Infraspinatus Muscle Pain
What is the Infraspinatus Muscle?
Infraspinatus muscle pain is a common issue that affects the shoulder’s functionality and stability. This muscle, located in the upper back and forming part of the rotator cuff, is essential for external rotation of the arm and overall shoulder support.
Pain in this area often results from repetitive strain, poor posture, overuse, or direct injury. It may lead to symptoms such as localized discomfort, reduced range of motion, and weakness in the shoulder.
Understanding the infraspinatus muscle’s role and the factors contributing to pain is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Repetitive shoulder motion is most likely the cause of infraspinatus pain. It is more common among carpenters, painters, tennis players, and swimmers. Additionally, the likelihood increases with age.
Infraspinatus pain can have a number of reasons. None are life-threatening, although some are significant.
Causes of Infraspinatus muscle pain?
Minor strains or wear and tear can occasionally be the cause of infraspinatus pain. In these situations, rest will probably make the pain go away. However, more serious disorders or injuries may also be the source of your pain.
Infraspinatus tears come in two varieties:
Although it doesn’t go all the way through, a partial tear will harm the tendon. It is typically caused by age or recurrent stress.
A full-thickness, or complete, rip separates the infraspinatus from the bone. Usually, an acute injury like falling causes it.
Symptoms
- Arm weakness and soreness during repose and at night
- pain when your arm is raised or lowered
- If you have an acute tear, you may experience a crackling feeling when moving your arm, which can result in abrupt, intense pain and weakness.
Infraspinatus tendinopathy
A less serious lesion to the infraspinatus is called infraspinatus tendinopathy. Two categories exist:
Tiny rips in the tendon that don’t generate significant inflammation are known as tendinosis.
Among the causes of tendinopathy are:
Overuse, particularly while reaching above or throwing, can cause shoulder injuries, arthritis, or another inflammatory illness, as well as typical aging wear and strain.
Symptoms
- pain that becomes worse when using the shoulder
- Your shoulder and upper arm hurt dullly at night.
- weakness in the shoulders
- Shoulder stiffness, partial loss of shoulder mobility,
- pain when reaching up or down, and
- pain when reaching behind you.
Infraspinatus impingement
Impingement is the compression of a tendon, typically caused by inflammation or a bone spur. People who do not participate in sports like tennis that require overhead tossing are unlikely to get infraspinatus impingement. It is especially prevalent among athletes younger than thirty.
Symptoms
- shoulder pain that radiates down the arm and grows worse with time
Bursitis
Bursitis is caused by inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that sits between the top of your arm bone and the point of your shoulder. This may limit the mobility of the infraspinatus muscle and produce pain.
Bursitis is most frequently caused by overuse, however, it can also result from:
- arthritis
- gout
- diabetes
- thyroid disease
- tendonitis
- acute injury
Symptoms
- shoulder pain and
- swelling when you move your shoulder.
Pinched nerve
Infraspinatus pain may result from a pinching of the suprascapular nerve in your shoulder. The most common causes of a pinched nerve include trauma, overuse injuries, or other shoulder problems.
Symptoms
- Back and upper shoulder pain that is unresponsive to most standard therapies
- weakness in the shoulders
- In rare instances, atrophy of the infraspinatus.
Symptoms of Infraspinatus Muscle Pain
- Pain and Weakness
- Unable to utilize your shoulder
- Sleeping on your affected shoulder is difficult.
- restricted range of motion
- A sensation of grinding or catching when your shoulder moves
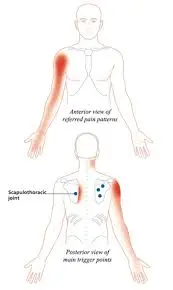
What are infraspinatus trigger points?
Trigger points are believed to be hard, painful areas in a muscle, yet not all doctors agree that they exist.
Active trigger sites hurt even in the absence of touch or motion, whereas latent trigger points hurt when pressed. In addition to causing pain, they can also limit movement and weaken muscles.
Both localized and transferred pain can be caused by active trigger points. Pain in other parts of the body, typically those close to the trigger point, is referred to as pain.
Trigger points are often triggered when a muscle is under tension. You may have shoulder and arm pain if you have activated trigger points in your infraspinatus.
Diagnosing infraspinatus pain
A doctor will first review your medical history in order to determine the reason for your infraspinatus pain. They’ll question you regarding:
- shoulder pain and
- swelling when you move your shoulder
- A doctor will first review your medical history in order to determine the reason for your infraspinatus pain.
If you engage in repeated shoulder motion activities, such as playing sports,
After that, they will perform a physical examination to determine which movements cause pain in your shoulder, whether you have a limited range of motion, and whether your shoulder muscles are weak.
To identify an infraspinatus issue, a physical examination and medical history are typically sufficient.
A doctor may inject a local anesthetic into the infraspinatus muscle if they are unsure if you have tendinopathy or a tear in the muscle. Your muscular strength will return to normal and the pain will subside if you have tendinopathy. Your arm function will still be restricted if you have a rip.
Infraspinatus pain test
To determine if your shoulder pain is originating from the infraspinatus or another area, you can do an infraspinatus pain test.
As you rotate your arms outward, a doctor will press against them. You probably have an infraspinatus issue if this hurts.
Treatment Infraspinatus Pain
A physician would often advise attempting nonsurgical therapy for infraspinatus pain. The majority of patients respond well to these therapies, albeit a mix of nonsurgical procedures can be required.
In the event that nonsurgical therapy becomes ineffective, surgery can be considered.
Medical Treatment
Rest
Repetitive motion is a common cause of infraspinatus injury. Your shoulder will have a chance to recover if you rest it. Your doctor may advise you to temporarily avoid activities that aggravate your arm pain or to rest it in a sling.
Heat and ice
Your shoulder’s inflammation will go down if you ice it. This may be done at the beginning of your ailment or after stretching or working out.
Your infraspinatus will relax with the aid of heat. Heat should be used before stretching or working out. Warm baths or showers work well, as does using a heating pad.
NSAIDs
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and other NSAIDs treat pain and edema caused by injuries.
Steroid injections
Depending on your particular ailment, your doctor will inject this mixture straight into your bursa or infraspinatus.
Although these injections may offer short-term respite, repeated use may cause muscular injury.
Physical Therapy Treatment:
Infraspinatus pain stretches and exercises
In order to prevent more injuries, they will also assist you in strengthening your muscles. These stretches and exercises shouldn’t hurt at all. Stop and let your doctor know if they do.
Pendulum
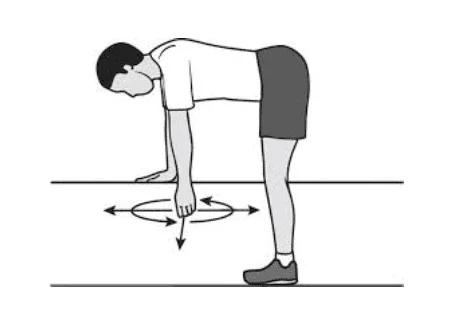
- In order to prevent a frozen shoulder, this exercise helps lengthen your muscles and the area they travel through.
- At an angle, lean forward. Support yourself with your unaffected arm.
- After that, move it in little circles.
- Perform two sets of ten each.
External rotation
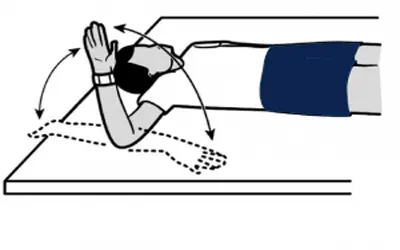
- You can stretch and strengthen your infraspinatus with this workout. You can begin adding weights as you recover.
- Rotate your arm slowly while keeping your elbow by your side. With your hand in the air, it should come out 90 degrees bent.
- Rotate the arm back down slowly.
- Perform two sets of ten.
- Continue on the opposite side.
Passive external rotation
- This stretch should be felt at the rear of your shoulders. You’ll need a light stick, such as a yardstick or broom handle.
- Hold the stick loosely at both ends.
- Wait 30 seconds.
- Take a half-hour to relax.
- Do this three more times.
- Continue on the opposite side.
Surgical Treatment:
If alternative therapies have failed or the injury is serious, surgery may be necessary. Only severe, acute injuries, such as a full rip from a fall, are usually treated with it as a first step.
Prognosis:
First, your doctor will probably advise stretching, exercises, and rest. You should see your doctor again for a more thorough assessment if those don’t begin to assist within a few weeks.
At this stage, they could advise you to keep exercising or provide a steroid injection. Within a few days, injections often start to relieve pain.
After six months, your doctor may decide that surgery is the best course of action if your pain persists. Compared to arthroscopic surgery, which involves several tiny incisions, open surgery, which involves a single big incision, requires more time to recover.
After surgery, it typically takes six months for your shoulder function to recover to normal. Depending on how quickly you recover, you can probably resume some of your previous activities.
Summary
Although infraspinatus pain might have a major impact on your functioning, be aware that your symptoms are probably just transitory. These symptoms are often relieved by conservative measures such as physical therapy, NSAIDS, rest, and ice.
In uncommon situations, surgery or even a steroid injection can be required. Getting a medical evaluation for your shoulder is a crucial first step in getting back to your regular activities.
FAQs
How is the infraspinatus muscle relaxed?
Rest: Stop participating in sports or other activities. Ice it: For fifteen to twenty minutes, place a towel filled with ice over your shoulder. Stretching activities: You could start doing some simple stretches and exercises to strengthen your rotator cuff and muscles after your symptoms subside.
What is the infraspinatus pain pattern?
A severe, deep ache in the front of the shoulder is the most typical pain pattern caused by infraspinatus trigger points. The biceps brachii, the anterior deltoid muscle, and even the radial forearm and hand may be affected.
What’s causing my infraspinatus pain?
Repetitive shoulder motion is most likely the cause of infraspinatus pain. It is more common among carpenters, painters, tennis players, and swimmers. Additionally, the likelihood increases with age.
What is infraspinatus’ primary action?
The infraspinatus, one of the rotator cuff’s four muscles, is primarily responsible for externally rotating the humerus and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
Can neck pain result from infraspinatus?
According to frequency, the anterolateral aspect of the arm (above the elbow), the lateral forearm, the upper posterior neck, and the radial aspect of the hand (containing a finger) were the sites of referred pain from MTrPs in the infraspinatus muscle in this investigation.
What is the infraspinatus muscle’s primary purpose?
The location, function, and innervation of the infraspinatus muscle…
The movement of shoulder external rotation also referred to as shoulder lateral rotation, is also produced by this muscle.
What is the duration of the healing process for infraspinatus?
Depending on the extent of the tear, the recuperation period following surgery may range from four to twelve months. With physical therapy, a patient may be able to regain full function in two to four weeks if the rupture is relatively minimal.
Which exercises are effective for infraspinatus?
The side-lying wiper exercise is a new and efficient way to work the infraspinatus muscle while using the posterior deltoid and middle trapezius muscles as little as possible.
What is the infraspinatus pain test?
Against the examiner’s opposition, the patient is instructed to externally rotate both forearms. When external rotation is painful or feeble, the test is considered affirmative. External rotation weakness clearly signals an infraspinatus tear because these rips are typically painless.
Is it possible to massage the infraspinatus muscle?
Shoulder Pain Massage
The ideal self-massage instrument for the infraspinatus muscle may be a little rubber ball. This location is not only a little difficult to locate, but it is also difficult to get to. The difficulty level of self-massage is greatly increased by this.
What is the sensation of a strained infraspinatus?
You can’t use your shoulder. Sleeping on your affected shoulder is difficult. restricted range of motion. a sensation that occurs as you move your shoulder, like grinding or catching.
How can infraspinatus pain be relieved?
Although infraspinatus pain might have a major impact on your functioning, be aware that your symptoms are probably just transitory. These symptoms are often relieved by conservative measures such as physical therapy, NSAIDS, rest, and ice. In uncommon situations, surgery or even a steroid injection can be required.
References
- Hersh, E. (2020, January 15). What Causes Infraspinatus Pain and How Can I Treat It? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/infraspinatus-pain
- WebMD Editorial Contributor. (2023, June 5). What to Know About Infraspinatus Pain. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/what-to-know-infraspinatus-pain
- Ocs, T. P. D. (2024, March 7). What Causes Infraspinatus Pain and How Can You Treat It? Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/infraspinatus-pain-8575751