Café-Au-Lait Spots
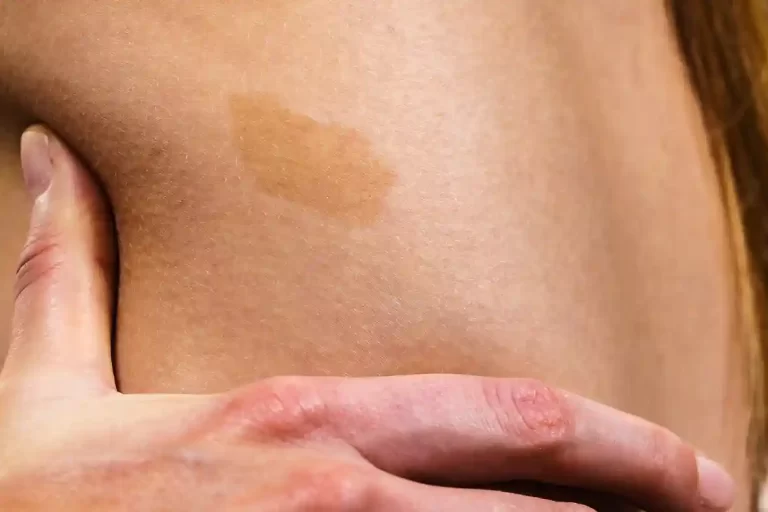
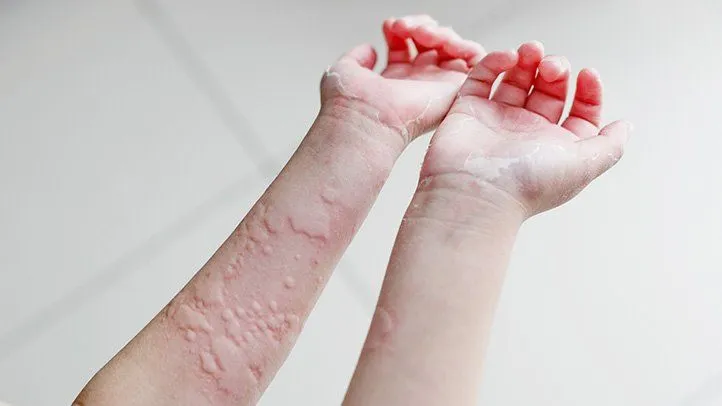
Introduction Light to dark brown pigmented birthmarks known as café-au-lait spots are frequently seen on a newborn’s skin. Over time, the number and size of spots may vary. Over six café-au-lait spots may indicate neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) or another underlying genetic disorder. Flat, hyperpigmented birthmarks are known as café au lait spots or café…