Biceps Muscle Tightness
What is a Biceps Muscle Tightness?
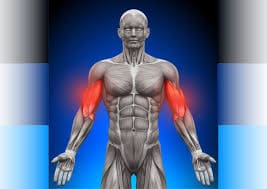
Biceps muscular tightness is defined as a sense of stiffness, discomfort, or tension in the upper arm’s biceps muscles. Tightness in the biceps can be caused by various conditions, limiting your ability to move your arm freely.
Anatomy of Biceps Muscle
- Biceps Muscle:
- The scapula’s long head and the coracoid process’s small head are the two heads.
- Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6, C7) provides innervation.
- Blood flow is via the brachial artery.
Causes of Biceps Muscle Tightness
- Overuse or Exercise
- Muscle Strain or Injury
- Dehydration or Electrolyte Imbalance
- Poor Posture
- Inadequate Stretching
- Tension from Stress
- Muscle Imbalance
Overuse or Exercise: Overworking the biceps with repetitive or intensive exercises like lifting weights, rowing, or pulling motions can cause muscle tightness. This is frequent after performing strenuous arm exercises such as curls or pull-ups.
Muscle Strain or Injury: A strain, tear, or other damage to the biceps muscle (such as a pulled muscle) can cause tightness because the body reacts with inflammation and muscular guarding.
Dehydration or Electrolyte Imbalance: Not remaining hydrated or having low levels of electrolytes such as potassium and magnesium can lead to muscular cramping and tightness, including in the biceps.
Poor Posture: Poor posture can put excessive stress on the biceps and cause muscular stiffness, particularly when sitting for long periods of time or lifting incorrectly.
Tension or Stress: Tight muscles, particularly in the arms and upper body, can be caused by mental stress and tension.
Lack of Stretching or Warm-Up: Having tight muscles might result from improper warming up before exercise or from not stretching.
Symptoms
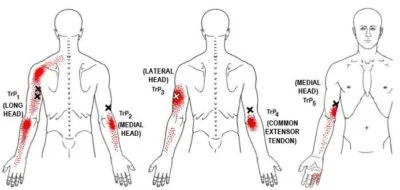
Stiffness: Stress in the arm that makes it difficult to bend or move.
Soreness: A dull pain or ache that usually occurs after working out.
Pain: A muscular tear or strain is one example of an injury that can cause sharp or throbbing pain.
Weakness: A sensation of diminished arm strength that makes lifting or carrying out activities more difficult.
When to See a Doctor
- if rest and self-care don’t relieve the tightness.
- If there is extreme pain, swelling, or bruising.
- if you feel tingling or numbness in the arm, or if you have difficulty using it.
Muscle tightness will usually go away with time and the right care, but it’s a good idea to see a doctor if you’re concerned about an injury or if the tightness doesn’t go away.
Treatment of Biceps Muscle Tightness
Here are a few methods for treating biceps tightness that will help reduce pain and increase range of motion:
- Rest
- Stretching
- Foam Rolling or Massage
- Heat and Cold Therapy
- Hydration and Nutrition
- Over-the-Counter Medications
- Strengthening Exercises
- Posture and Ergonomics
- Compression and Support
Over-the-counter Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help decrease swelling and ease pain if you experience both tightness and pain. Additionally, topical treatments containing arnica or menthol might offer calming relief.
Heat and Cold Therapy:
Cold Therapy: Applying an ice pack wrapped in a towel helps numb the region and decrease inflammation if the tightness is caused by an injury (such as a strain). Apply many times throughout the day for 15 to 20 minutes.
Heat Therapy: Using a heating pad or warm compress might help relax the muscle if the tightness is caused by stress or exhaustion. Apply many times throughout the day for 15 to 20 minutes.
Physical Therapy Treatment
- Manual Therapy
- Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises
- Strengthening Exercises
- Dry Needling or Acupuncture
- Electrical Stimulation
Manual Therapy:
Massage Therapy: To assist in relaxing the biceps and relieve tension or muscular knots, the therapist may employ methods like trigger point release or deep tissue massage. This helps break down any adhesions or scar tissue that could be causing tightness, increases blood flow, and lessens stiffness.
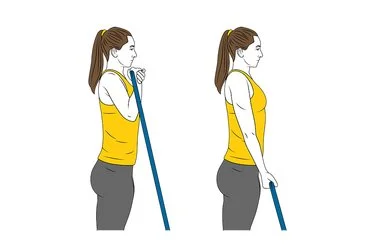
Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises:
Passive Stretching: To increase flexibility and relieve tension, the therapist could gently stretch the biceps. These stretches assist in extending the range of motion (ROM) of the muscle and preventing further muscle fiber shortening.
Active Stretching: The therapist may give you instructions on how to do stretches. The biceps can be stretched, for example, by outstretching the arm and gently pulling back on the hand with the other hand.

Strengthening Exercises:
To relieve biceps stiffness and avoid further muscular strain or damage, strengthening activities are crucial. Some efficient exercises to assist in developing the biceps and associated muscles are included below. They will increase arm strength overall, improve flexibility, and lessen tension.
- Bicep Curls (Dumbbell or Barbell)
- Hammer Curls
- Resistance Band Bicep Curls
- Eccentric Bicep Curls
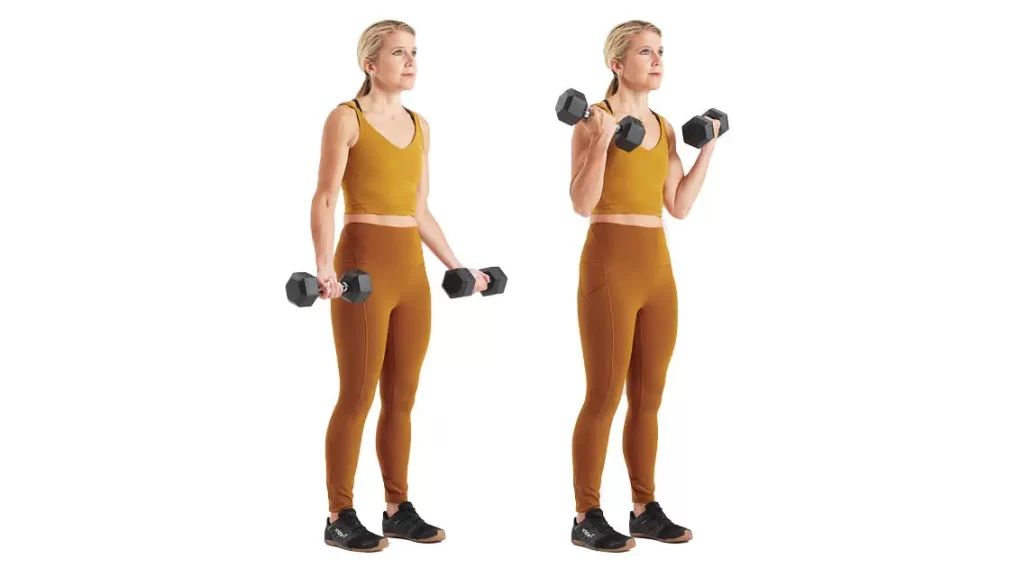
Bicep Curls:
Hold a dumbbell in each hand( or a barbell in both), with your arms completely extended and palms facing onward while standing with your bases shoulder range apart. To activate your biceps, curl the weights upward while maintaining a tight elbow position.
Squeeze your biceps as you pause at the peak, again gradually return the weights to the beginning position. Three sets of ten to twelve repeats.

Hammer Curls:
While standing with your bases shoulder range apart, hold a dumbbell in each hand with the palms towards your trunk (neutral grip). Keeping your elbows in a fixed position, curl the weights toward your shoulders. When the exercise reaches its height, pause and then slowly move the dumbbells back to their starting position.

Eccentric Bicep Curls:
Use dumbbells or a barbell to do a standard bicep curl, but concentrate on reducing the weight gradually over three to five seconds during the eccentric (lowering) phase. Manage the weight’s fall to increase biceps tension. Three sets of six to eight repeats.
Dry Needling or Acupuncture:
Dry Needling: This method involves inserting a tiny needle into the muscle at particular trigger sites. This promotes better blood circulation, eases pain, and releases tense muscles. It works well for biceps muscle tension linked to certain knots or trigger points.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture works similarly to dry needling in that it targets particular sites along meridian lines to ease pain, relax tense muscles, and restore the body’s energy flow.
Electrical Stimulation
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Low-voltage electrical currents are used in this method to assist ease pain and tight muscles. It might assist the muscle relax and offer instant relief.
NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation): This helps to enhance muscular activation and strength, encourage healing, and activate the muscle, particularly after extended periods of weakness or inactivity.
Prevention
You may lower your chance of developing biceps tightness by:
- Warm Up and Cool Down Properly
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles
- Stay Hydrated and Balanced
- Take Regular Breaks
- Maintain Good Posture
Summary
Often brought on by overuse, poor posture, muscular fatigue, or injury, biceps tightness is the result of the biceps muscle becoming rigid, tense, or painful. Repetitive motions, poor lifting technique, dehydration, lack of stretching, or prior muscular strains are common reasons. Treatments for biceps stiffness include strengthening exercises, massage, stretching, and heat therapy.
Physiotherapy can assist by employing methods such as ultrasonography, manual treatment, and targeted strengthening exercises. Proper posture, hydration, warm-up, and rest are all preventive actions. If tightness continues or hurts, it’s crucial to get expert guidance.
FAQ’s
What causes biceps muscle tightness?
Overuse, poor posture, incorrect lifting techniques, muscular exhaustion, dehydration, lack of stretching, and prior muscle injuries are some of the causes of biceps tightness. Additionally, stress, repeated motions, or an underlying injury may be the cause.
Can tightness in the biceps indicate an injury?
Although tightness is frequently the result of overuse or muscular exhaustion, it can also indicate tendinitis, muscle strain, or other ailments. To rule out an injury, it’s critical to get medical help if the tightness is severe, ongoing, or accompanied by pain.
When should I see a doctor or physiotherapist for biceps tightness?
Despite self-care practices, the tightness continues.
You feel excruciating agony, numbness, bruising, or swelling.
The arm is difficult to move or has a restricted range of motion.
Other symptoms like tingling or weakness that accompany the tightness might be signs of nerve involvement.
What are the best exercises for biceps tightness?
Bicep curls, hammer curls, and resistance band curls are exercises that improve strength and decrease stiffness.
Can dehydration cause biceps tightness?
In fact, cramping and stiffness in the muscles, particularly the biceps, can result from dehydration. For muscles to work correctly, they need enough water and electrolytes, and dehydration can make them more prone to tense and painful muscles.