Ease Sciatic Nerve Pain with These Daily Mobility Moves
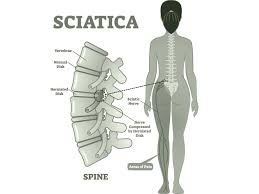
Introduction: We have all heard about sciatic nerve pain, and it is a very prevalent condition. Ten to forty percent of people suffer from sciatic nerve pain. Although Sciatica is a term used to describe symptoms, many people think it’s the name of a disease. When a portion of the sciatic nerve is pinched or…