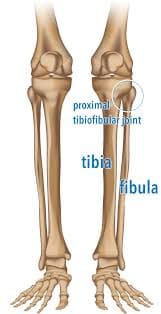
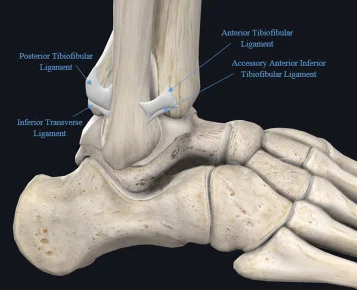
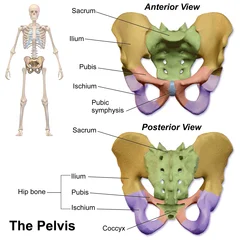
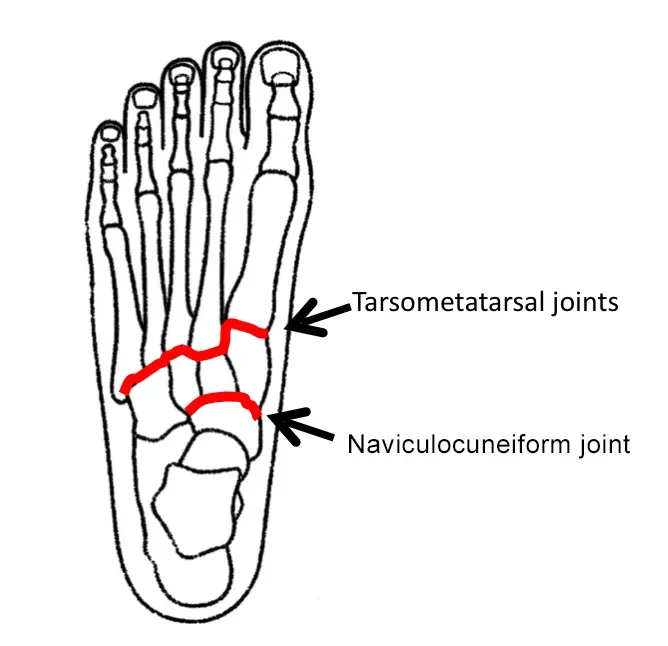
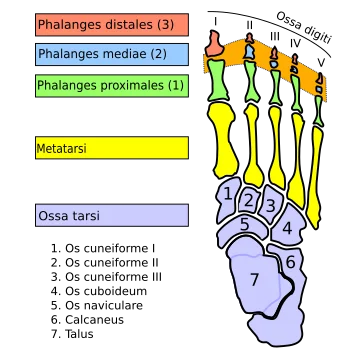
Proximal Tibiofibular Joint
Introduction The proximal tibiofibular joint is a synovial joint located between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. It plays a key role in stabilizing the lower leg and allowing slight movement to accommodate ankle motion. Although it contributes minimally to knee movement, it helps distribute forces during activities like…