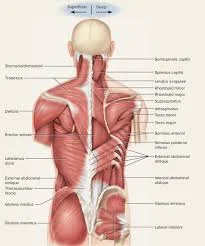
Trigger Points in Trapezius Muscle
A Trigger Point: What Is It?
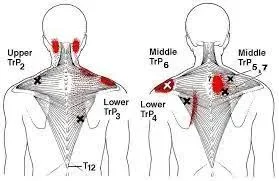
Trigger points in the trapezius muscle are common sources of pain and tension, often affecting the upper back, neck, and shoulders. The trapezius muscle, which spans from the base of the skull down to the mid-back and across to the shoulders, is highly prone to developing these sensitive areas of tight muscle fibers.
A trigger point is a tight band or hypersensitive “knot” in the muscle or fascia. Depending on the muscle, it usually relates to pain in a certain pattern to another part of the body. Latent and active trigger points in the myofascial tissues are two different categories. In addition to causing discomfort, active trigger points restrict the range of motion. Although latent trigger points usually don’t hurt, they can restrict the range of motion and make the affected muscle weak. You will probably have more activated trigger points if you suffer from pain on a regular and severe basis.
What are TTP(Trapezius Trigger Point):
A frequent long-term muscular problem that can affect anybody is trigger points.
The trapezius muscle is where TTP occurs. This is a huge back muscle that runs down the back of your neck, up to your shoulders, and below your shoulder blades.
The elevated regions in your muscle could be palpable. They could look like a knot in your upper back, shoulder, or neck. Touching the trigger points may cause excruciating pain that spreads beyond the local region.
Trigger points can be either latent or active. When you move, active trigger spots hurt. Only when pressure is applied along the elevated portion of the muscle can latent trigger points become painful.
The trapezius muscle’s anatomy:
Origin
occipital bone’s medial region, the superior nuchal line. the external protuberance of the occipital region. nuchae ligamentum. All thoracic vertebrae (T1–12) and the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) have spinous processes and supraspinous ligaments.
Insertion
the lateral third of the clavicle’s posterior edge. medial acromion boundary. prominence on the top border of the crest of the scapular spine.
Action
Pull the shoulder girdle up (elevation) using the upper fibers. Assist in avoiding shoulder girdle depression when a weight is held in the hand or on the shoulder.
Middle fibres: the scapula retracts (adducts).
Lower fibers: depress the scapula, especially when there is resistance, such as when getting out of a chair with your hands.
The scapula is rotated by the upper and lower fibers working together to raise the arm above the head.
Nerve
the auxiliary XI nerve as the motor supply. Proprioception (sensory supply): ventral ramus of cervical nerves C2, 3, and 4.
Why does TTP occur?
TTP happens for a variety of reasons. Among the reasons are:
- trauma-related repetitive motion
- Participating in athletics or exercising
- lack of activity
- bad posture,
- keeping your head up too much, holding your phone to your ear with your shoulder, and sitting on a chair without armrests or back support
- Using inadequate lifting techniques to move big things
- carrying bulky bags,
- backpacks, or purses on one shoulder when suffering from a vitamin shortage
- Having a previous joint issue and not getting enough sleep
What signs of Trapezius Trigger Point are present?
Trigger points are not only painful, but they can also restrict your motor range. You could see that the pain extends across the muscle or is located around the trigger point.
Beyond only your muscles, you could also have trigger point trapezius symptoms, which might include:
- a headache,
- ringing in the ears,
- jaw discomfort,
- tilting of the neck
What is the usual location of TTP?
TTP may develop in a few locations along the shoulder blades, along the tops of the shoulders, and at the back of the neck.
Other muscles may also be affected by trigger point discomfort. Trigger points, for instance, can also develop at the front of the neck, the chest, the area next to the elbows, and the area close to the front and rear of the knees.
When should I visit my physician?
If the pain seems to be becoming worse, interferes with your everyday activities, or makes it difficult for you to participate in sports or regular activity, you might want to consult a doctor about TTP.
Pain or soreness in your upper back, shoulders, or neck may make it difficult for you to feel comfortable, sleep well, or finish activities at work.
To diagnose TTP, your doctor will do a physical examination and enquire about your medical history.
This examination will check for variations in your trapezius muscle, including:
- tightness
- the existence of a twitching nodule
- Additionally, your doctor will enquire about the kind of discomfort you endure.
How do you handle TTP-related pain and discomfort?
TTP can be treated in several ways. These include prescription drugs, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies.
To assist manage the disease, a doctor could advise you to try a variety of strategies. Some of these methods will be covered in the sections that follow.
Drugs
To aid with TTP discomfort, a doctor could provide a sleeping pill, muscle relaxant, or oral painkiller. Your doctor could also suggest a local anesthetic or even a steroid injection if these drugs don’t work.
Changes in lifestyle
- To lessen TTP agony and discomfort, you can try a few different techniques at home.
Applying heat or ice to the affected region is a straightforward method of easing TTP agony.
To rest the trapezius muscle for a few days or weeks, you could also want to change your training regimen or avoid your usual sporting activities.
Pain and discomfort can also be managed by stretching and altering your regular routines. For instance, one study discovered that performing isometric neck exercises three times a day for 15 days, together with improving posture, somewhat reduced TTP discomfort.
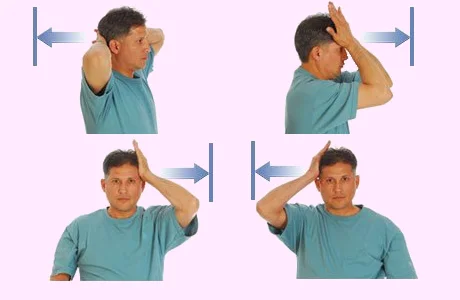
Among the exercises were:
- circling the shoulders
- extending and bending the neck
- rotating the neck
- To stretch the trapezius, you can attempt a variety of activities.
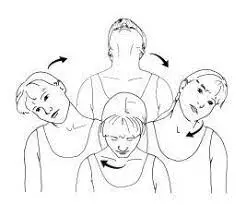
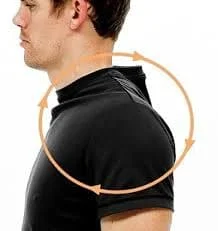
Avoiding rubber cushions, using seats with supportive backs and appropriate armrests, and sitting up straight when using a computer were some ways to enhance posture.
Additionally, the research advised participants to stretch and move around by getting up from their workstations every 20 to 30 minutes.
Complementary and alternative therapies
To treat TTP, you can try several different therapy approaches. These techniques are regarded as complementary therapies if you combine them with painkillers or other medical interventions prescribed by your physician.
Among the alternative therapies are:
- massage
- cupping
- cryotherapy
- acupuncture
- acupressure
- dry needling
Physiotherapy treatment:
Regaining a complete range of motion and motor coordination may benefit from physical therapy that includes mild stretching and exercise. Muscle-strengthening workouts can begin once the trigger points have been removed, promoting the local muscle system’s long-term health. Based on your symptoms and indicators, a physiotherapist can create a strategy to help you feel better.
Treatment for a trapezius muscle trigger point will be more effective if you visit your doctor as soon as symptoms appear and before trigger points are formed. Combinations of massage, trigger point injections, myofascial release treatment, and physical therapy may be required for certain persistent instances of myofascial pain. To control your pain and repair damaged muscles, your healthcare provider may probably combine several different therapies. physical therapy for muscular strengthening, stretching, and relaxation. Your muscular knots and trigger points can benefit from trigger point treatment and myofascial release (MFR) procedures. The fascia that surrounds the muscles is believed to be more aligned with myofascial release. Your muscles’ natural range of motion and circulation may both benefit from this.
Manual pressure release
Manual pressure release is a massage technique that may be useful in treating TTP. Essentially a massage method applies pressure to a trigger point using the thumb or fingertip. This is said to help stretch the muscle and ease discomfort and tension.
Ischemic compression
Ischaemic compression is an additional form of massage. A skilled therapist can apply pressure to the trigger points using a rubber, plastic, or wood instrument. According to one study professional basketball players’ trigger point discomfort was reduced after just one session of this therapy.
Cupping
Another alternative therapy that could help with TTP pain and discomfort is cupping.
China is where this technique first appeared thousands of years ago. To apply pressure to acupuncture sites and alter blood flow, a practitioner employs cups that suction the body.
Ear to shoulder
To extend beyond the shoulder to the ear:
- Take a chair and sit up straight.
- after that tilt your head to the left like you are trying to touch the left shoulder.
- For a more thorough stretch, place the left hand on the head and slowly draw it towards the shoulder.
- Maintain the posture for 20 seconds.
- After releasing the head, similarly extend the right side.
Hug stretch
To perform a stretch hug:
- Get to your feet.
- While stretching the right arm across the chest, hold the left shoulder. On the other side, carry out the opposite activity.
- Put pressure on the left shoulder with the right hand while tilting the head to the right.
- For around 20 seconds, hold the stretch.
- Continue on the opposite side.
Pain control
Cold lasers and low-level light treatment are lasers that trigger the release of hormones that reduce pain. Cold laser, another name for low-level light treatment, exposes the trigger point to near-infrared light.
Therapeutic Ultrasound: Therapeutic ultrasound may help soft tissues damaged by a calf muscle trigger point recover by using sound waves to warm and circulate blood. These devices use a sound-conducting gel on the skin to transfer sound waves into the soft tissue. Muscles may be warmed and relaxed by the sound waves, which also increase blood flow and eliminate scar tissue. There might not be much pain relief. However, if this therapy is performed before stretching, it may lessen stiffness and improve mobility. Using sound waves to pierce soft tissues or muscles is known as pulsed ultrasound. Since this treatment has been effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis pain, you might want to talk to your doctor about it.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, or TENS, is a technique that uses electrodes affixed to your skin to provide low-voltage electric signals to a painful location.
Posture training
Myofascial discomfort can be alleviated by improving posture, especially in the neck muscles. You may avoid overworking any one muscle by performing exercises that strengthen the muscles around the trigger point.
Kinesiotape: Kinesio tapping increases blood flow and elevates the top skin. You may prevent trigger points and tightness in the upper trapezius muscle by performing corrective exercises and stretches at home.
If there is a joint limitation component to the upper trapezius muscle discomfort, chiropractic treatment may help.
What safety measures ought to be taken?
Keep in mind that alternative therapies are approaches that are not included in traditional medical care.
Before attempting any of these treatments, see a physician because some of them might be harmful to your health. Additionally, to guarantee that you’re getting high-quality treatment, make sure you look for services from qualified specialists.
Home advice
The following remedies are available for use at home:
- As in a heating pad, heat. Ice or cold packs help some individuals.
- Work out. In particular, aerobic workouts to increase oxygen delivery to the muscles, stretching exercises to assist muscles stretching, and weight-bearing exercises to help strengthen muscles.
- NSAIDs like naproxen or ibuprofen, or over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen. If you are using NSAIDs or analgesics that your doctor has recommended, avoid taking these medications.
- Breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga to stretch, reduce stress, and relax the muscles are examples of relaxation techniques.
- Make dietary adjustments to stay away from foods that are known to trigger inflammation.
In warm water, soaking. - massages.
Several reasons determine how quickly this trigger point trapezius resolves, including:
- Your general health.
- Diet.
- Amount and quality of sleep.
If you have this trapezius trigger point, take care of yourself. Maintaining your physical well-being via self-care practices may help you focus on managing your discomfort.
Takeaway
TTP may be the source of your back, shoulders, and neck pain. For instance, a physician could suggest a mix of prescription drugs, lifestyle changes, and complementary therapies.
Make sure to talk to your doctor about any possible side effects from TTP therapy.
FAQs
Does trapezius discomfort have a pressure point?
Usually the highest position on the upper trapezius muscle, this pressure point is situated halfway between the base of the neck and the shoulder.
What signs of upper trapezius trigger points are present?
Typical Trapezius Trigger Point Indications
Back of Shoulder Pain.
Mid-Thoracic Back Pain.
Upper Thoracic Back Pain.
Back of Head Pain.
Back of Neck Pain.
Cheek Pain (like Sinusitis)
Headaches or Migraines.
Temple and Eyebrow Pain.
How can tense trapezius muscles be released?
Simple stretches or yoga postures like Thread the Needle, Eagle, Child’s Pose, and Cat-Cow can help relieve tight traps. Naturally looser trap muscles might also result from exercising to reduce physical and emotional stress and maintain good posture throughout the day.
How should the trapezius muscle be treated?
putting cold or heat on the affected region.
stretching your back or neck gently.
either dry needling or manual therapy.
physical treatment.
What is the tight trapezius pressure point?
It is found in the upper trapezius muscle tissue, which is the highest part of the shoulder.
References
- Stelter, G. (2018, September 29). Stretches to Loosen Your Trapezius Muscles. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/fitness-exercise/trapezius-stretches
- Hackenberger, K. (2022, September 29). Trigger Points: Techniques to Release Knots in Your Shoulder – Alaska Hand Rehabilitation. Alaska Hand Rehabilitation. https://akhandrehab.com/blog/trigger-points/
- Winer, J. (2022, January 18). Trigger Point Therapy – Treating the Trapezius Muscle. Niel Asher Education. https://nielasher.com/en-in/blogs/video-blog/trigger-point-therapy-treating-the-trapezius-muscle?srsltid=AfmBOoodmhxqmh5hpfsLpsTgE83L5gAny658utygkMlCN6w5n7s1citK
- De Pietro Crt, M. (2023, November 10). What is the trapezius (traps) muscle? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324251#stretches
- Dr.Esha Patel. (2023, January 26). Trigger point trapezius – Cause, Symptoms, Treatment. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/trigger-point-trapezius/