Arm Muscle Pain
What is Arm Muscle Pain?
Arm muscle pain is characterized as discomfort and pain felt anywhere along the arm, sometimes extending to the wrist, elbow, and shoulder joints. There are several reasons why this pain arises, but the most frequent ones are pain or overuse.
Depending on the cause of the arm, the pain may begin suddenly, subside, or worsen over time. The RICE principle and physical therapy treatment can relieve this pain.
Causes of arm muscle pain?
- Overuse:
- When an arm is overexerted, moved repeatedly, and used for extended periods of time.
- Numerous pain result from overusing this muscle.
- Pinched nerves:
- These disorders arise when a nerve exerts excessive pressure on the arm’s surrounding muscles, tendons, cartilage, and bones.
- Sprains:
- Sprains are caused by the ligaments and tendons stretching or rupturing.
- It’s a typical pain.
- Sprains are classified as mild, moderate, or severe based on their severity.
- Tendonitis:
- Tendon inflammation is the cause of this disease.
- The wrist, elbow, and shoulder joints are affected by this tendonitis.
- Mild to severe tendinitis can occur.
- Rotator cuff pain:
- People that execute overhead motions in their daily tasks, such baseball players and painters, are more likely to sustain this pain.
- Broken bones:
- When bones are damaged or fractured, the arm experiences excruciating pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term inflammatory condition that mostly affects the joints.
- Angina:
- Chest pain caused by insufficient oxygen delivery to the heart.
- It causes pressure in your chest, neck, or back, as well as pain in your arm and shoulder.
Symptoms of the arm muscle pain?
The cause will determine your symptoms:
- You experience too much dull, stinging pain.
- You are shown to have arm soreness, edema, and redness.
- You experience arm muscle weakness and stiffness.
- Additionally, there are trigger points and a sensitivity sensation in the painful location.
- You may experience tingling and numbness in the vicinity of the pain.
- Additionally, you notice a reduction in arm range of motion.
- You have trouble moving your arms as well.
- You may also have shortness of breath and dizziness at times.
- Additionally, experiencing shooting or radiating pain when experiencing arm ache.
Diagnose of arm muscle pain?
- Initially, the physician is attempting to identify the source of the pain.
- Thus, the doctor is questioned about the patient’s medical history and physical examination first.
- Inquire about your activities, possible pain, and symptoms as well.
- The ROM is then requested to be examined by the physician.
- Blood tests assist your doctor in identifying certain illnesses, such as diabetes and joint inflammation, that are caused by arm pain.
- A doctor can diagnose fractured or broken bones with the use of X-rays.
- Your doctor is also suggested to perform certain tests when determining whether your arm pain is related to any possible cardiac issues.
- Doctors can identify issues with joints, ligaments, and tendons with the use of ultrasounds.
- In order to obtain a more complete image of the soft tissues and bones for a more thorough diagnosis, your doctor may occasionally recommend MRIs and CT scans.
Nerve Conduction Study:
When a tiny quantity of electrical current is given, this technique helps measure nerve impulses to identify pain nerves.
Electromyography (EMG):
In order to assess electrical activity and identify damage to the nerves that supply muscles, a needle electrode is inserted into the muscles.
When is it necessary to call a doctor in an emergency?
- In most cases, arm pain does not require medical attention.
- While home remedies can be used to alleviate arm pain in many circumstances, there are some conditions that require emergency care.
- If you experience any of the following symptoms, you need to dial 911 right away:
- when you get pressure and pain in your chest.
- when the upper body, neck, and back start to feel this ache.
- the sensation of lightheadedness and vertigo.
- when you experience dyspnea and nausea.
- if the pain is too sharp or intense for you.
- When you have obvious physical abnormalities, such as an angled arm or wrist joint
- if you have trouble bending or turning your hands, fingers, or arms.
Which condition causes by pain in the arm muscles?
- Carpal tunnel syndrome:
- is a frequent ailment caused by repetitive motions of the fingers, wrists, or hands.
- This causes your arms, palms, and fingers to become tingly, numb, and weak.
- The tennis elbow:
- is another name for lateral epicondylitis, a condition that is primarily caused by repetitive motions in the arms, elbows, and wrists. It causes pain and weakness in the elbow or forearm, as well as tenderness and trigger points on the outside of the elbow joint.
- Frozen shoulder:
- is sometimes referred to as sticky capsulitis.
- Adults between the ages of 40 and 60 are typically affected by this less prevalent ailment.
- Pain and restricted range of motion (ROM) are symptoms of this illness.
- This disorder is caused by thickening and inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint.
- Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity:
- It happens when a blood clot forms in an arm’s deep vein, causing arm tiredness, severe pain, and swelling.
Risk factor for arm muscle pain?
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is more likely to occur in women.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is more likely to occur when you have thyroid issues.
- Nerve damage is another consequence of diabetes.
- Being obese increases the pressure on nerves and raises the possibility of compression.
- Being pregnant
- Overuse of any activity
- Always loosen your grip, which indicates that you should not clutch a pen, handle, or anything else more forcefully than is necessary to complete the work at hand.
- Take breaks: To prevent pain, always take a little respite from repetitive activity.
- Making sure your hand reaches the mouse at a comfortable angle is the first step in optimizing your computer mouse.
Treatment for arm muscle pain?
RICE principle:
A doctor is recommended to use the RICE concept as a main treatment or at-home remedy when you experience arm muscle soreness.
- R-rest is reducing forearm activity, which aids in the recovery of pain tendon, ligament, muscle, bone, and nerve. You should do this sporadically rather to staying inactive for extended periods of time.
- Avoid the activity until the pain has completely gone away if the person has forearm pain from sports.
- I – ice To help reduce inflammation and pain, I applied ice to the affected area for 20 minutes. You can also use an ice pack and frozen peas to relieve the pain.
- C-compression.
- E-elevation.
Pain medication:
- Your doctor may occasionally prescribe painkillers, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, if the pain does not go away.
- The doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids to treat inflammation, which helps you lessen the underlying cause and the resulting pain.
- These anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken orally, intravenously, or as injections.
- Applying pain-relieving gel and spray, such as volini gel and spray, to the area of muscle soreness and swelling is another option.
Physical Therapy Treatment for arm muscle pain?
- The doctor has recommended physical therapy to reduce forearm pain if the muscular soreness does not go away after home remedies and painkillers.
- Massage, electrotherapy, and exercise therapy are all part of the physical therapy treatment.
Massage:
- The therapist is suggested to use massage therapy to relieve muscle pain when trigger and tender points are present in the affected area.
- When you are unable to relieve your muscular pain after two to three days of using the RICE method, you should have a massage.
Electrotherapy treatment:
- If the RICE principle, pain medicine, and massage do not alleviate the muscle pain, electrotherapy is employed to release the pain.
- Therapists are encouraged to use US (ultrasound treatment) to relieve muscle pain when trigger and tender points are present.
- A pain reduction therapist applies TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), IFC (interferential current therapy), and SWD (short wave diathermy) to the affected muscle.
- SWD, or short wave diathermy, is a type of hot therapy used to relieve muscle pain.
- Gel and electrodes are used to apply TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) and IFT (interferential therapy) to the affected muscle area.
- The area of muscle pain is treated with this therapy for ten minutes.
Exercise therapy for arm muscle pain:
- The physical therapist suggests exercise treatment to alleviate muscular weakness and tightness after you feel comfortable and relieved of your muscle pain.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises are part of the exercise therapy for muscle pain.
- Both strengthening exercises and stretching exercises can help you release muscle weakness and tension.
Stretching exercise:
The physical therapist is instructed to stretch to relieve muscle tightness after electrotherapy has been used for two to three days to relieve muscle pain.
When you feel comfortable and your pain has subsided, you apply this stretching.
- Shoulder stretch
- Neck release
- Triceps stretching
- Across-the-chest stretch
- Doorway shoulder stretch
- Towel stretch
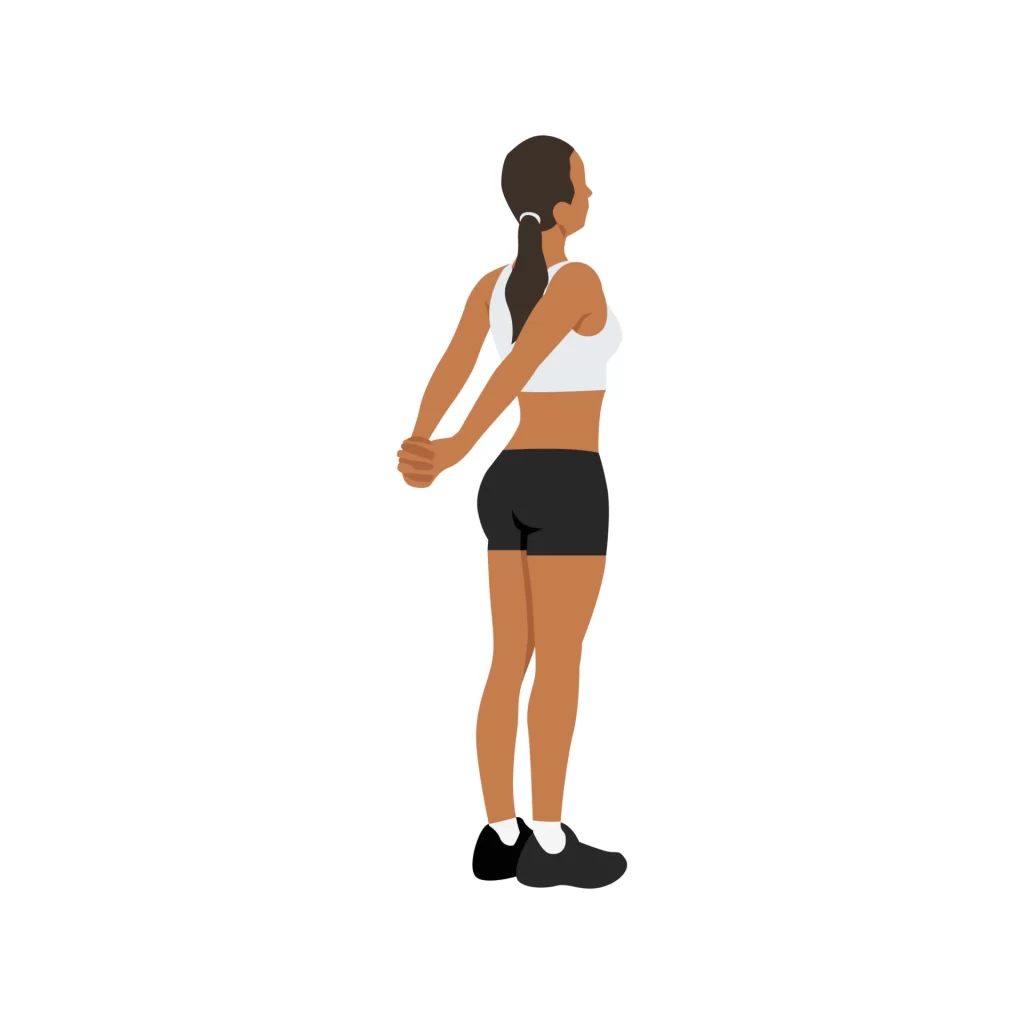

Shoulder stretch:
- You’re standing right now.
- Make an effort to elevate your shoulder joint.
- For ten seconds, hold this exercise.
- Next, squeeze your shoulder joints together and back.
- For ten seconds, hold this exercise.
- Pull your shoulder blades down as much as you can.
- For ten seconds, hold this exercise.
- Unwind and perform this exercise ten times.
Neck release:
- You may gently relieve stress in your shoulder and neck joints with this workout.
- You can do this stretching while standing or sitting.
- The nape of your neck feels stretched.
- To stretch your right shoulder joint, try tilting your head slightly to the left.
- Repeat on the other side after holding this stretching stance for up to 30 seconds.
- Stretch each side three to five times.
Triceps stretching:
- You are either standing or seated.
- Try raising one arm above your head and bending it such that it reaches behind your head and toward your back.
- Gently press back on the bent elbow with the other hand.
- Feel the tricep muscle stretch after 30 seconds of holding this exercise.
- Stretch each side three to five times.
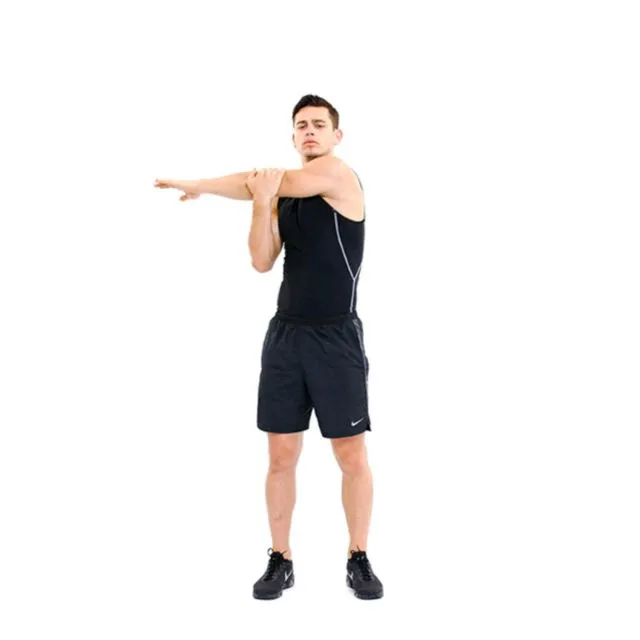

Across-the-chest stretch:
- You can either stand or sit as you do this stretching exercise.
- Start by crossing your right arm across your chest.
- Next, position the arm in the elbow joint’s crease.
- Your arm is being supported by your hand.
- Repeat on the other side after 30 seconds of holding this stretching stance.
- Stretch each side three to five times.
- Raise your arm to shoulder joint height to increase the stretch’s depth.
Doorway shoulder stretch:
- Your arms and elbow joint are at a 90-degree angle as you stand close to a doorway.
- Start by pressing your palms against the door frame’s sides and stepping forward with your right foot.
- Make an effort to lean forward and use your core muscles.
- Then put your left foot forward and repeat the stretching.
- Perform this stretching exercise two or three times on each side.
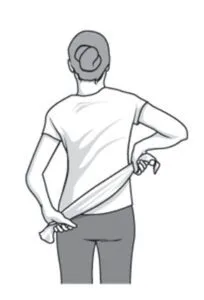
Towel stretch:
- To begin, grasp one end of a three-foot-long towel behind your back and use your other hand to grasp the other end.
- The towel is being held horizontally by you.
- To stretch the affected arm, you must pull it upward with your good arm.
- With your towel placed over your good shoulder joint, you are also doing a more complex variation of this exercise.
- Next, use the affected arm to grasp the towel’s underside.
- Using the unaffected arm, try to draw the arm toward the lower back.
- Ten to twenty times a day, do this.
- Following two to three days of electrotherapy and massage to relieve muscle pain, the physical therapist recommends strengthening activities for weak muscles.
- All of these strengthening exercises help with muscle soreness and weakness.
- Chest expansion
- Eagle arms spinal rolls
- Shoulder circles
- Pendulum exercise
- Wand exercise
- Lateral raises
- External shoulder rotation
- Internal shoulder rotation
- Scapula Setting
- Scapular Retraction/Protraction movement
- Pully exercise
- Finger ladder Exercises
- Shoulder Roll
Chest expansion:
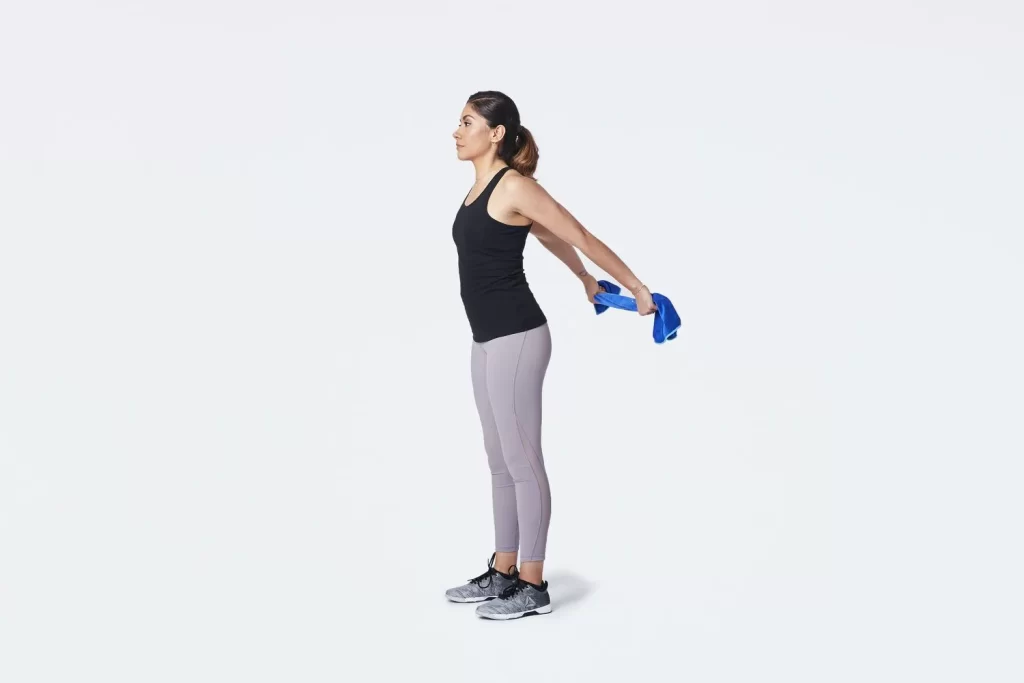

- This exercise is performed while standing.
- Next, use both hands to grasp an exercise band, strap, and towel behind your back.
- As you move your shoulder joints toward one another, try to widen your chest.
- Next, raise your chin and gaze at the ceiling.
- Hold for a maximum of 30 seconds.
- Do this three to five times.
- Place your hands, the towel, and the strap closer together to intensify the exercise.
Eagle arms spinal rolls:
- Stretch your arms out to the sides while you are seated.
- With your right arm on top, try to cross your elbow joint in front of your body.
- Place the backs of your hands or forearms together and bend your elbow joint.
- Next, bring your hands together by extending your right hand around.
- For fifteen seconds, maintain this workout position.
- As you draw your elbow joint in toward your chest during an exhale, roll your spine.
- As you inhale, raise your arms and open your chest.
- After a minute, repeat same exercise motion on the other side.
- Do this three to five times.
Shoulder circles:
- With your left hand on the back of a chair, you are standing.
- Let your right hand dangle down after that.
- Using your right hand, try to draw a circle five times in each direction.
- On the other side, repeat this exercise.
- Perform this workout three times a day.
Pendulum exercise:
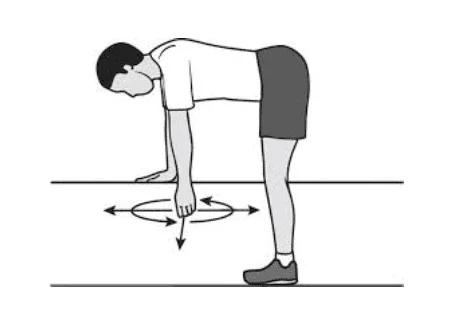
- The patient is standing next to a table, with their feet somewhat wider than shoulder-width apart and their unaffected shoulder’s hand resting on the table.
- Allow the affected arm to droop toward the floor while bending the hip joint to around 75 to 90 degrees.
- Try shifting the weight from one side to the other while allowing your arms to swing freely.
- Next, Allow the arms to swing freely from front to back while shifting the weight forward and backward.
- Move the body until the arm swings in a circle after they are at ease with these motions.
- Surely Don’t make the circle larger than 8 inches.
- Keep going for 30 seconds.
- Increase the duration to three to five minutes each day.
Wand exercise:
- You can increase your range of motion with this workout.
- Using both hands, you are holding the wand.
- Make an effort to move your elbow and shoulder joints.
- Using the wand, do the following movements: elbow flexion, extension, external and internal rotation, shoulder flexion, abduction, and adduction.
- Every workout is performed two to three times a day.
Lateral raises:
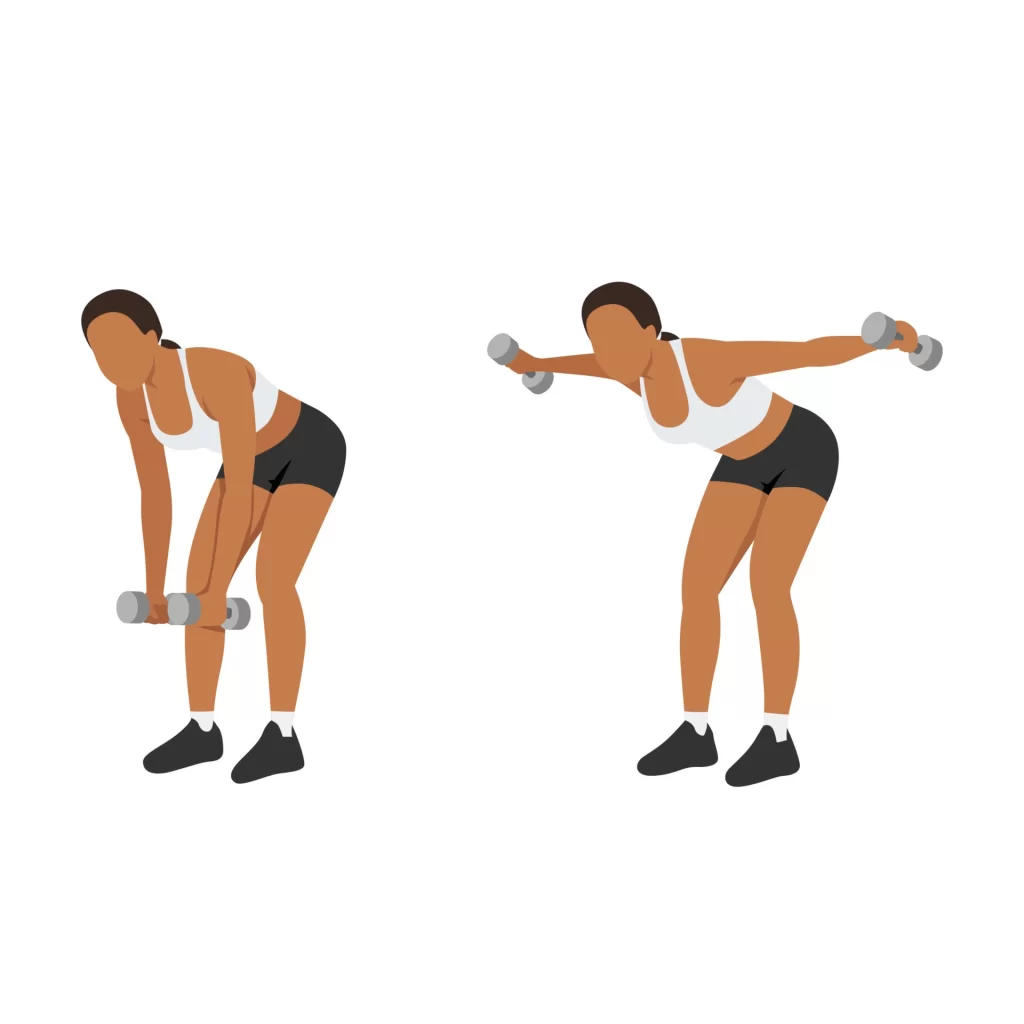

- For this workout, you are first holding a pair of light dumbbells.
- You are standing with your feet a little wider apart than the distance between your hips.
- Aim to elevate the weights to shoulder level by moving them to the sides.
- It’s important to keep in mind to contract your core muscles and gradually reduce the weights to the sides.
- Do this exercise three to four times a week for two sets, with each set consisting of 12 to 15 repetitions.
External shoulder rotation:
- The light resistance band is first held in both hands.
- Both arms must be bent at the elbow joint and kept at the sides of the body.
- Next, while keeping the elbow joint bent at a 90-degree angle, rotate the opposite arm away from the body while keeping the first arm still.
- After five seconds of holding this workout stance, carefully bring the arm back toward the body.
- Do this exercise three to four times a week for two sets, with each set consisting of 12 to 15 repetitions.
Internal shoulder rotation:
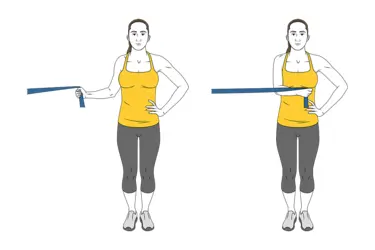
- You start by fastening a big elastic band and a resistance band to a doorknob.
- One hand is used to hold the other end of this band.
- Pull the forearm toward the body and attempt to bend the arm at the elbow joint.
- After five seconds of holding this workout stance, carefully bring the arm back toward the body.
- Do this exercise three to four times a week for two sets, with each set consisting of 12 to 15 repetitions.
Scapula Setting:
- With your arms by your sides, you are in a prone position, meaning you are laying on your stomach.
- For comfort, you start by placing a pillow beneath your forehead.
- As much as you can, try to gently pull your shoulder joints together and down your back.
- Hold this exercise for 10 seconds after easing it halfway off from this position.
- Repeat this exercise ten times while relaxing in the exercise position.
Scapular Retraction/Protraction movement:
- Your damaged arm is dangling over the side of a table and bed as you lie on your stomach in a prone position.
- You must lift the weight gradually and maintain a straight elbow joint.
- Squeeze your shoulder joint as much as you can in the opposite direction.
- After then, carefully go back to where you were before and repeat the practice.
Pully exercise:

- You start by holding a rope pully in both hands, and then you move your shoulder.
- Abduction, flexion, and internal and exterior rotation.
- This workout is done three times a day and ten times in a single session.
Finger ladder Exercises:
- You are facing a ladder that is suspended over a wall while you are standing.
- Position the affected hands at a low position on the ladder.
- Try starting the finger ladder gently, working your way up to the top, and then carefully descending back to the beginning.
- This workout is done three times a day and ten times in a single session.
Shoulder Roll:
- You are standing with your feet apart and your back straight.
- Put your arms by your sides first.
- Breathe deeply, then raise your shoulder joint to rotate it slowly.
- When lifting something, try to shift your shoulder joint back so that the muscles in your shoulder joint are squeezed together.
- Lower your shoulders when you exhale.
- You feel a stretch around the rear of your shoulder joint when you move it forward.
What are the complications of Arm Pain?
- It becomes extremely difficult to type, write, talk on the phone, and carry out your everyday tasks when you have aches and pains in your arm, shoulder, or wrist joint.
- Other forms of inflammation and pain that go unnoticed and untreated might cause severe tissue damage that necessitates surgery.
How to prevent arm pain?
- Always attempt to adhere to these preventative guidelines as many occurrences of arm pain can be avoided:
- Always stretch your muscles, especially before working out.
- Always perform the exercises with the right form, which also helps to avoid pain.
- When participating in sports, make an effort to use protective gear.
- Carefully and correctly lift the objects.
Conclusion
If left untreated, arm pain can worsen and lead to several consequences. Using the R.I.C.E. approach or taking anti-inflammatory drugs at home will assist a normal or minor arm pain return to normal. However, whether it may be disregarded or requires emergency medical attention depends greatly on its severity and duration.
FAQs
What is the primary line of treatment for sore arm muscles?
For the first few days following the pain, apply an ice pack or ice and water slush bath for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, repeating every two to three hours while you’re awake. compression. Apply an elastic bandage to the affected area and squeeze it until the swelling subsides.
Does a massage help with arm pain?
An arm massage stimulates the lymphatic system, improves blood circulation, and reduces swelling in order to alleviate delayed onset muscular soreness. An increase in capillarization and vasodilation during an arm massage improves blood circulation.
How can I get rid of arm pain?
Apply a cold pack or ice to your arm for ten to twenty minutes at a time. During the next three days, if you sit or lie down, support the aching arm with a pillow. Aim to maintain it higher than your heart.
Why does nighttime make arm ache worse?
Tendons and muscles may glide easily across boney surfaces thanks to bursas, which are fluid-filled sacs. The elbow and shoulder contain many bursae that are susceptible to irritation or inflammation. The pressure on the bursae may increase while you sleep on your side, which could cause throbbing arm pain at night.
Which medication works well for arm pain?
Using over-the-counter medicine is another method of treating arm pain. This does not imply that you should take it without first seeing a doctor, but after seeing you and evaluating your condition, they will probably give you some form of acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve your pain.
How can someone with arm pain sleep?
Put a pillow underneath the entire affected arm, including the shoulder, to avoid this. By doing this, the shoulder is raised, avoiding pain from gravity pressing on the joint. If you are a side sleeper, you must sleep on the side that is unaffected in order to prevent shoulder pain.
What vitamin helps with arm pain?
If your doctor recommends it, you might think about taking supplements if your diet isn’t providing enough niacin. Pain and stiffness caused by diseases like arthritis can be reduced when your body has the proper amount of niacin. One strategy to positively maintain your health is to include vitamins for pain in your diet.
Is pain in the arm muscles normal?
A common symptom with numerous potential explanations is arm pain. It can be a minor ache that subsides with massage and painkillers. Or it can be severe enough to interfere with your ability to carry out your daily tasks.
What is the greatest exercise for pain in the arms?
Arm workouts: Stretch, Press, and Triceps. Discover how to use this triceps press stretch to lengthen the shoulders and back of the arms.
March…. Resistance Band Reverse Fly…. Resistance Band Row…. Resistance Band Triceps Extension…. Resistance Band Shadow Boxing.
Which pain reliever works best for arm pain?
Conservative treatments like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or over-the-counter aspirin may be used as the first line of treatment. Following the directions on these over-the-counter drugs can help relieve some types of arm pain. To lessen muscle cramps, you might also think about at-home care practices like drinking lots of water.
How can arm muscle pain be relieved?
Self-care
Get some rest. Take a vacation from what you usually do.
Ice. Three times a day, apply an ice pack or bag of frozen peas to the aching spot for 15 to 20 minutes.
compression. To reduce swelling and offer support, wrap the region with a stretchable bandage.
elevation.
Does arm pain respond well to physical therapy?
Shoulder pain can be effectively relieved with physical therapy exercises. These exercises increase flexibility and range of motion in addition to easing pain. It’s crucial to collaborate with a licensed physical therapist who can create an exercise regimen tailored to your requirements and health.
Are there any forms of therapy that I can do at home?
As instructed by your doctor or therapist, you can carry out a number of therapies at home, including stretching, mild mobilizations, and elevating the affected area.
What if there is an underlying cause for my arm pain?
If this is the case, our skilled medical professionals will identify it and request that you have the necessary tests and examinations to aid in the diagnosis.
Will I receive the right care from the doctor?
Depending on the severity and underlying cause of your pain, the doctor will assess your physical condition, diagnose it, prescribe medicine, and provide appropriate treatment. In order to assist you return to your regular self, the doctor will also assign you simple physical tasks to complete.
What’s causing the ache in my arm?
There are numerous reasons for arm pain, including acute pain and underlying medical conditions like arthritis. Finding the underlying cause is crucial, and your doctor will assist you in doing so.
References
- Ladva, V. (2024e, December 11). Arm muscle pain cause, symptoms, treatment, exercise | Samarpan. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/arm-muscle-pain/
- Hospitals, A., & Askapollo. (2024, October 15). Arm pain. Apollo Hospitals Blog. https://www.apollohospitals.com/health-library/arm-pain/