Biceps Femoris Muscle Pain
Biceps Femoris Muscle Pain occurs due to strain, overuse, or sudden movements, affecting the back of the thigh. It can cause tenderness, stiffness, and difficulty in knee movement. Proper stretching, strengthening, and rest help in recovery and prevention.
What is a Biceps Femoris Muscle Pain?
- When you feel pain in the rear side of the legs, it is considered muscle soreness in the biceps femoris muscle.
- This muscular soreness arises largely due to the misuse of the biceps femoris muscle.
- Muscle strains, rips, and tendon rupture are among the major conditions that might occasionally result from this muscle soreness.
- pain, swelling, and spasms in the affected area accompany pain from the biceps femoris muscle.
- The RICE concept, pain medication, and physical therapy treatment alleviate the pain in the biceps femoris muscle.
Anatomy of the biceps femoris muscle?
- The biceps femoris muscle is the most prevalent portion of the hamstring muscle.
- This muscle is a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh & placed in the posterolateral aspect.
- Long-head superficial, and short-head deep are the two heads that emerge proximally from this muscle.
- The biceps femoris muscle’s long head is derived from the ischial tuberosity.
- The biceps femoris muscle’s short head: linea The femur bone’s aspera and lateral supracondylar line
- The lateral aspect of the fibular head is equal to the insertion of the biceps femoris muscle. The muscle’s actions include:
- The long head of the biceps femoris muscle helps in external rotation of the thigh when the hip joint is extended, flexion of the knee joint, extension of the hip joint, and external rotation of the lower leg when the knee joint is slightly flexed.
- When the knee joint is slightly flexed, the short head of the biceps femoris muscle externally rotates the lower leg.
What does the muscle known as the biceps femoris contain?
- Thousands of small, elastic muscular fibers make up the biceps femoris muscle.
- The biceps femoris muscle fibers aid in the contraction and tightening of the muscles.
- These are red and white muscular fibers.
- This biceps femoris muscle, visible beneath the skin, is striated, or striped.
Causes of biceps femoris muscle pain?
- Knee joint overuse and overexertion during regular activities are the primary causes of biceps femoris muscle pain.
- Microtears in the muscle fibers are the cause of this pain.
Muscle injury:
- Muscle injuries in the biceps femoris are the primary cause of muscle pain.
- During everyday activity, the biceps femoris muscle lengthens, contracts, and shortens, resulting in strains and tears.
- Additionally, during everyday activities, this muscle injury causes the biceps femoris muscle to be overextended.
Tendinitis:
- Muscle pain results from tendinitis, a tendon inflammation after daily activity.
- After the knee joint is repeatedly moved during regular activities, tendonitis develops.
- As you move, the pain in your muscles from tendinitis gets worse.
Tendon rupture:
- Rarely, tendon rupture is the cause of muscle soreness.
- Large tendon tears occur with this syndrome.
- Both partial and complete tendon ruptures can occasionally occur.
Symptoms of biceps femoris muscle pain?
- A dull, aching sensation is felt across the biceps femoris muscle.
- The biceps femoris muscle is tearing and ripping, which causes this muscle pain.
- Bruising is occasionally seen close to the location of muscular pain.
- In muscle pain, you can also feel the trigger point and tenderness.
- In the area of your muscles that hurt, you are seen to have swelling and spasms.
- As a result of this muscle soreness, you have heard popping and clicking sounds when moving your legs.
When is it necessary to contact a doctor in an emergency?
- when daily activities do not alleviate the biceps femoris muscle soreness within a day or two of home treatment.
- as your pain worsens over time.
- Sometimes, following certain activities, you experience a slow onset of tingling or numbness and weakness in the leg.
- When a skin rash spreads, it feels warm to the touch, similar to a fever.
Treatment for biceps femoris muscle pain?
The RICE concept is recommended by a doctor as a primary treatment or at-home remedy for biceps femoris muscle pain.
- R-rest = When you experience muscle soreness following an activity, your doctor may recommend that you take a break. This can involve complete rest or even the use of crutches and other mobility assistance to support your weight.
- I-ice = You apply ice to the area of pain for 20 minutes, allowing swelling and muscular pain to subside. To avoid ice burn, always use a cloth between the ice and your skin. You can also use frozen peas and an ice pack for ice treatment.
- C-compression = around reduce swelling and mobility, think about applying an elastic wrap around the thigh.
- E-elevation: To reduce swelling, try to keep the leg raised onto the cushion.
Pain medications:
- When you have pain from a biceps femoris muscle injury, an over-the-counter medication can assist.
- Oral NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications that are useful for temporary pain relief, such as ibuprofen or another over-the-counter pain reliever like Tylenol.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, or topical NSAIDs, are used in creams and gels to help reduce pain.
- It is important to consult a physician before self-medicating if the patient feels seriously hurt.
- Applying pain-relieving gel and spray, to the area of muscle soreness and swelling is another option.
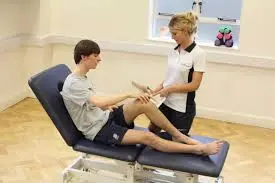
Physical therapy treatment for biceps femoris muscle pain?
- The doctor has recommended physical therapy as a treatment for muscle pain if it does not go away after home remedies and painkillers.
- You can get relief from pain, edema, spasms, and tightness in your muscles with physical therapy treatment.
Massage:
- When you are unable to relieve your muscle pain and soreness after two to three days of adhering to the RICE principle, a massage is administered.
Electrotherapy treatment:
- Muscle discomfort can be relieved with electrotherapy if the RICE principle, pain medication, and massage are ineffective.
- To lessen discomfort, edema, and spasms, the therapist is advised to employ electrotherapy.
- Many machines are used by the treatment therapist in electrotherapy.
- In order to alleviate muscle discomfort when trigger and tender points are present, therapists are advised to employ ultrasound treatment, or US.
- For five to ten minutes, the hurting area is treated with a gel.
- Pain and edema are lessened with this treatment.
- Short wave diathermy (SWD), interferential treatment (IFT), and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) are applied to the afflicted muscle by a pain reduction therapist.
- One kind of hot therapy used to treat muscle soreness is called short-wave diathermy, or SWD.
- IFT (interferential therapy) and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) are applied to the afflicted muscle region using gel and electrodes.
- Ten minutes are spent applying this therapy to the affected muscle area.
Exercise treatment for pain in the biceps femoris:
- The RICE approach, main therapy, and pain medication help you feel better after two to three days.
- When you are excessively calm and pain-free, the physical therapist recommends exercise to relieve stiffness and weakness in your muscles.
- Muscle pain exercise therapy includes both strengthening and stretching activities.
- While stretching exercises help you loosen up tense muscles, strengthening exercises assist you loosen up weak muscles.
Stretching exercise:
The physical therapist recommends stretching to relieve muscle tightness after the patient has received follow-up electrotherapy for two to three days to relieve muscle pain.
- Lying hamstring stretch
- Sitting hamstring stretch
- Standing hamstring stretch
- Strap Stretch
- Hurdler Hamstring Stretch
- Biceps Femoris Stretch
Lying hamstring stretch:

- You lie flat on a mat with your legs spread wide.
- Grasp the rear of the right knee joint with both hands to extend the right leg.
- The goal is to draw the leg up to the chest.
- Gradually extend the knee joint until the muscle stretches.
- For 30 seconds, maintain the stretching position.
- Do this stretching exercise three times a day and three times in one sitting.
Sitting hamstring stretch:
- With the left foot pointing inward and the left leg bowed at the knee, you sit on the ground.
- Make an effort to extend the right leg while maintaining a little bend at the knee.
- Next, bend forward at the waist in a straight back position.
- 30 seconds should be spent in this stretching position.
Standing hamstring stretch:

- Your spine is in a neutral position and your posture is straight.
- Place the leg with the foot flexed in front of the body.
- The heel is pressed into the ground, while the toe points upward.
- Next, slightly bend the left knee joint.
- With your hands on the straight leg, try to stoop a little forward.
- A neutral spine must be maintained.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
- Do this stretching exercise three times a day and three times in one sitting.
Strap Stretch:
- You have a resistance band wrapped around the bottom of one foot while you lay on your back on the floor.
- Next, pull the foot in your direction while extending the leg with the resistance band into the air.
- The rear of the leg feels stretched.
- By pushing on the band even further, you can also intensify the strain.
- Hold this exercise position for 30 to 60 seconds.
- Do this stretching exercise three times a day and three times in one sitting.
Hurdler Hamstring Stretch:

- One leg is out in front of you while you sit on the floor.
- Try to bend the second leg at the knee joint by placing its sole against your opposing inner thigh.
- Then, bending at the waist as comfortably as possible, reach forward over the straight leg with your arms extended.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Biceps Femoris Stretch:
- The hamstring muscle group includes the biceps femoris, which is situated at the rear of the thigh.
- A basic method for stretching the biceps femoris is to sit on the floor with one leg outstretched and the other bent at the knee, pressing the sole of the bent leg on the straight leg.
- Reach for the outstretched leg’s toes while leaning the torso forward.
- This stretching exercise should be done three times a day and three times in one sitting.
- The physical therapist recommends massage for two to three days to relieve pain and strengthening activities for weak muscles following electrotherapy.
- It is often advised to do this strengthening activity when you are at ease and wish to reduce pain.
- This is an all-strengthening routine that will help strengthen and tone your muscles.
- Nordic hamstring curl
- High Kicks
- Cross-leg Toe Touch
- Seated Toe Touch
- Standing knee flexion
- bridge exercises
- Seated hamstring curl
- Good mornings
- Single-Leg Deadlift
- Lying Leg Curl
Nordic hamstring curl:
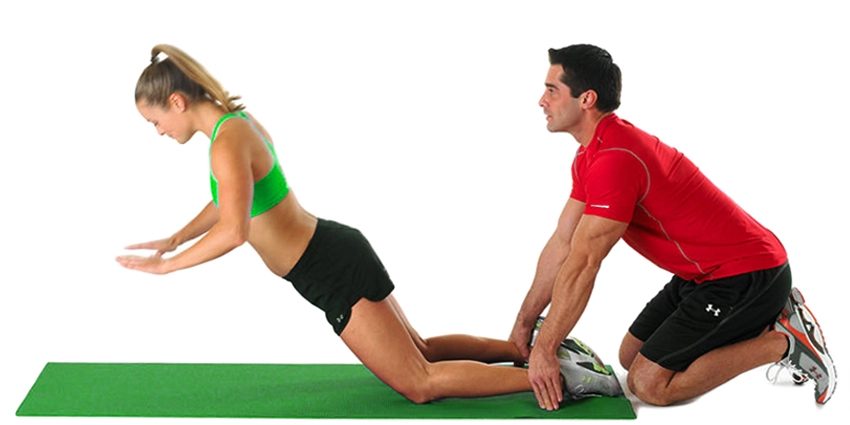

- Kneeling, you place a mat or pillow in front of yourself.
- When you’re ready, have someone support your ankles as you carefully descend your upper body.
- Stretch your arms out in front of you when you’re ready.
- As you approach the floor, stop yourself.
- Make an effort to touch the floor.
- After then, return to your starting point and repeat this practice.
- Three times a day and ten times in a single session, do this exercise.
High Kicks:
- A dynamic warm-up for the biceps femoris workout frequently includes high kicks.
- To begin, stand up straight.
- You’re using one leg to execute a high kick.
- Kicking the leg up to mid-chest height and beyond is the goal of this exercise.
- To contact the toe at the apex of your kick, you are reaching out with the arm on the same side of your body.
- You can also perform this exercise by moving forward with a high kick on each leg.
Cross-leg Toe Touch:
- begins with your feet together and you standing erect.
- Bend forward and cross one foot over the other.
- Make an effort to extend your hands toward your toes.
- After 30 seconds of maintaining this hunched posture, switch legs.
Seated Toe Touch:
- placing both feet out in front of you while seated on the ground.
- Attempt to touch your toes by extending your hands forward.
- Avoid bending at the knee.
- For the duration of the stretch, try to maintain the legs straight.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this workout stance.
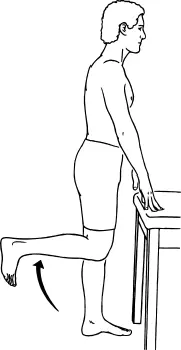
Standing knee flexion:
- With only gravity acting as resistance, you stand on one leg while bending the other.
- This is an early-stage exercise that should be started cautiously and gently.
- This exercise’s goal is to perform three sets of ten repetitions once a day, gradually increasing to four sets of twenty.
- To add weight to the ankle joint, this exercise requires an increase in load.
Bridge exercises:
- You perform this exercise while lying supine with your back knee bent.
- Raise the hip joint to engage the biceps femoris and gluteal muscles.
- To start, try to push up with both feet on the floor.
- For a short time, hold this workout stance and then lower yourself.
- Build up to 3 sets of 12 reps from 3 sets of 8 reps.
- This practice progresses to single-leg bridges.
Seated hamstring curl:

- A resistance band’s first end is fastened to a stationary point.
- A therapist holds a resistance band while the other end is fastened to the foot.
- Pull your heel into your buttocks if you can.
- For ten seconds, maintain this exercise position.
Good mornings:
- A more complex variation of the single-leg ball pick-up, the Good Morning exercise strengthens the hamstrings or lower back eccentrically, primarily the fibers that run up the top of the thigh.
- Start by performing the single-leg ball pick-up exercise.
- Then maintain a straight back while bending forward at the waist.
- For ten seconds, maintain this exercise position.
Single-Leg Deadlift:
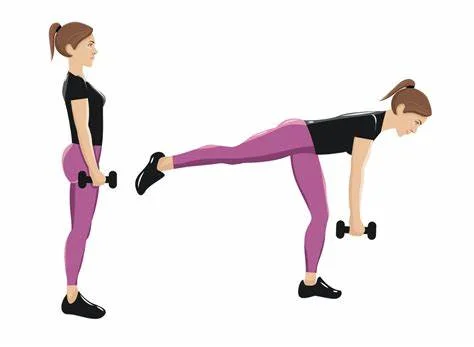
- You are standing on your right leg, bending your knee joint.
- Hold a kettlebell with your right hand first, keeping your left foot off the ground.
- Keep your left leg straight back behind you and your chest high.
- Continue as far as you can until your right hamstring starts to tense.
- You can either go back to the initial position or stand up straight again and clench your glutes.
- Before switching to the left leg, finish all of the repetitions on the right leg.
- Perform eight to ten reps for each leg.
Lying Leg Curl:
- Make sure your heels are lying on the roller pad before beginning this exercise.
- The roller pad is placed on top of your lower calves while you are in the prone posture.
- Next, grasp the machine’s grips on either side.
- While keeping your hips on the bench, try to raise your feet and flex your knees or draw your ankles in toward your glutes.
- After a little pause, carefully drop your leg back to the beginning position.
- Perform the ten to fifteen repetitions.
- You are selecting a weight that is sufficiently light to allow for tight form.
- Reduce the weight if your hip joint is separating from the bench during curling.
Home exercise for the Biceps Femoris muscle:
- Do a 90-degree leg lift and strengthen and stretch your biceps femoris muscle?
- You are in a supine position on your yoga mat, with your back pleasantly flat.
- Have both legs bowed when you begin this exercise.
- With the exercise band wrapped around the sole of your foot, try to straighten one leg onto the mat while gradually raising the other leg.
- The lifting angle is as near to 90 degrees as it can be.
- Keep your back and opposite leg as flat on the floor as you can.
- For a maximum of one minute, maintain this workout position.
- This exercise should be done three times, using the opposite side each time.
- Avoid straining your head and neck when you lift and release your legs.
FAQs
How should a strain of the biceps femoris be treated?
Avoid engaging in intense activities if the pain and decreased mobility are severe. Additionally, your physical therapist could suggest rest, applying heat or ice, and, if required, taking pain medication. They might also advise you to use straps or braces for support.
Which workouts are beneficial for pain in the biceps femoris?
Exercises like kettlebell swings, squat jumps, and burpees are excellent examples. These vigorous motions work the muscles and build strength in a way that promotes recovery.
Why do I have tight biceps femoris?
Nerve entrapment is one of the main reasons for hamstring pain. The sciatic nerve can occasionally become trapped behind the bicep femoris muscle, which runs over it.
What’s causing my femoris muscle pain?
One of the strong quadriceps muscles is the rectus femoris. Overuse or explosive stresses on the muscle, such as during kicking or sprinting, can cause a rupture of the tendon at the top of the muscle close to the hip. During physical activities that include the usage of this muscle, groin pain is caused by inflammation of the muscle.
How may an pain to the biceps femoris be healed?
For four to six weeks, non-operative treatment consists of rest, ice, non-steroid anti-inflammatory medications, mild stretching, and therapeutic exercise. Non-operative treatment is usually used for myotendinous ruptures and isolated biceps femoris tendon ruptures.
How is pain in the biceps femoris tested?
Particularly helpful in eliciting these diagnostic symptoms are tests such as the bent-knee stretch test and the Puranen-Orava test. The ‘taking off the shoe’ (TOST) is a self-administered test that shows good sensitivity and specificity in identifying biceps femoris tendon pain.
How can the bicep femoris be relaxed?
Turn your leg slightly so that your foot is facing inward. The Bicep Femoris is positioned on the outside rear of your thigh, and this is where you will feel it now. Release after around 30 seconds of holding. Don’t forget to stretch your other leg.
What is the term for biceps femoris in everyday speech?
The biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus muscles comprise the hamstring muscle. The popliteal fossa, a triangular area behind the knee, is bounded by the hamstring muscles.
Which workouts are beneficial for the rehab of the biceps femoris?
Therefore, the flywheel leg curl and Nordic hamstring curl are great workouts for strengthening the hamstrings in general or for focusing on the biceps femoris short head, semitendinosus, and membranosus. The Russian belt exercise is a great addition.
Why do pain to the biceps femoris occur most frequently?
Given that the biceps femoris requires more force to perform a longer stretch in the same amount of time than the semimembranosus or semitendinosus muscles, making it more prone to pain, one such application would be to propose that, if these other hamstring group muscles could.
What causes soreness in the biceps femoris?
A common cause of pain in the biceps femoris, a hamstring muscle involved in knee flexion and hip extension, is overuse pain or strain from physical activity. Pain, swelling, and weakness at the back of the leg are signs of biceps femoris pain, which can be mistaken for sciatica.
How can pain in the bicep femoris be treated?
Make an appointment for physical therapy right away if you have biceps femoris tendinopathy. In most cases, it does not improve without treatment. In the interim, you can start applying a bag of frozen peas or crushed ice wrapped in a moist cloth to the sore area for 15 to 20 minutes every one to two hours.
The biceps femoris is controlled by which nerve?
The sciatic nerve
The root values of the tibial and common fibular divisions (spinal nerves L5, S1, and S2) are identical.
What is the recuperation period for biceps femoris?
Biceps femoris central tendon pain required a much longer recovery period (72 to 91 days). It makes sense that when the central tendon is torn, healing takes longer since tendon blood flow is lower than that of muscle fibers.
Which workouts are beneficial for tendinitis of the biceps femoris?
However, alternate activities that incorporate jumping become more appropriate in situations such as biceps femoris tendonitis, where jogging is discouraged during rehabilitation. Exercises like kettlebell swings, squat jumps, and burpees are excellent examples.
What is biceps femoris calcific tendinitis?
The rotator cuff tendons are most frequently affected by calcific tendinitis, a prevalent source of periarticular pain. Less frequently, it may affect the gluteus maximus, longus colli, and Achilles tendon. A very uncommon location of involvement that results in lateral knee pain is the distal tendon of the biceps femoris.
References
- Ladva, V. (2024g, December 11). Biceps femoris muscle pain : Cause, symptoms, treatment. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/biceps-femoris-muscle-pain/