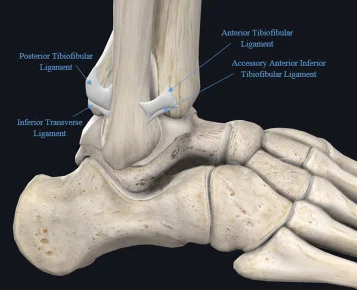
Annular Ligament
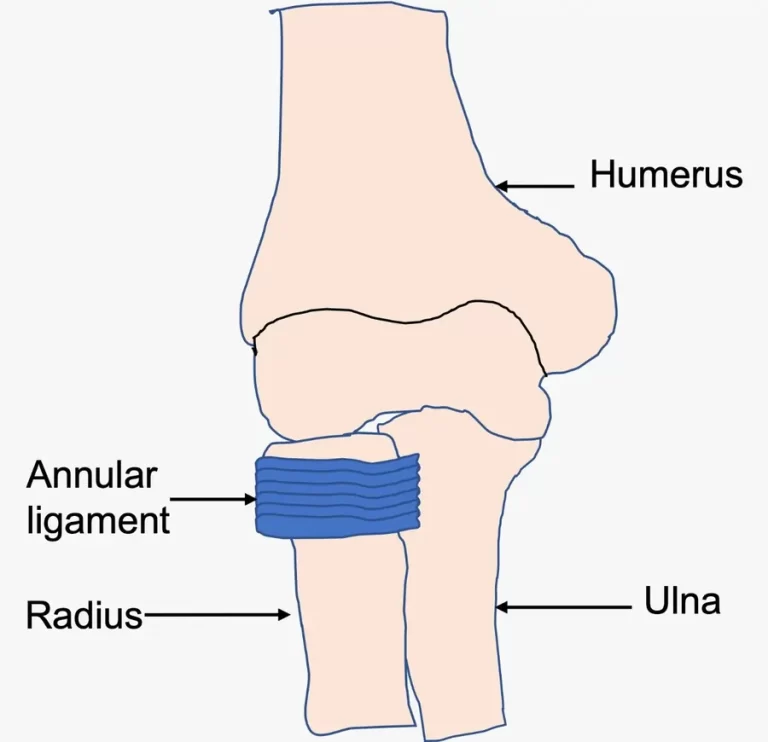
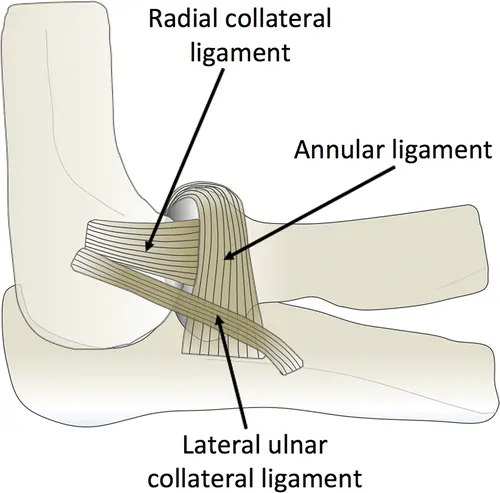
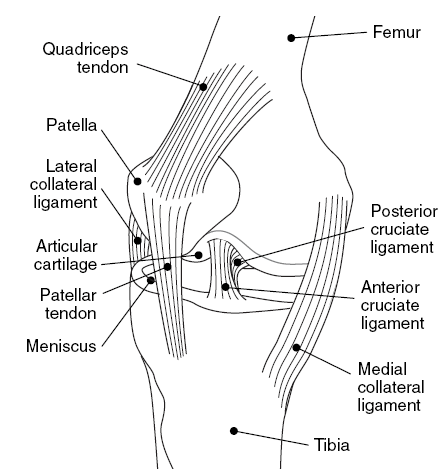
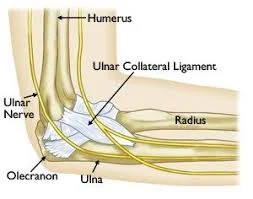
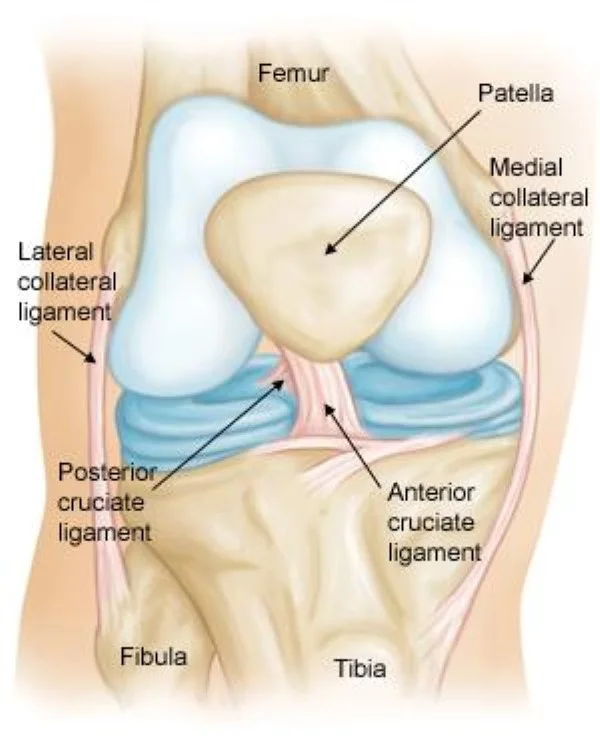
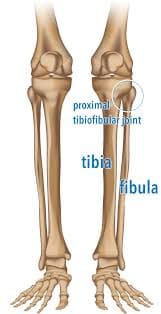
Introduction The annular ligament is a strong, circular band of fibrous tissue that wraps around the head of the radius, securing it to the ulna at the proximal radioulnar joint. It allows the radius to rotate smoothly during forearm movements like pronation and supination while maintaining joint stability. The annular ligament is made of thick…