Kernig’s Sign
What is Kernig’s Sign?
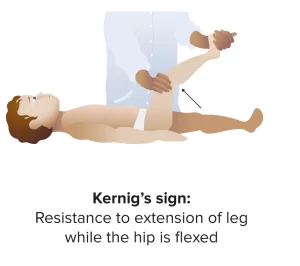
Kernig’s sign is a clinical test for meningeal irritation, often seen in meningitis. It is positive when extending the knee from a flexed hip position causes pain or resistance in the hamstrings, suggesting meningeal inflammation.
To check for meningeal irritation, it is frequently evaluated along with Brudzinski’s sign.
Purpose
The Kernig’s test’s primary objective is to assist in identifying meningitis. When medical professionals suspect meningitis, they may employ this test as one of several.
Technique
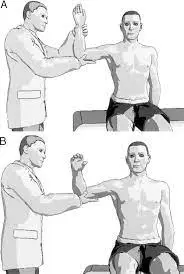
The patient is in a supine position with their legs and hips bent at a 90-degree angle.
Next, while maintaining hip flexion, the examiner tries to passively extend the patient’s knee.
Test is positive if
Resistance to knee extension or hamstring pain during the movement are signs of a positive Kernig test. It suggests inflammation or irritation of the meninges.
Kernig’s Sign Examination Video
Clinical Significance
When evaluating meningitis clinically, the Kernig test is a useful tool, especially in areas with limited resources where lumbar puncture may not be easily accessible.
When combined with additional clinical signs, a positive Kernig test might increase the possibility of meningitis and need additional testing and care.
The Kernig test is not a perfect diagnostic tool, though, and its findings should be interpreted in light of the patient’s overall clinical presentation as well as the results of other diagnostic tests.
Indications
- Patients suspected of having meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes (meninges) around the brain and spinal cord, are the main candidates for the Kernig test.
- Infections with bacteria, viruses, or fungi can all result in meningitis.
- Meningitis symptoms often include:
- A rather bad headache
- stiff neck
- A fever
- Vomiting and feeling faint
- Light sensitivity
- Irritation
- Seizures of Confusion
Contraindication
In some circumstances, it might not be appropriate or needs to be avoided. Among these contraindications are:
Babies who are tight or have strong muscles: Accurately performing the Kernig test in neonates may be challenging due to increased muscular tone or stress.
Babies who are extremely sleepy or unconscious:
In these situations, the baby might not be able to comply throughout the test, and the findings might not be accurate.
People who have lower body paralysis or paraplegia: The Kernig test might not be appropriate for these people because their legs do not have the required motor function.
People with injuries to their legs, knees, or hips: The Kernig test may worsen the damage or provide more pain in some situations.
Evidence
Specificity and Sensitivity:
The Kernig test can overlook a sizable portion of meningitis infections due to its limited sensitivity (about 5%), according to studies.
On the other hand, a positive test is more likely to suggest meningitis due to its high specificity (about 95%).
Therefore, rather than ruling out meningitis, the Kernig test is more helpful in confirming a diagnosis when additional clinical symptoms are present.
Limitations
Because of the low sensitivity of the Kernig test, meningitis is not always ruled out by a negative result.
A positive result is more likely to suggest meningitis since it is more specific, but more testing is necessary for confirmation.
FAQs
Which sign is Kernig’s vs Brudzinski?
Put the patient in a supine posture with their hips 90 degrees flexed to demonstrate Kernig’s sign. The test appears positive if passive extension causes pain in the knee. To demonstrate Brudzinski’s sign, place the patient in a supine posture and passively flex their neck. The test is considered successful if the hip and knee flex instinctively as a result of this motion.
What is the sensitivity of Kernig sign?
Patients with bacterial or tuberculous meningitis had a 57% sensitivity for Kernig’s sign. These clinical findings are now believed to be indicators of meningeal inflammation.
What are 5 symptoms of meningitis?
Fever and / or vomiting. …
Severe headache. …
Cold hands and feet / shivering. …
Pale or mottled skin. …
Breathing fast / breathless
What is a positive Kernig sign?
If the knee hurts when passively extended, the test is positive.
Is Kernig’s sign seen in pneumonia?
yes, kernig’s sign is positive in Pneumonia.
What are the causes of Kernig’s sign ?
Kernig’s sign is caused by inflammation of the meninges, which are membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
References
- Kernig’s sign – Meningeal stretch test : Emergency Care BC. (n.d.). https://emergencycarebc.ca/clinical_resource/procedural-video/kernigs-sign-meningeal-stretch-test/
- Kernig’s sign of meningitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia Image. (n.d.). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/imagepages/19077.htm
- Wikipedia contributors. (2025, January 31). Kernig’s sign. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernig%27s_sign
- Adcox, M. (2023, September 8). How to recognize Kernig’s Sign. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/kernig-sign
- Mph, E. B. (2022, December 20). What is Kernig’s sign? Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/kernig-sign-6889604