Hamstring Muscle Tightness
What is a Hamstring Muscle Tightness?
Hamstring muscle tightness is a common condition that can affect people of all ages and activity levels. It occurs when the muscles at the back of the thighs become shortened and less flexible.
The hamstrings consist of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus, which play a critical role in hip extension, knee flexion, and overall lower-body movement.
Tightness in the hamstrings can affect individuals of all activity levels, from sedentary people to athletes, and is often linked to prolonged sitting, inadequate stretching, or overuse during physical activity. It may lead to discomfort, limited range of motion, and increased risk of injury, such as muscle strains or lower back pain. Proper assessment and management, including stretching and strengthening exercises, are essential to alleviate tightness and maintain optimal muscle function.
Anatomy and Function of Hamstring Muscle
- Three hamstring muscles are present:
- the semimembranosus
- semitendinosus
- biceps femoris
As seen, they join to the inside or outside of the knee after starting at the back of the pelvis.
According to the conventional description, their primary purpose is to flex( bend) the knee, raising the ankle toward the rear end. They also help the glutes extend the legs backward when walking or running. On the other hand, they oppose the knee’s ability to straighten.
Function of the hamstring
In the complex gait cycle that occurs during walking, the hamstrings are crucial for protecting the knee and hip joints as well as absorbing kinetic energy. The hamstrings slow the tibia’s forward shifting during the stepping swing phase. The contraction of the quadriceps, a muscle that opposes the hamstrings, and the contraction of the hamstrings interact closely.
Causes of Tight Hamstring
Exercise or other high-intensity activities frequently cause tight hamstrings. Tightness may result from exercises that significantly strain the hamstrings. For instance, engaging in activities like soccer or hamstring curl exercises will strengthen the hamstring muscles.
Usually, the tightness happens after beginning a new fitness regimen or suddenly raising the intensity of being one. After extended ages of sitting or inactivity, some people develop tight hamstrings. For case, tightness may be affected by spending numerous hours seated at an office.
In other situations, the tightness may be the result of an injury, conceivably a chronic one that increases the hamstrings’ susceptibility to tightness. Additionally, the tightness can indicate a strain or sprain in the region.
Symptoms
Three hamstring muscles are present
- The semitendinosus
- biceps femoris
- semimembranosus
They facilitate walking, running, and jumping, among other physical activities. All of these movements can be impacted and mobility is restricted by tight hamstrings. They may feel less flexible and rigid. Tight hamstrings can occasionally coexist with other symptoms, including
- pain from cramps
- swelling
- bruises
- tenderness
- redness
- Additionally, tight hamstrings can make injuries more likely.
When to see your doctor
However, visit your healthcare provider, If you frequently experience tight and painful hamstrings. Persistent pain could indicate an injury.
other signs of an injury include
- abrupt, sharp pain
- The feeling of popping or tearing,
- pain or swelling
- bruising or abrasion
- muscle weakness
Treatment
- Medications
- Physical Therapy
- Massage Therapy
Medication
In most cases, owning tight hamstrings isn’t a reason for concern. They can generally be treated with stretches and exercises. RICE( rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and over-the-counter( OTC) pain medicines may help you manage a minor strain at home. Schedule a visit with your doctor if you’re in too much pain when taking more than four steps. A total muscle tear may result from severe stress. Some might even need surgery.
PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT
After that, your physical therapist will lead you through a variety of stretches, exercises, and other treatments tailored to your particular needs. Your particular objectives will determine how many appointments you require. You will also be expected to apply the stretches you’ve learned to your regular practice.
Physical Treatment includes:
- Exercise
- Stretching
Stretching:
Standing hamstring stretch
Bring your right leg in front of you, bend your left knee slightly, and keep your spine neutral. Place your hands on your right bowed leg and bend forward gradually. Hold for ten to thirty seconds.
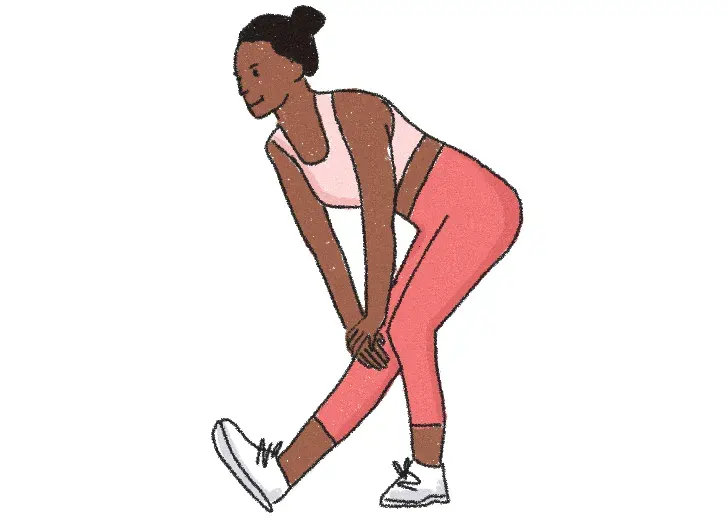
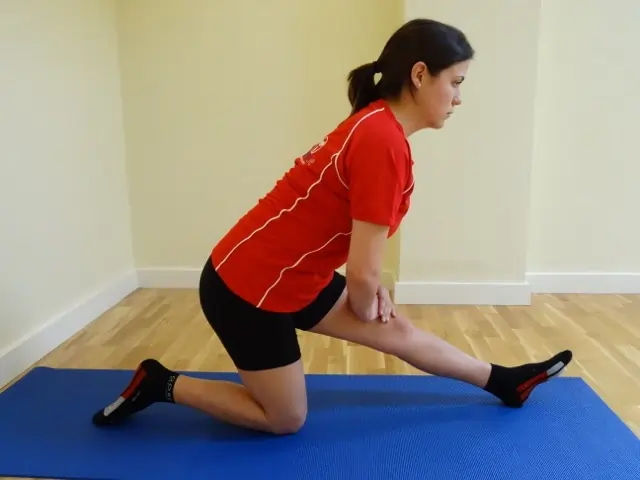
Kneeling hamstring stretch
Put your hands on your right bowed leg and progressively bend forward. With one hand, slowly reach your toes while maintaining a straight spine and toes pointed upward.

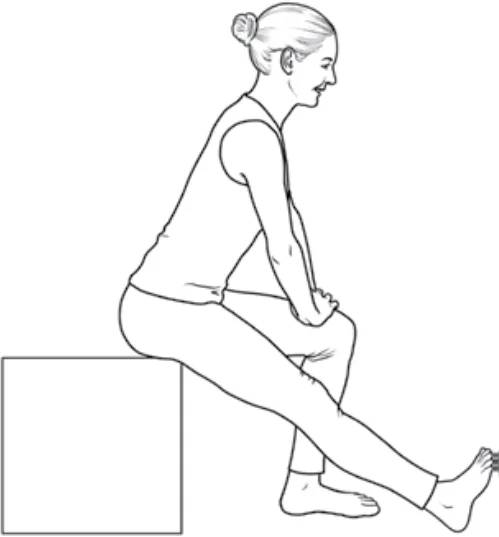
Hamstring chair stretch
Lean forward gradually, placing your hands on your bowed right leg. Maintain the posture, then let go. Hold for ten to thirty seconds.
Massage Therapy
Utilizing their grasp, massage therapists work with the body’s muscles and other soft tissue. Massage can help ease stress, discomfort, and tense muscles.
Prevention
You may prevent tightness before it begins by doing a few things. Asking your doctor for advice on particular conditioning exercises might also be beneficial.
- Before engaging in sports or other vigorous activities, warm up.
- Hamstring pain may be avoided by at least ten minutes of walking, light running, or simple gymnastics.
- It may also be possible to avoid tightness by stretching your hamstrings frequently before and after your activity.
- Before and after your sports or activities, try to stretch for three to five minutes.
- Maintain a strong body, not only for your particular interests.
- Consume a nutritious meal and lots of water to keep your muscles fueled and rehydrated.
Conclusion
In most cases, having tight hamstrings is not a reason for alarm. Although they may cause pain and restrict movement, these symptoms typically go away on their own. Regular hamstring stretches and leg strengthening exercises can be beneficial.
If you frequently have tight hamstrings, it is important to contact a physical therapist. They can offer appropriate stretches or exercises and look for underlying issues. important to contact a physical therapist. They can offer appropriate stretches or exercises and look for underlying issues.
FAQ’s
What causes extremely tight hamstrings?
Exercise or other high-intensity activities frequently cause tight hamstrings. Tightness may result from exercises that significantly strain the hamstrings. For instance, engaging in activities like soccer or hamstring curl exercises will strengthen the hamstring muscles.
Why is my hamstring so tight?
When the muscles on the back of the thighs shorten as a result of an accident or prolonged sitting, hamstring tightness results. Those who play sports that include a lot of running, direction changes, and jumping may also have stiff muscles in these areas.
Can tight hamstrings be cured?
One effective treatment for hamstring tightness is physical therapy. To ease hamstring tightness, physiotherapists can offer specific exercises, stretches, and lifestyle changes that emphasize building strength and flexibility in the hip flexors, glutes, and lower back.
References:
- Kandola, A. (2020, July 7). What to know about tight hamstrings. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/tight-hamstrings-symptoms-causes-and-treatments
- Marcin, A. (2019, June 10). How to Treat and Prevent Tight Hamstrings. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/tight-hamstring
- Webb, J. (2022, July 25). Tight Hamstrings: Causes, Prevention and Treatment – Does Stretching Help? Brighton Physiotherapy: A Whole Body Approach to Physiotherapy for Less Pain. https://www.physiotherapybrighton.co.uk/injury/why-hamstrings-get-tight