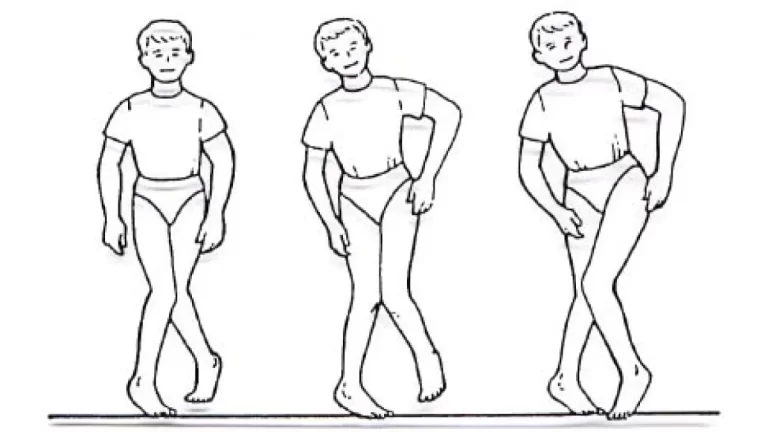
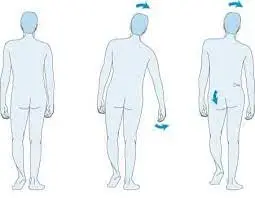
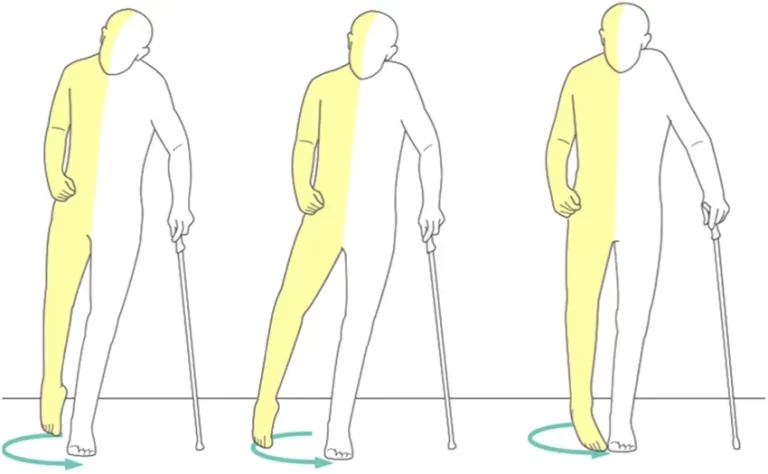
Stroke
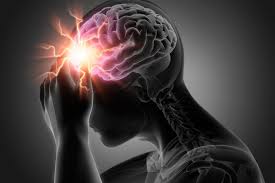
What is a Stroke? A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or significantly reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Without prompt treatment, brain cells begin to die within minutes. Strokes are a major medical emergency that requires immediate attention….