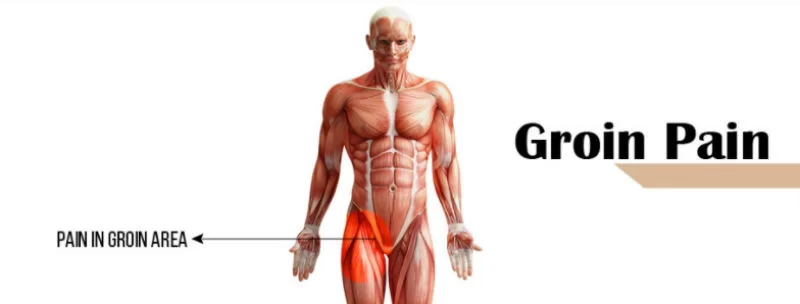
Muscle Pain in the Groin area
What is a Muscle Pain in the Groin area?
Muscle pain in the groin area is often caused by strain, overuse, or injury to the adductor muscles, which run along the inner thigh. Common causes include sports injuries, sudden movements, or inadequate warm-ups.
It can also result from hip issues or nerve compression. Rest, ice, gentle stretching, and strengthening exercises can help alleviate pain and prevent recurrence. If the pain persists or worsens, medical evaluation may be necessary.
- Muscle strains, inguinal hernias, and numerous other conditions can cause this pain.
- Adults experience this pain the most frequently.
- You experience a range of groin pains, including dull, acute, throbbing, searing, mild, and severe.
- Different methods are used by the doctor to diagnose this condition.
- RICE therapy, painkillers, and physical therapy all help to relieve this pain.
A generic phrase for pain, discomfort, or unusual feelings in the region where your abdominal (belly) meets your upper thigh is “groin pain.” The area directly above or below the fold that separates your belly and thigh is where you may have groin pain. Your right or left groin may be the site of the discomfort. It could develop slowly or start out abruptly.
Groin pain can be caused by a lot of causes. A strain, or injury to the groin muscle or tendon, is the most frequent cause. Pulling your thighs’ adductor or hip flexor muscles causes this. As soon as this injury occurs (usually during activity), there is a severe pulling or tearing sensation. Then, when you move about, you can get a persistent groin pain. For a few days or even weeks, this might be felt.
In addition to injuries sustained during activity, groin discomfort can result from a variety of different conditions and injuries. Hernias, hip arthritis, bone fractures, UTIs, ovarian cysts, and disorders of the nervous system are among them. In rare cases, medical emergencies such as testicular torsion, appendicitis, or strangulated hernias hernias that have lost their blood supply, cause groin pain.
If you experience groin pain, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional because there are numerous potential explanations. They will identify the root cause of your discomfort and suggest the best course of action to alleviate it.
What is your groin area?
The region of your hip joint between your stomach and thigh is called the groin.
This ache is where your legs start and your abdomen finishes.
Five muscles that cooperate to move your leg must be surrounded by this groin area.
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor longus
- Pectineus
- Adductor brevis
- Gracilis.
Cause of Groin Muscle Pain:
Groin pain can result from a variety of conditions and traumas. This is because your groin area is surrounded by or passes through numerous muscles, tendons, nerves, and other systems. Your groin may hurt if there are problems with any of those structures.
As with a muscular strain or hernia, pain may start in the groin. Alternatively, it can start elsewhere (like your back) and use nerve signals to travel to your groin.
Primary and secondary groin pain are terms used by medical professionals. A medical condition or injury is the cause of primary groin discomfort. It has nothing to do with a prior procedure. One consequence of surgery is the development of secondary groin pain.
The most prevalent cause of primary groin discomfort is straining or pulling the groin muscles. Groin strains are more likely to occur in sports that involve a lot of direction changes, pivoting, kicking, or running. Soccer, hockey, football, basketball, figure skating, and tennis are a few of these. However, groin strains can also occur in other circumstances. Furthermore, primary groin pain might have a wide range of causes that are not connected to sports.
Muscle Strain:
- The pulled groin muscle is another name for a groin strain.
- This frequently happens as a result of sports injuries.
- Additionally, it occurs as a result of an uncomfortable hip joint movement that causes the inner thigh muscles to stretch and tear.
Inguinal Hernia:
- Groin soreness is another symptom of this condition.
- It happens when adipose tissue and the intestines push through a weak spot in the abdominal wall that has been ruptured.
- Occasionally, this hernia manifests as an obvious groin protrusion.
Prostatitis:
- Your prostate gland may expand or become infected with the disease.
- You have pain and urination with this situation.
Epididymitis:
- In this disease, the tube containing the sperm swells, and an infection is also caused.
Orchitis:
- This disorder causes one or both testicles to enlarge, which results in issues with fertility.
- It is also caused by orchitis, the same infection that causes epididymitis.
- Orchitis can occasionally be caused by the mumps virus.
Testicular torsion:
- When a testicle becomes twisted inside your scrotum, this condition occurs.
- You feel as though you were kicked in the groin by this pain.
- This is a serious medical situation.
- Twisting: Torsion stops your testicle’s blood flow.
Testicular cancer:
Kidney stones:
- This malignancy typically manifests as a painless bump on your testicle. However, it can get too painful at times.
- Although it is not a common cancer, it is usually treated and cured when discovered early.
- Kidney stones are caused by tiny crystals that develop in the kidney and become lodged in the tubes that lead to the bladder.
- When the pain is too bad, it radiates to your scrotum and the tip of your penis in addition to your back or belly.
- You will require surgery if this stone is quite large.
Kidney infection:
- This syndrome typically occurs when an infection penetrates one or both kidneys from the bladder.
- Groin pain, frequent urination, and blood or pus in your urine are all symptoms of an infection.
- E. coli is the bacterium that causes this infection.
- When arthritis in the hip joint leads to leg pain during leg movement.
- Groin discomfort can also occasionally result from this disorder.
Femoral Acetabular Impingement – FAI:
- Bone spurs are hard growths that form around the hip joint’s ball and socket as a result of this disorder.
- Your hip joint movement will be restricted as a result of this condition.
- This FAI causes pain in the exterior of the hip joint and in the groin.
Hip Labrum Tear:
- The cartilage layer of the hip joint is referred to as the labrum.
- The ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint is surrounded by this flexible and firm tissue.
Hip Fracture:
- A hip fracture is a break in the thigh bone’s upper portion.
- Falling is the most frequent cause of hip fractures.
- A direct hit to the hip can occasionally result in breakage.
- The groin region is frequently where hip fracture pain is felt, and it gets worse when you try to flex and rotate the hip joint.
Hip Osteonecrosis:
- This disorder is sometimes called avascular necrosis.
- This condition happens owing to bone cells that are dying from a lack of blood flow.
- Bone cells start to break down when this condition affects the hip joint.
- This condition is characterized by dull, aching, or throbbing pain in the buttocks or groin.
Nerve Problem:
- Groin discomfort is caused by a pinched nerve in the lower spine.
- numbness and tingling in the groin area as a result of nerve issues.
- Lumbar radiculopathy is the name given to this disease.
Abdominal & Pelvic Conditions:
- Groin pain is a symptom of some gastrointestinal disorders.
- Among these conditions are:
- Diverticulitis is a gastrointestinal inflammatory disease.
- An abdominal aortic aneurysm occurs when a portion of the aorta, a significant blood vessel, enlarges.
- Pelvic disorders such as ovarian cysts, which are tiny fluid-filled pockets that develop on or within the ovaries.
Osteitis Pubis:
- It is an inflammatory condition that affects the pubic symphysis and causes dull, aching pain in the pelvis and groin area.
- Both athletes and non-athletes can have this condition.
Symptoms of groin muscle pain:
- One side of your scrotum hurts, and it starts slowly.
- You also experience inner thigh muscle spasms and weakness in your leg muscles.
- You may also have fever, milky discharge from your penis, and difficulty passing gas and poop. When this pain is caused by an inguinal hernia, you may experience dull groin pain when coughing or lifting objects, as well as stabbing pain, numbness, swelling, and redness in the groin area.
How do you diagnose?
- Groin discomfort usually doesn’t need to be treated by a doctor.
- However, get in touch with a doctor if you have significant discomfort, fever, or edema.
- Your symptoms will be assessed by the first doctor, who will also inquire about any recent physical activity.
- Doctors can use this information to diagnose the issue.
- In addition to various tests, the doctor then does a physical examination of the groin area.
- Hernia test:
After sticking one finger into the patient’s scrotum, the doctor asks if the patient coughs.
Coughing causes your intestines to be forced into the hernia opening and increases abdominal pressure. - X-ray & ultrasound:
Doctors utilize X-rays and ultrasounds to try to determine the sources of discomfort, such as ovarian cysts, testicular masses, and bone fractures. - Complete blood count – CBC:
Doctors can use this kind of blood test to find out whether an infection is present.
Under what conditions is it appropriate to contact a physician in an emergency?
- If blood is seen in your urine
- If you observe any physical alterations in the testicles, such as swelling and tumors,
- In the event that your lower back, chest, and abdomen begin to hurt
- You have a fever, chills, and nausea in addition to your discomfort.
- The aforementioned symptoms are indicative of more severe conditions such as testicular torsion (twisted testicle), testicular cancer, and infection.
Treatment for Groin Muscle Pain?
RICE principle:
- R-rest = In order to alleviate muscle pain, your physician could suggest that you stop doing specific activities.
- I-ice = For 20 minutes, you apply ice to the sore spot to help reduce swelling and muscle soreness. Keep a towel between your skin and the ice at all times to prevent ice burns. For ice treatment, you can also use frozen peas and an ice pack.
- C-compression: You are also using athletic tape or compression gear to wrap your groin area, which reduces swelling.
- E-elevation: When you experience groin pain, you should apply pressure to the pillow beneath your leg to reduce swelling and be mindful of your sleeping position.
Pain medication:
- Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are examples of over-the-counter pain medications that can help you feel better.
- Opioids are recommended for extreme pain, however they should not be used for extended periods of time (seven to ten days).
Physical therapy treatment for groin muscle pain:
Massage:
- In cases when trigger and tender points are present in the affected area, the therapist is advised to employ massage treatment to alleviate muscle.
- Following the RICE method for two to three days, massage is given when you feel as though the pain has decreased.
- A massage is given for five to ten minutes with the use of oil.
- Three massages are performed at home each day.
Exercise therapy for groin muscle pain:
Stretching exercise:
- Hip adductor stretch
- Hamstring stretch on wall
- Standing Groin Stretch
- Seated Groin Stretch
- Squatting Groin Stretch
- Hip Opener & Groin Stretch
- Gate stretches
- Crossover stretch
- Lunge stretch
- Butterfly stretch
Hip adductor stretch:
- To the sides, let your knee joint drop open.
- Make an effort to press your foot soles together.
Hamstring stretch on the wall:
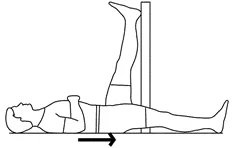
- Place yourself on your back next to a doorway.
- Your affected leg should be placed near to the doorframe on the wall.
Standing Groin Stretch:
- You stand with your legs spread wide.
- After that, shift your weight to the left.
- You feel like your right groin is strained.
Seated Groin Stretch:
- This workout is best started while seated.
- Applying pressure to the inner thigh can be achieved by lightly pressing the elbow joint on the knees.
- You feel a little tugging and too much groin strain.
- Do not bounce or exert too much pressure.
Squatting Groin Stretch:

- Bend to a 90-degree angle and squat down gradually until your knee is exactly over your ankle.
- To open your hips, try placing your hands on top of your inner thighs and gradually pushing outward.
Hip Opener & Groin Stretch:
- Press your right elbow gently onto your right knee and then twist your torso to the left.
- With your left arm extended behind you, gently extend your right groin and lower back.
Gate stretches:
- Turn out and open your right knee joint away from your body after raising it to hip level.
- Your groin feels stretched in this position.
- Closing the gate involves lowering your leg and bringing your knee joint back around in front of your torso.
Crossover stretch:
- Standing is required for this activity.
- Next, take another leftward stride with your left foot.
- Repeat this stretch the other way.
Lunge stretch:

- It found out that the first stand with your feet in a wide stance was about 45 degrees.
- To lengthen the inner thigh muscles in the extended position and straighten the right leg, try bending the left knee joint and lunging slightly to the left.
Butterfly stretch:

- Put your hands around your ankles as best you can.
- Next, carefully force the legs apart with your elbow joint while slowly bending forward at the waist.
- When bending forward, avoid rounding your back.
Half-Kneeling Hip Stretch:
- Make an effort to turn your upper body, or trunk, to the same side as your front leg.
- Add a slight lean forward if you don’t feel stretched.
- Hold for 30 seconds, then take a 15-second break.
Side lunge groin stretch:

- With your right foot, take a sidestep and then slowly lower yourself into a lunge.
- Both feet’s toes must remain pointed straight front.
- To begin one repetition, press back.
- Repeat on the other side after completing the 6–10 reps.
- Perform the two to three sets, taking a 30- to 60-second break in between.
Simple Isolated Long Groin Stretch:
- Your legs are arranged in a broad “V” configuration while you sit up straight.
- For 30 seconds, hold this mild stretch, and then take a 30-second break.
- Perform three to five sets per day.
Strengthening Exercises:
The physical therapist recommends strengthening activities for neck muscular weakness after electrotherapy and massage for two to three days to relieve neck muscle pain.
- Straight leg raise
- Resisted hip flexion
- Leg swing
- Groin Activation against the Wall
- Single-Leg Rock Back Exercise
- Frog Rock Back
- Foam Rolling Adductor
- Bridge with Ball Squeeze
Straight leg raises:
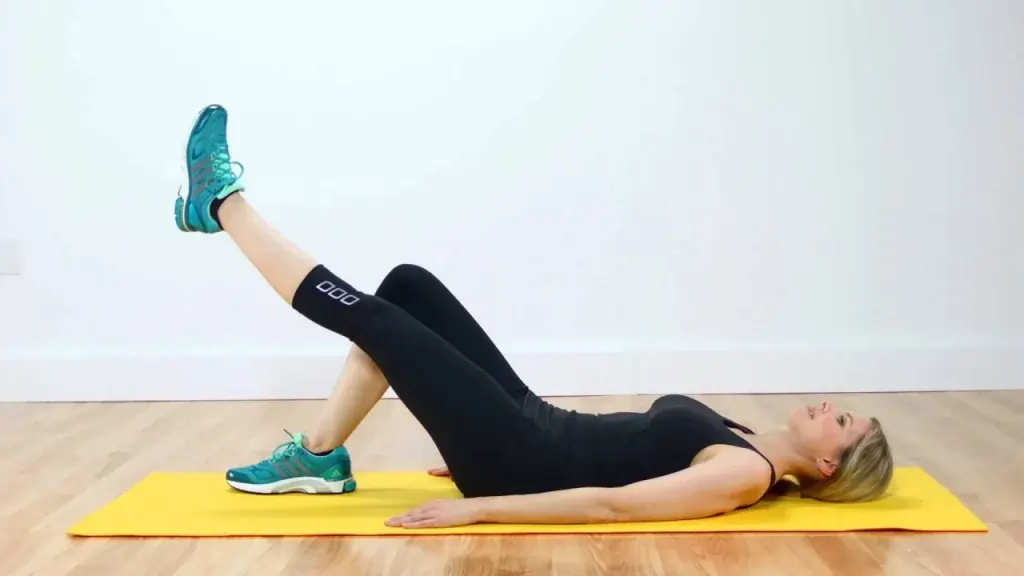

- Make an effort to plant your foot firmly on the ground.
- Next, Lift your leg eight inches above the ground and then lower it back down.
Resisted hip flexion:
- With your back to a door, you stand.
- Place the resistance band around your affected leg’s ankle in an attempt to form a loop.
- After that, wrap the resistance band’s opposite end around an anchor point.
Groin Activation against the Wall:
- Lift your right leg and the affected area to hip joint level to begin this exercise.
- With your left hand, you are holding a stick or pole.
- For roughly ten seconds, maintain this exercise position.
- You might feel your groin area getting stretched.
Frog Rock Back:
- To begin, place your hands on the floor for support while kneeling on the floor.
- When you turn your toes out and place the inside of your feet on the floor, spread your knee joint on the side.
- Keep your knees wide and try to sit your butt in the rear.
- As you do this, you must also feel the stretch.
- Before continuing, take a few moments to sit back and keep this position, paying attention to your breathing.
- Then, as you continue to open your knee joint, you rock back and forth two or three times.
Foam Rolling Adductor:
- Your forearms and the second leg are supporting your body while you lie on your front.
- Put your left leg on the foam roller if you can.
- The foam roller is then progressively rolled down at a rate of one inch per second.
- Hold the foam roller for around 30 seconds while attempting to reach a sore place on your adductor muscle.
- It’s important to maintain muscle relaxation while performing foam rolling.
Foam Rolling Quad and Hip Flexors:
- With your arms supporting you, begin this exercise with your back to the floor.
- Next, The foam roller should be placed beneath your hip joint.
- Start rolling up and down on your hip flexor or quadriceps slowly.
- It’s time to bend and extend your lower leg roughly 20 times once you’ve found a tight region.
Bridge with Ball Squeeze:

- To begin, place your feet on the floor, your back on the floor, and your glutes muscle 12 to 16 inches away.
- After that, position the ball between your knees.
- As you raise your pelvis into a neutral bridge posture, it’s time to plant your feet firmly on the ground.
- As you raise your pelvis, be sure you can see it.
- While you squeeze the ball roughly 20 times, maintain this exercise position.
- After one repetition, go back to the beginning position.
Surgical treatment for groin muscle pain:
- The doctor recommends surgery if the discomfort is not eased by medicinal and physical treatments.
- Very severe is groin muscle pain treated with surgery.
- However, surgery may be necessary for some severe conditions. such as hip joint infection and testicular torsion, require immediate surgery.
- Surgery for a hip joint infection involves flushing the affected area with saline solution and removing the contaminated tissue.
- Following the surgery, antibiotics are administered to prevent infection.
Other types of surgery include of:
- Hip arthroscopic surgery to repair certain labral rips
- For severe hip arthritis, hip replacement
- Hip osteonecrosis treated with core decompression surgery.
How can groin pain be managed at home?
- In order to allow your strain to heal naturally, you should rest and avoid physical activity for two to three weeks when you get groin pain.
- Take painkillers, such as Tylenol or acetaminophen.
- Several times a day, apply to ice packs for 20 minutes.
How to Prevent groin muscle pain?
- Always stretch gently to avoid getting hurt.
- To lower your chance of a groin injury, warm up slowly and steadily before engaging in any physical activity.
- Keep your weight in check, exercise caution while lifting large objects, and avoid hernias.
- You can reduce your risk of muscular strains by increasing your body temperature with a light jog and other exercises.
- Put on shoes that are supportive and comfortable.
- When you have tightness or soreness in your groin and inside thigh, stop exercising.
- Engage in frequent thigh muscle building workouts.
Conclusion:
Groin pain is not just a problem for athletes or even people who go to the gym sometimes. Groin pain is a symptom of many different medical disorders, some of which are unrelated to sports. Because of this, it’s critical that you contact a healthcare professional if you experience this symptom. They will conduct a thorough examination and inquire about your emotional state in order to put together what’s going on.
Seeking medical attention is crucial to be certain of the cause, even if you believe you know it. In order to address the underlying issue, alleviate your discomfort, and enable you to move safely once more, a healthcare professional will suggest remedies.
FAQs
For groin pain, what kind of physician do you see?
Make an appointment with an orthopedic or sports medicine professional if your groin injury lasts for a few days or weeks and still interferes with your everyday activities. An expert will try to determine the origin and severity of your injury.
Is groin pain a result of excessive walking?
Walking-related groin pain may be caused by hip joint injury, overuse, or muscular strains. After a few days of recuperation, it’s crucial to gradually resume your activities. Most groin pain may be resolved with conservative methods, but keep an eye out for any lingering symptoms.
What are some natural ways to treat groin pain?
The RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) approach is a home remedy for groin discomfort. In addition, you can try stretching and strengthening exercises and take pain medication.
Does groin pain respond well to heat?
Following the reduction of the initial edema and inflammation, some people prefer to use therapeutic heat, such as a heating pad. This can improve range of motion and help relax tense muscles. Another well-liked technique for easing groin muscle stress while healing after a pull or rupture is massage.
Does the groin get massaged by therapists?
The muscles of the chest wall, breast, gluteal region, upper inner thigh, anterior pelvic region, and groin area are among the body parts that may be requested to be treated by massage therapists.
When I have groin pain, what should I avoid?
How can you alleviate the pain in your groin? Rest: Steer clear of activities that aggravate your muscles and avoid overstretching them during the first 48 hours. As your pain permits, you can often begin doing mild strengthening and range-of-motion activities after 48 hours.
How can someone who has groin pain sleep?
I’ve found that lying half-on your stomach with your other knee raised up, your bottom arm behind you, and your bottom leg completely extended is the ideal position. To keep your thighs apart if you must sleep on your side, place a pillow between your knees.
Which scan is best for groin pain?
The most popular scans for diagnosing groin discomfort are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound (US). X-rays, CT scans, and bone scans are further scans that might be utilized.
Can groin pain be relieved by walking?
The majority of people can walk with a strained groin. However, while you’re healing from a groin strain, you shouldn’t run, work out, or engage in strenuous exercise. You run a higher risk of re-injuring your muscles if you resume exercising or participating in sports before they have fully recovered.
What is a warning sign for pain in the groin?
Get medical help right away if you have: accompanied by chest, stomach, or back pain and groin pain. severe, unexpected testicular pain. nausea, vomiting, chills, fever, unexplained weight loss, or blood in the urine, in addition to testicle pain and swelling.
Can a massage help with groin strain?
Physical therapy is essential for the best possible recovery during the rehabilitation process for both acute and chronic groin strains. In order to facilitate healing, remedial massage relieves muscle tension, lowers swelling, eases muscle spasms, increases blood flow, and realigns the muscle fibers.
Can groin discomfort be helped by a physical therapist?
Management of Physical therapy
The adductor muscles should be stretched and massaged. Releasing the hip flexors, which include the iliopsoas, quadriceps, and lower abdominal muscles, is also recommended in many groin pain instances. enhancing the strength of the “core” muscles, which include the lower back, pelvic floor, and abdominal muscles.
How can a groin muscle be rehabilitated?
Squeezing an isometric adductor ball
Place a football between your knees while lying on your back with your legs bent. Hold the contraction while you squeeze your knees together. Hold for 30 seconds, then take a 5- to 10-second break before repeating ten times.
Can pain in the groin extend to the testicles?
It is possible for testicular pain to radiate from the groin. There are several potential causes for this, such as hernias, muscular injuries, and other diseases.
References
- Ladva, V. (2024b, December 11). Muscle Pain in the Groin area Cause, Symptom, Treatment. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/muscle-pain-in-the-groin-area/