Pubofemoral Ligament
Introduction
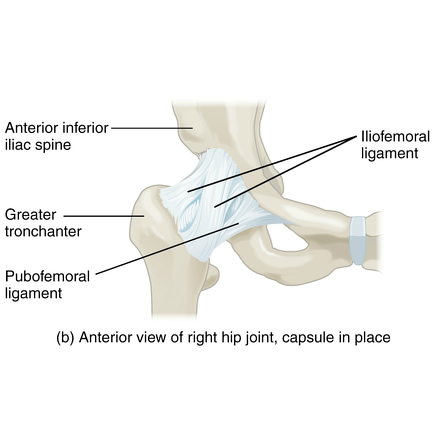
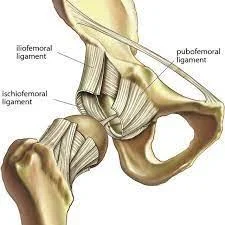
The pubofemoral ligament is a strong, triangular ligament located on the anterior side of the hip joint. It connects the pubic bone to the femur and helps prevent excessive hip abduction and extension, providing stability to the joint.
Pain, stiffness, and trouble moving can also be symptoms of pubofemoral ligament injuries. Complete recovery requires the right diagnosis and care. By taking precautions such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising with proper form, injury risk can also be reduced.
Structure of the Pubofemoral Ligament
A robust, thick band of connective tissue that connects the pubic bone to the femur is called the pubofemoral ligament. With a broad base that connects to the pubic bone and a narrow apex that connects to the femur, it has a triangular form. The strength and stability of the ligament come from the crisscrossed arrangement of collagen fibers that make up this structure.
The capsule of the hip joint, a thin, fibrous membrane that envelops and supports the joint, merges with the pubofemoral ligament at the pubic bone. The ligament connects to the intertrochanteric line, a bony ridge on the upper portion of the thigh bone, at the femur.
One of the three ligaments that aid in hip joint stability is the pubofemoral ligament. Ischiofemoral and iliofemoral ligaments are the other two ligaments. These ligaments cooperate to keep the hip joint from moving too much and to keep the femur and pelvis in the right position.
Therefore, the pubofemoral ligament’s structure is ultimately appropriate for its function in maintaining the stability of the hip joint. The ligament can function slowly from the attachment points at the femur and pubic bone, and its strong collagen fibers and triangular shape allow it to withstand the forces applied during physical activity.
Function of the Pubofemoral Ligament
The pubofemoral ligament plays a crucial part in keeping the femur and pelvis in the correct alignment and stabilizing the hip joint. Together with the iliofemoral and ischiofemoral ligaments, it prevents the hip joint from moving excessively in all directions, including adduction, rotation, and abduction.
The hip joint experiences a variety of forces during exercise, which may lead to instability. Through its strong and stable connection between the pubic bone and the femur, the pubofemoral ligament aids in the counteraction of these forces. This helps to avoid injuries and permits the hip joint to move smoothly and under control.
Apart from its function in hip joint stability, the pubofemoral ligament also contributes to the preservation of appropriate pelvic alignment. The ligament keeps the pelvis level and stops it from tilting or rotating too much. When engaging in physical activity, is crucial for preserving appropriate posture and balance.
All things considered, the hip joint’s pubofemoral ligament is a vital part that keeps the joint stable and in the right alignment. It is ideal for supporting the hip joint during physical activity because of its strength and stability.
Blood supply of the Pubofemoral Ligament
The blood supply to the pubofemoral ligament comes from a variety of sources. A branch of the deep femoral artery, the medial femoral circumflex artery provides the ligament with its primary blood supply. The pubofemoral ligament receives blood from the branches of the medial femoral circumflex artery, which runs along the medial aspect of the femur.
The obturator artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery, provides blood to the pubofemoral ligament in addition to the medial femoral circumflex artery. The pubic bone receives blood from the obturator artery’s branches, which then deliver blood to the pubofemoral ligament.
The pubofemoral ligament’s blood supply is crucial to preserving its health and functionality. The ligament may weaken or sustain injury in the absence of a sufficient blood supply, increasing the risk of injury and hip joint instability.
In conclusion, the obturator artery and medial femoral circumflex artery supply blood to the pubofemoral ligament. These arteries support the ligament’s strength and functionality by supplying it with vital nutrients and oxygen.
Symptoms of the Pubofemoral Ligament Injury
The hip joint is stabilized by the pubofemoral ligament, a robust band of connective tissue that extends from the pubic bone to the femur (thigh bone). This ligament injury can result in a variety of symptoms, such as:
- Pain: Groin or hip pain is the most typical sign of a pubofemoral ligament injury. The pain may be mild or severe, and it may worsen with movement or activity.
- Stiffness: Hip joint stiffness resulting from pubofemoral ligament injuries can make walking and movement difficult.
- Swelling: A pubofemoral ligament injury may result in swelling in the hip or groin region.
- Weakness: Weakness in the hip and leg muscles can result from injury to the pubofemoral ligament, which stabilizes the hip joint.
- Instability: Severe injuries to the pubofemoral ligament may result in hip instability, which makes it difficult to stand or walk unassisted.
- Clicking or popping: Following a pubofemoral ligament injury, some people may feel as though their hip joint is clicking or popping when they move.
- Limited range of motion: It may be difficult to carry out specific activities or movements due to a pubofemoral ligament injury that restricts the hip joint range of motion.
As untreated pubofemoral ligament injuries can result in long-term complications like chronic pain and hip joint instability, you must seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Injuries of the Pubofemoral Ligament
An injury to the pubofemoral ligament can result from a variety of activities, including:
- Sports: Sports like basketball, volleyball, and soccer that require quick direction changes or jumping can strain the pubofemoral ligament and raise the risk of injury.
- Running: Running puts a lot of strain on the hip joint and can cause injuries to the pubofemoral ligament, particularly if the runner overuses their muscles or has poor form.
- Lifting weights: Lifting weights and performing leg exercises like lunges and squats. It raises the possibility of injury and may put a strain on the pubofemoral ligament.
- Pregnancy: The pubofemoral ligament may become weaker and more prone to injury as a result of weight gain and hormonal changes.
- Trauma: A pubofemoral ligament injury may result from trauma to the hip joint, such as a fall or auto accident.
- Repetitive motions: Over time, the pubofemoral ligament may be strained by repetitive motions that involve the hip joint, such as prolonged standing or sitting.
- Genetics: A person’s genetic composition or underlying medical conditions may make them more vulnerable to pubofemoral ligament injuries.
It is vital to take preventative measures, such as warming up appropriately, using proper form, and wearing appropriate footwear, when engaging in activities that can raise the risk of a pubofemoral ligament injury. To avoid more injury and long-term issues, you must seek medical attention as soon as you notice any signs of a pubofemoral ligament injury.
Treatment of the Pubofemoral Ligament
There are two effective approaches for treating pubofemoral ligament injuries: conservative treatment and physical therapy.
Conservative treatment
Physical therapy, pain management, and rest are usually the three main components of conservative treatment for injuries to the pubofemoral ligament. Conservative treatment aims to heal the hip joint, lessen pain and inflammation, and return it to normal function.
Rest: The healing of the injured pubofemoral ligament depends on rest. Avoiding activities like sports or heavy lifting that exacerbate the injury may be one way to do this.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy has the potential to enhance hip joint strength, flexibility, and range of motion. This could involve stretches to increase flexibility as well as exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip joint. To aid in healing, a physical therapist may also use techniques like electrical stimulation or ultrasound.
Pain management: If required, prescription painkillers may be used in addition to over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Pain and inflammation can also be lessened with the use of heat or ice therapy.
Bracing: To help support the hip joint and lessen the strain on the pubofemoral ligament, a brace or other support may be suggested in certain situations.
Surgery: The pubofemoral ligament may need to be repaired or rebuilt in rare instances when conservative treatment is ineffective. Surgery, however, is usually reserved for extreme cases and is only advised if conservative measures have failed.
Even after symptoms subside, it is crucial to adhere to your doctor’s conservative treatment recommendations and perform any physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises as directed to avoid further injury or recurrence.
Physiotherapy treatment
To increase the hip joint’s range of motion, strength, and flexibility, physiotherapy treatment for pubofemoral ligament injuries usually consists of a mix of exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques. Physiotherapy aims to promote healing, lessen pain and inflammation, and get the hip joint back to its normal function.
The following are typical physiotherapy interventions for injuries to the pubofemoral ligament:
Strengthening exercises: By increasing the strength of the muscles surrounding the hip joint, strengthening exercises can support the pubofemoral ligament. Exercises for hip abduction, hip adduction, hip extension, and hip flexion are a few examples.
Stretching exercises: By increasing hip joint flexibility, stretching exercises can lessen the strain on the pubofemoral ligament. Examples include stretches to strengthen the hamstrings, IT bands, and hip flexors.
Manual therapy: Manual therapy methods like trigger point release, joint mobilization, and massage can help improve the range of motion and lessen hip joint pain and inflammation.
Modalities: To encourage healing and lessen hip joint pain and inflammation, modalities like electrical stimulation or ultrasound may be used.
Gait analysis: To find any anomalies that might be causing your pubofemoral ligament injury, a physiotherapist may examine your gait or the way you walk. To lessen the strain on the hip joint, they might suggest alterations to walking habits or footwear.
Working with your physiotherapist regularly is crucial to creating a customized treatment plan that meets your unique needs and objectives. To get the best results from your physiotherapy treatments and exercises, you must be consistent.
Risk factors of the Pubofemoral Ligament
A robust band of connective tissue called the pubofemoral ligament joins the femur (thigh bone) to the pubic bone. It lessens excessive movement and stabilizes the hip joint. However, some things can make injuries to the pubofemoral ligament more likely. These consist of:
- Overuse: The pubofemoral ligament may sustain microtrauma as a result of repetitive strain on the hip joint, resulting in pain and inflammation. Athletes who play sports that require running, jumping, or abrupt direction changes frequently exhibit this.
- Trauma: A pubofemoral ligament injury, such as a sprain or tear, can result from a direct hit to the hip or from falling onto the hip.
- Muscle imbalances: Having weak or taut hip-area muscles can change how the joint moves and put more strain on the pubofemoral ligament. The ligament may be strained, for instance, by excessive hip adduction (inward movement) brought on by weak gluteal muscles.
- Joint hypermobility: People who have hypermobile joints—those that move outside of their typical range of motion—may be more susceptible to injuries to the pubofemoral ligament because of excessive hip joint movement.
- Bad posture: Bad posture can put more strain on the pubofemoral ligament and other hip joint structures. One example of this is an excessive anterior pelvic tilt, or forward tilt of the pelvis.
- Aging: Our joints’ connective tissue loses its elasticity and becomes more vulnerable to injury as we get older. Injury to the pubofemoral ligament may become more likely as a result.
To lower the risk of pubofemoral ligament injuries, it is critical to address these risk factors through appropriate training, stretching and strengthening exercises, and postural correction.
The ways to reduce the risk of pubofemoral ligament injury
In the hip joint, a band of connective tissue called the pubofemoral ligament joins the femur and pubic bones. It aids in hip joint stabilization and protects against overuse that can lead to injury. The following methods can help avoid pubofemoral ligament injuries:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Carrying too much weight increases the risk of injury by putting additional strain on the hip joint. It is possible to lower this risk by keeping a healthy weight.
- Stretch and warm up: It’s critical to properly stretch and warm up the muscles before beginning any physical activity. By doing this, the risk of injury is decreased and the body is better prepared for the activity.
- Use appropriate technique: To prevent undue strain on the hip joint, it’s critical to use appropriate technique when engaging in any physical activity. This can involve running with the right foot placement or lifting weights with the right form.
- Wear the right shoes: When engaging in physical activity, wearing the right shoes can lessen the impact on the hip joint. Shoes with adequate cushioning and arch support can help absorb shock and lower the risk of injury.
- Take breaks to rest: Overuse of the hip joint can cause injury. Regular rest intervals during exercise can help avoid this by giving the joint time to rest and heal.
- Increase hip muscle strength: By strengthening the muscles surrounding the hip joint, you can lower your risk of injury by adding more stability and support. These muscles can be strengthened with exercises like lunges, squats, and leg lifts.
- Seek medical attention: It’s critical to get medical help if you’re experiencing hip joint pain. Healing can be accelerated and additional harm can be avoided with early diagnosis and treatment.
You can help keep your hip joint healthy and avoid injuries to the pubofemoral ligament by following these recommendations.
FAQs
The pubofemoral ligament: what is it?
In the hip joint, a band of connective tissue called the pubofemoral ligament joins the femur and pubic bones.
What is the pubofemoral ligament’s main function?
The hip joint is stabilized by the pubofemoral ligament, which also helps to limit excessive movement that may lead to injury.
How can I avoid sustaining a pubofemoral ligament injury?
Maintaining a healthy weight, warming up and stretching, using the right technique, wearing appropriate footwear, taking rest periods, strengthening your hip muscles, and getting medical help for pain are all ways to avoid injuring your pubofemoral ligament.
Which exercises are good for strengthening the hip muscles?
The muscles surrounding the hip joint can be strengthened with exercises like leg lifts, lunges, and squats.
References
- Patel, D. (2023b, August 8). Pubofemoral ligament – structure, function, injury. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/pubofemoral-ligament/