soft tissue mobilization are two more manual treatment procedures that can assist reduce muscle soreness and stress.
Soft cervical collar.

This is a cushioned neck ring that secures around the neck with Velcro. Your doctor may suggest wearing a soft cervical collar to help you relax the muscles in your neck and reduce neck motion. This may help lessen the pinching of the nerve roots that happens when the neck is moved. Wearing a soft collar for an extended length of time can weaken the muscles in your neck.
Active neck movements for a range of cervical spine :
- Neck Flexion and Extension: To extend your neck, gently tilt your head back. To flex your neck, gently lower your chin towards your chest.
- Neck Side Bending: To extend the muscles in your neck, tilt your head sideways in the direction of each shoulder.
- Neck Rotation: Look over each shoulder as you turn your head to the right and left.
Strengthening Exercises:
Exercise for scapular stabilisation:
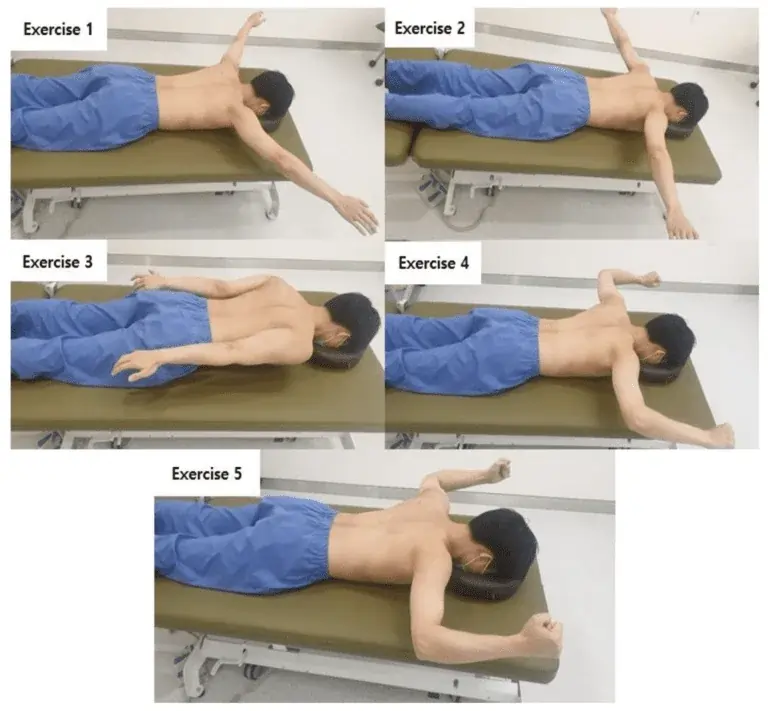
Goal: to ease neck pain
- Start by laying down on your back with your arms hanging at your sides, your shoulders relaxed, and your head up.
- Pull the shoulder blades back and down while repositioning the shoulders gradually.
- When doing this move, the chest should only slightly thrust forward.
- Hold for five seconds.
- After doing the three repetitions twice a day, gradually extend the time.
- Next, as a progression, a person can pull towards you with both ends of a thera band while performing a scapular squeeze.
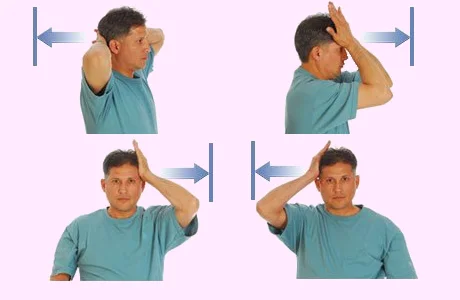
The purpose of isometrics is to strengthen the muscles in the upper back and neck.
- Put your hand on your forehead.
- Do not bend the neck in any way; instead, press the head against the palm.
- Hold for five seconds.
- Five times a day, repeat
Levator scapular stretch:
- The idea is to stretch the levator scapulae, which is often the big knot in your upper back.
- Begin by adopting the proper seating position and lowering your shoulders.
- Using one hand, grasp the seat’s bottom.
- Turn the chin slightly towards the armpit until the other side of the neck feels comfortably extended.
- Repeat on the other side, holding for ten seconds.
- Do two sets of five repetitions every day.
Chin tuck:
Starting from an erect sitting position, tuck your chin slightly, creating the appearance of a double chin. Verify that your chin and nose are pointing upward rather than downward. Keep your posture for five seconds. Do this thirty times.
Scapular Retraction:
Sit up straight to begin. Tense the muscles between your shoulder blades by gently pressing them together. 30 repetitions of holding this posture for 5 seconds are required.
Pectoralis Stretch:
Stretch your pectoralis by placing one hand up to your shoulder level on a door frame. Bend forward gradually until you feel your chest stretching.
Adjusting posture:
Better posture might help to lessen the tension on the cervical spine. You might learn the right ways to sit, stand, and sleep from your physical therapist.
Massage with effleurage to ease tense muscles:
What is the process?
A form of massage called effleurage aids in muscle relaxation and promotes lymph and blood flow. Effleurage, often known as gliding, is a widely used massage method that is applied in a way that avoids attempting to move the muscles that are immediately beneath the skin.
Complications of Text Neck Syndrome:
Text neck can result in more serious diseases or complications if left untreated, such as:
- Chronic pain: If text neck is left untreated, it can eventually turn into upper back and chronic neck pain, which can have a serious negative impact on a person’s quality of life and day-to-day activities.
- Muscle imbalances: The neck’s and upper back’s muscles and ligaments may become constantly strained, resulting in muscular imbalances. In addition to causing discomfort, this may have an impact on posture and general musculoskeletal health.
- Spinal misalignment: Text neck may alter the spine’s natural curvature, which may result in disorders such as an excessively curved upper or lower back.
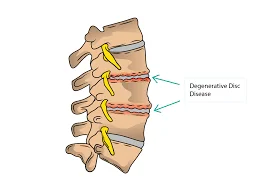
- Degenerative disc disease: Improper posture can put more strain on the cervical spine, which can hasten the intervertebral discs’ deterioration. This could aggravate degenerative disc degeneration, which causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected area.
- Nerve compression: Long-term compression of the neck’s nerves can result in disorders such as radiculopathy, or pinched nerves, which can cause discomfort, tingling, or numbness in the hands and arms.
How to Protect Your Text Neck?
Here are some preventive measures that can be useful:
Adjust the way you hold the phone.
To avoid having an excessively forward-leaning head, raise your phone to eye level. To align your ear with your shoulders, maintain a neutral spine, advises Cupp. This will stop the head from cocking forward.
Take phone pauses.
Every hour, even a quick two- to three-minute break from the phone can be helpful.
The consensus for preventing text neck is to break the habit of looking down to use a phone or do any work, however, most people find this to be quite uncomfortable. Thus, Goodrich suggests that individuals attempt to deliberately take breaks from using their phones. Utilize a Post-it note or set up a computer or phone reminder. This small realization has the power to alter history.
Check out the Text Neck app.
A green or red light indicates the “instant real-time feedback” that an Android app called Text Neck gives you about your posture. Additionally, you can choose to have a beep reminder alert you when you’ve reverted to old, unhealthy behaviors.
If your pain lasts for a long time, identify the source.
It is advised to get adjusted if your pain lasts for a long time. This will aid with pain relief and will treat the structural problems that text neck causes over time. And perhaps they have a point. According to a reliable study published in 2007, chiropractic care is one of the main nonpharmacological treatments for both acute and chronic back and neck pain that is thought to be helpful.
Practice yoga for ten minutes.
Yoga is a superior approach to prevent and manage back and neck discomfort, according to Goodrich. The rationale is that it involves breath work, enhances body awareness, and assists with movement patterns. Daily yoga practices can help rectify muscular imbalances, such as tight rhomboids, which are the source of neck pain. Text neck conditions can be improved by performing the aforementioned exercises or by practicing yoga for ten minutes each day.
Outlook
The increasing usage of electronic gadgets has led to an increase in concerns around text neck syndrome. Text neck may go away in time if it is detected early and is not too severe. As long as a person practices proper self-care, such as better posture, consistent stretching, and using over-the-counter pain medications, this is acceptable.
Rehabilitation can also be accelerated by lifestyle changes like reducing screen time and using ergonomic devices.
Moderately severe cases could take several months to become betterTrusted Source. Exercises to strengthen the muscles in the neck and upper back, as well as physical therapy and chiropractic adjustments, may be helpful. Recovery depends on consistent devotion to these treatments and lifestyle modifications.
Serious text neck sufferers could need extra time to heal, particularly if they also have other medical issues such as disc compression or nerve impingement.
FAQs
How much time does text neck syndrome recovery take?
Recovery times from text neck syndrome can depend on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, their willingness to modify their lifestyle and adhere to treatment guidelines, and the specific therapy they use.
How should someone with text neck syndrome sleep?
Research suggests sleeping on the side or back if a person has upper or lower back pain, claims a 2019 review trusted Source. The authors do note that additional high-caliber research is required.
How can someone with a text neck sleep?
While sleeping on your side has its advantages as well, laying on your back keeps your spine in the most neutral posture.
Which illnesses make text neck syndrome more likely to occur?
Prolonged downward gaze with the cervical spine in flexion is the primary factor aggravating this clinical condition.
Is massage therapy beneficial for tech neck?
Massage is effective in easing stiffness and soreness in the muscles.
Can text neck cause anxiety?
Because incorrect posture patterns force the body to move forward and down, which can lead to hyperventilation, stress, and anxiety, they can also cause poor breathing, poor balance, and headaches in the neck and lumbar region.
References
- Parmar, R. (2022, June 11). Text Neck: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Exercise – Mobile P. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/text-neck-cause-treatment-exercise/
- Therapy, C. P. (2022, October 31). Text neck: Signs, Symptoms and What You Can Do. Clarity Physical Therapy & Wellness Center. https://claritypt.com/blog/text-neck-signs-symptoms-and-what-you-can-do/
- Ames, H. (2023, November 10). What to know about text neck syndrome. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/text-neck-syndrome#faq
- Clinic, C. (2024, June 27). How Your Smartphone May Be Giving You ‘Text Neck.’ Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/text-neck-is-smartphone-use-causing-your-neck-pain
- Dalwani, D. (2024, April 29). Cervical Radiculopathy – Cause, Symptoms, Treatment. Physical Therapy Treatment and Exercise. https://physical-therapy.us/cervical-radiculopathy/