Salt Therapy
Introduction
Halotherapy, often known as salt therapy, is breathing in air containing microscopic salt particles to enhance one’s breathing.
Halotherapy is frequently administered in spa-like salt chambers. This therapy can also help you relax and manage skin issues and allergies. Salt therapy is a mild approach to treating a variety of diseases that involves breathing pharmaceutical-grade dry salt in a comfortable and regulated atmosphere.
As you relax, a device called a halogenerator releases tiny salt particles into the air throughout the room. You will inhale these small particles deep into your airways and lungs, as well as on your skin.
This therapy is safe for newborns, children, and adults and can adequately relieve a variety of skin, respiratory, and lifestyle disorders.
Halotherapy is a sort of salt therapy that may be beneficial for respiratory disorders. Many of these claims, however, are unsupported by data, and there have been complaints of negative effects. More study on the advantages and risks is required.
Salt treatments have a long history of usage in several regions of the world, including Eastern Europe, although they are less popular in the United States.
This page discusses the potential advantages of halotherapy, what the research shows, and whether or not there are any negative effects.
Halotherapy is an alternative treatment in which patients breathe saltwater air. Some people believe it helps cure respiratory diseases like asthma, chronic bronchitis, and allergies. Others say it can also:
Benefits of smoking include relief from symptoms like coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing, as well as treatment for sadness and anxiety. Additionally, it can treat some skin disorders including psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
Halotherapy dates back to the medieval age. However, experts have just lately begun investigating its possible advantages.
History of salt therapy
Salt caverns abound in Eastern Europe, offering a sought-after location for indulging in halotherapy. However, this is less prevalent in the United States.
A German doctor also discovered that spending time in salt caverns positively impacts respiratory health. Salt chambers were popular kinds of therapy during the 1950s and 1960s.
Polish salt miners developed a modern version of halotherapy that mimics a salt cave environment with controlled temperature and humidity. Even after spending lengthy hours toiling in the mines, Polish miners maintained robust health and were entirely devoid of respiratory problems. They were unlikely to catch the typical colds and coughs.
According to research, miners’ exposure to salty air helped prevent infection and allergens in their lungs. Eastern European salt mines and caves eventually became attractive tourist sites. Visitors from all over the world come to inhale the salty air and relieve their lung issues.
How would it work?
Advocates of halotherapy argue that it can
- Improve lung function.
- Remove pollens, poisons, and viruses from the lungs and nasal passages.
- Reduce inflammation.
- Clean the nasal canals and sinuses.
- alleviate specific skin problems.
- Moreover, there is scarce scientific data to support these claims There are limited large-scale investigations in this field.
Types of Halotherapy
Passive salt rooms feature reduced salt concentrations compared to active salt rooms. These chambers are typically utilized for relaxation and meditation purposes, as opposed to halotherapy.
The salt room is now active. This chamber has a halo generator, which is a machine that adds salt. The device converts the salt into microscopic particles that circulate the space.
Passive salt room. This sort of room lacks a mechanism for breaking down salt. Instead, the space is filled with various salts, including Himalayan salt. It is a copy of a salt cave, with manual needed temperature and humidity.
Passive salt rooms typically have lower salt concentrations compared to active salt rooms. These settings are typically used for relaxation and meditation, rather than being focused mainly on halotherapy.
Salt treatment has two kinds
Dry salt treatment
Dry salt treatment. This form is referred to as halotherapy. It is performed in active salt rooms with the assistance of a halo generator. This permits microscopic dry salt particles to move through the air and into the lungs and skin. This dry therapy typically takes place in artificial “salt caves” that lack humidity, with sessions lasting around 30 to 45 minutes.
A halo generator is a device that grinds salt into small particles and then releases them into the room’s air. The inhalation of salt particles is believed to help remove allergens and toxins from the respiratory system. Advocates argue that this procedure helps break up mucus and reduce inflammation, ultimately leading to clearer airways.
Salt particles absorb germs and pollutants from the skin, which can cause various skin disorders. Salt is also thought to form negative ions. This may boost serotonin levels, which contribute to happiness. Many individuals use Himalayan salt lamps to benefit from negative ions in their homes. However, there is little evidence that these lights provide any benefits beyond creating ambiance.
Wet salt treatment. This comprises swimming in mineral-rich salt water, gargling, ingesting, or transferring salt water through the nasal canal.
Halotherapy is also performed using a salt and water solution. Wet approaches to halotherapy include the following: There are several ways to use salt water: gargling, drinking, bathing, nasal irrigation, and flotation tanks.
What do studies on halotherapy say?
Science has failed to catch up with the halotherapy hoopla. While some studies have shown potential, the majority of research remains equivocal or inconsistent.
Here are some of the research findings:
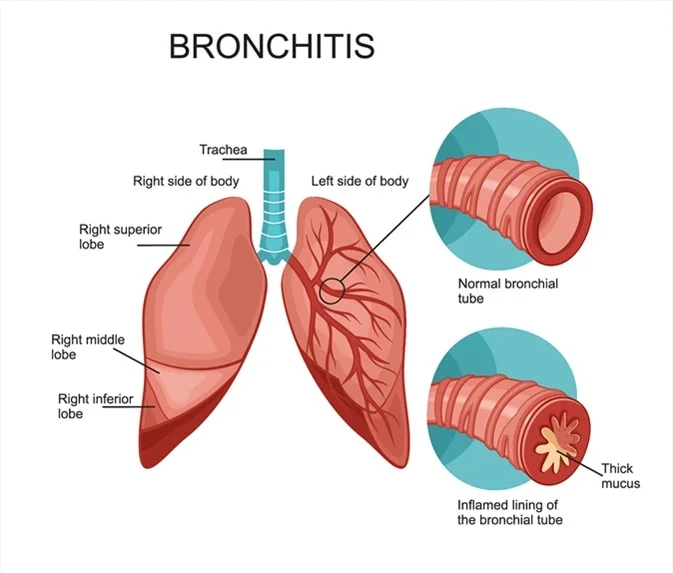
In a 2007 research, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) reported fewer symptoms and an improved standard of life following halotherapy. However, the Lung Institute does not promote it as medical recommendations have not been developed. A 2014 review found that the majority of halotherapy trials for COPD were faulty. A 2013 research found that halotherapy did not enhance lung function tests or quality of life in persons with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. This sickness makes it an ailment to clear mucus from the lungs.
According to a 2014 study, halotherapy helps improve inflammation and allergens in those with bronchial asthma or chronic bronchitis. Almost all research on halotherapy to exert depression or skin diseases is anecdotal, which means that it is based on an individual’s personal experiences.
What makes salt so effective?
Dry salt is extremely absorbent and contains anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Inhaling salt thins and liquefies mucus, facilitating the removal of germs, debris, and contaminants.
Dry salt particles are quite important in boosting your body’s cilia activity. Cilia keep our airways clean of mucous and debris, allowing us to breathe comfortably. However, the addition of salt expedites this process. However, with the addition of salt, this process is expedited. Consider salt as a toothbrush for your airways, cleaning mucous, grime, and bacteria.
Dry salt can absorb pollutants, adjust pH, and stimulate the growth of ‘healthy’ microorganisms on the skin. It enhances skin protection by lowering irritation and promoting natural exfoliation and regeneration.
Active
Active dry salt treatment is easy to grasp. Pure sodium chloride (NaCl), or salt, exhibits three major features such as:
- Salt is extremely absorbent, especially when dry.
- Salt is anti-bacterial.
- Salt is anti-inflammatory.
Dry salt is ground into micro-sized particles in a halogenerator before being spread in a confined space, such as a room or chamber.
Dry sodium chloride particles are breathed into the respiratory system as they pass through the salt chamber. It may also assist in decreasing inflammation and expanding the airways. Pure NaCl particles have a micro-sized crystal structure that effectively removes harmful substances.
This forms the basis of how dry salt therapy can help individuals with allergies, asthma, bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, COPD, and other respiratory disorders. The tiny particles may penetrate beneath the skin’s surface and absorb moisture into it. The bigger salt particles settle on the skin and absorb any germs or other substances. The dry salt promotes cell regeneration and enhances skin firmness.
A dry salt room must maintain precise temperature, humidity levels, and adequate ventilation to guarantee the efficacy of the salt therapy and provide a revitalizing environment for the user.
Passive
Passive salt chambers were designed to replicate natural salt caverns found throughout Europe. Salt rooms are climate-controlled spaces with extensive salt décor. These rooms may have walls, ceilings, and floors lined with salts from the Dead Sea, Himalayan, Rock, or other sources. Modern passive salt chambers resemble natural salt caverns but lack the same salt air particles due to the absence of direct mining activity(crushing, grinding, chiseling, etc.) to produce salt particles in the air.
Adding salt to a restricted place can improve air quality and modify energy frequencies. Salt dust can be caused by disturbances on the floor, such as people walking over it. Heating Himalayan salt, similar to bulb-heated salt lamps is said to produce negative ions that counteract the positive ions caused by technology and pollution.
Modern research requires precise dispersion of pure sodium chloride particles at specific concentration levels over time, which passive dry salt rooms do not offer.
Is it beneficial for any respiratory conditions?
If you experience difficulty breathing, halotherapy may help improve your condition. Several websites suggest that salt rooms can assist address:
- Asthma.
- Bronchitis.
- Chronic cough.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary lung disease (COPD).
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Respiratory allergies.
Fight infection
The concept of using salt to clean mucus out of your sinuses isn’t very novel. Saline sprays and rinses are commonly used to clear the nose and sinuses and improve breathing.
But does breathing in dry salt provide the same result? The assertion cannot be verified due to insufficient investigation.
Healthier skin
Allowing salt-saturated air to flow over your body can enhance skin moisture, resulting in a smoother and less splotchy appearance. Many people discuss regulating pH levels and treating eczema.
Stress reduction
In a softly illuminated space filled with soothing music and salt, you can find the perfect ambiance for meditation. Here, you can truly relax your nervous system and alleviate tension. However, removing the salt component would result in the same conclusion. You can succeed in getting the same effect without it.
Some individuals feel that salt treatments are beneficial for respiratory disorders like asthma. The next sections will provide a more in-depth overview of extant research.
Asthma
A 2014 research on rats revealed that salt treatment might assist with asthma. Researchers observed that exposing rats to a speleotherapy-like environment improved their respiratory cells. Nevertheless, at this point in time, investigations in this field are fairly restricted.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
According to certain studies, halotherapy could potentially offer benefits in managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A 2014 analysis revealed no evidence that halotherapy improves COPD symptoms.
Bronchiectasis
In a 2013 clinical research, 20 persons with bronchiectasis were treated with a salt spray for two months.
The experiment revealed no benefits to utilizing the salt spray.
However, 65% of the patients were pleased with halotherapy and intended to continue using it. The salt spray may not cure symptoms, but it can enhance relaxation and well-being.
Adenotonsillar syndrome
In a 2013 experiment, 45 individuals with adenotonsillar syndrome received 10 halotherapy treatments or a placebo.
After the experiment, those who received halotherapy reported modest relief in their symptoms.
Other conditions.
The STA claims that dry salt therapy has antimicrobial qualities that could be helpful with COVID-19. Bacteria do not cause COVID-19. To manage COVID-19, individuals should adhere to the guidelines provided by the CDC.
Halotherapy employs microscopic salt particles to regenerate skin cells and prevent aging and infection.
- Acne and rosacea
- Skin allergies
- Rash
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
- Fungal infections such as onychomycosis
- Wrinkles and signs of aging skin
Alternative salt therapies
Wet salt therapy is an alternate method of using salt to treat specific health concerns. This involves the usage of:
- saline solutions
- Nebulizers
- salt baths
- salt scrubs
- gargling solutions
- net pots
- exfoliation
- flotation tanks
Some individuals use wet salt therapy to help with respiratory issues like the common cold. Some utilize it for cosmetic treatments and skin wellness. The therapy encourages relaxation and general well-being.
Risks of Halotherapy
Halotherapy might have certain negative effects. You may experience coughing and increased mucus output as your nasal passages clear. You may occasionally get skin irritation, conjunctivitis, or pink eye.
Avoid using halotherapy if you have:
- Hyperthyroidism
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Tuberculosis
- Heart problems
- Respiratory failure
- Blood disorders like anemia, hemophilia, or clotting
- Infectious diseases
- Fever
- Open wounds
- Malignant diseases such as cancer
- Claustrophobia
Halotherapy is most likely safe for the majority of people, although no trials have been conducted to confirm this. Furthermore, halotherapy is often administered in a spa or wellness center, which lacks certified medical specialists to address crises. Consider this in mind as you consider the advantages and disadvantages of halotherapy.
Although halotherapy is intended to relieve asthma symptoms, it may also potentially irritate or constrict the airways in some individuals.
This may worsen coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Some patients have headaches during halotherapy.
Halotherapy is a complementary treatment that can be used alongside any medications you are currently taking. Do not discontinue any drugs without consulting with your doctor.
supporters of halotherapy argue that it is safe for both children and pregnant women. On the other hand, there is little evidence to support this claim. A 2008 study found that breathing a 3% saline solution is a safe and efficient therapy for babies with bronchiolitis. However, there is little uniformity across halotherapy centers. The amount of salt supplied might vary significantly.
Consult your doctor before considering halotherapy. They can assess your medical history and current health to see if it’s a suitable alternative.
You may cough more. All of those salt particles in the air may cause you to cough a little more. Many patients reported coughing excessively after going.
Summary
Halotherapy may be a soothing spa treatment, but there is no proof of its effectiveness. Research shows it might help with respiratory issues and depression. Most physicians remain unconvinced. However, if you’re thinking about trying it, it’s essential to consult your doctor beforehand. Follow up with them if you notice any new problems after using it.
Halotherapy may assist with some respiratory problems, but current research is limited and inconsistent. There are some possible adverse effects, such as a cough. Halotherapy, while not proven medically beneficial, can be calming.
Halotherapy practitioners are typically not medically trained. Consult a doctor before using halotherapy to avoid problems and negative effects.
FAQs
What is salt therapy used for?
What is Halotherapy? Halotherapy, often known as salt therapy, improves breathing by inhaling air containing microscopic salt particles. Halotherapy is widely used as a treatment for lung conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. Halotherapy is typically provided in salt chambers that resemble spa environments.
How do I do salt therapy at home?
At-Home Salt Therapy Options
Use a saline nasal spray or a saline solution that is evaporated into the air and inhaled.
For nasal irrigation, use a neti pot.
Gargle with salt water.
Saltwater Flush.
Soak in a salt bath.
Use a detox dome.
What to expect after salt therapy?
After the session
In general, you should anticipate feeling lighter and more energized, as if you’ve entered a relaxed state of ecstasy. To maintain the advantages of salt treatment, it’s important to establish a consistent habit.
How many sessions of salt therapy?
How many sessions do I need? Each experience is unique and depends on the severity of your disease. 1 to 10 sessions can effectively treat colds, flu, ear infections, and other brief respiratory discomforts.
Is salt therapy good for the skin?
Salt treatment is beneficial for treating a variety of skin diseases. The suggested treatment differs based on the ailment being treated. Acne therapy for kids and adults may be as simple as a facial.
What is the best salt for salt therapy?
To get the finest effects from salt treatment, utilize real rock salt. Although excessive salt consumption can be harmful, salt treatment involves inhaling salt particles that only reach the respiratory system rather than the digestive tract.
References
- What Is Halotherapy? (2023, October 11). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/balance/what-is-halotherapy
- What is Salt Therapy? – Salts of the Earth. (2021, August 15). Salts of the Earth.https:/saltsoftheearth.com.au/what-is-salt-therapy/
- Do Salt Rooms Offer Health Benefits? Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/salt-cave-benefits
- What are the benefits and risks of halotherapy? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/halotherapy
- Does Halotherapy Work? Healthline. https:/www.healthline.com/health/halotherapy
- the principles and benefits of halotherapy (salt therapy)| Salt Therapy Association (n.d.). Salt Therapy Association.