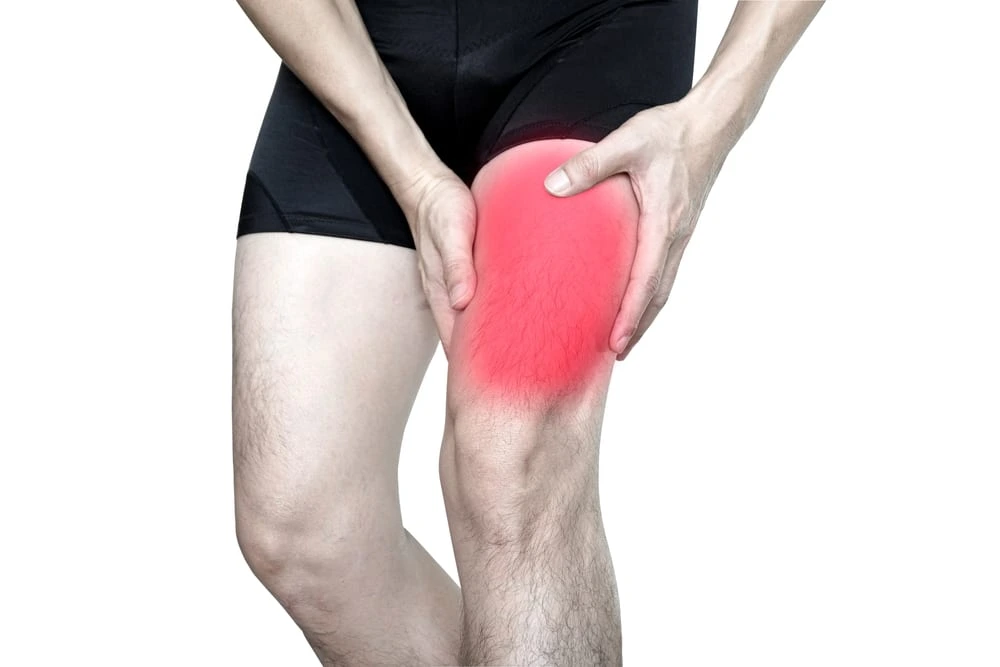
Quadriceps Muscle Pain
Quadriceps muscle pain can be caused by numerous factors, such as overuse, strain, direct trauma, muscular imbalances, and underlying medical disorders. Athletes are more prone to quadriceps muscle injuries, especially those participating in sports that need fast direction changes or repetitive leg motions.
Introduction
- The quadriceps muscles comprise the four front leg muscles. the majority of the anterior thigh is made up of this muscle group, which is essential for knee extension during activities including running, jumping, squatting, and ascending stairs.
- Furthermore, those who perform exercises like weightlifting or extended sitting that put an excessive amount of strain on their quadriceps may also feel pain or discomfort in this muscle area.
- A variety of injuries to the quadriceps muscle might cause pain in that region.
Anatomy
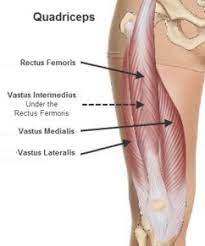
The quadriceps muscles group comprises four muscles:
Rectus femoris: is the quadriceps muscle that is the most superficial.
Vastus lateralis: is on the lateral side.
Vastus intermedius: In the center of the leg.
Vastus medialis: is situated on the thigh’s inside side.
- The quadriceps muscles link together at the knee, in order to form the quadriceps tendon, also known as the ligamentum patellae.
Origin and insertion:
Rectus Femoris: anterior inferior iliac spine.
Vastus Medialis: The medial supracondylar line and the medial intermuscular septum are the two structures located on the medial side of the femur that comprise this structure.
Vastus Intermedius: The vastus intermedius originates from the front and lateral sides of the femur’s bone.
Vastus Lateralis:
Origin: Greater trochanter (proximal attachments).
Insertion: over tibial bone and patella bone.
Nerve Supply
The femoral nerve(L2, L3, L4).
Quadriceps Muscles Function
- Here are a few instances of workouts that focus on the quadriceps muscles:
- Walking: helps to prevent excessive flexion of the knee while walking.
- All four muscles contract statically when standing on one leg to provide stability.
- Stepping Activities: like climbing stairs
- Squats and Patella Control: When knee extension reaches its peak, the vastus medialis is most active, regulating the patella’s mobility.
- Kicking A Ball: Rectus femoris are mostly used in this activity.
- Quadriceps muscle pain can be caused by numerous factors, such as overuse, strain, direct trauma, muscular imbalances, and underlying medical disorders. Athletes are more prone to quadriceps muscle injuries, especially those participating in sports that need fast direction changes or repetitive leg motions.
- In addition to occurring suddenly (quadriceps strain), quadriceps pain can also develop gradually and for no obvious reason. Participating in sports and active activities will worsen the pain.
- You will develop bad biomechanics or a poor gait when walking or running, which will lead to chronic pain, a stiff, tight lower back, and hips. Maintaining this “bad habit” may cause your quadriceps muscle to become more irritated, which will prolong and possibly worsen your pain.
Causes of Quadriceps muscle Pain
Injuries from overuse: Overuse difficulties can occur when someone exercises without warming up or overuses a muscle in or around the thigh.
- The primary indicator and reliable indicator of an overuse injury is pain after vigorous physical activity or other physical exertion. It could pain one or both thighs.
- As time passes, it usually gets worse.
Muscle injuries:
- The upper part of the leg is made of big muscles, if pain is present in this area, it is probably a muscle injury.
Muscle sprains and strains
- In our body many tendons, ligaments, and muscles can become strained or sprained.
- muscle strains are classified into grades.
- Grade 1 strains =Extend the muscles, not tear them.
Grade 2 strains =Involve more severe harm to a full muscle that is partially pulled.
Grade 3 strains = muscle tears entirely
Contusion/bruise:
- Quadriceps muscle discomfort is most commonly caused by a bruise or contusion to the anterior thigh, which weakens and destroys a section of the blood vessels inside the muscle.
Tendinitis:
- Patellar tendonitis can also result from pain in the quadriceps muscles. Inflammation under the patella, at the knee joint level, is seen in this disorder.
- It is characterized by a persistent degeneration of the quadriceps tendon, where muscle fibers change into tendons immediately above the patella or kneecap.
Compartment syndrome
- Compression inside the compartment raises the quadriceps muscle’s pressure above blood pressure and prevents the heart from pumping blood with high oxygen content to the muscular tissue, which leads to significant bleeding into the quadriceps muscle.
Ruptured Tendons
- This usually happens after a fall where the foot is planted and hands are trying to break the landing by gripping the thigh.
- The torn ends are firmly sutured after surgery, allowing for gradual recovery and protected loading.
- When anatomical repair is performed before retraction and scarring, excellent results are achieved. Athletes can eventually resume sports after fully recovering their strength and flexibility with timely treatment.
Sedentary lifestyle
- Chronic pain can be caused by muscular injury from either overusing one’s muscles or not exercising enough. Extended periods of sitting can strain the hips, legs, and other supporting musculature. Generalized muscle discomfort can also be caused by muscular weakening brought on by inactivity.
- Individuals with sedentary lifestyles who experience discomfort in their upper thighs may also experience pain throughout their body. Some persons with this kind of pain may have broad chronic pain, and the pain may move or alter in intensity over time.
Other :
- Chronic conditions
- Pain in the upper leg can be a result of several chronic illnesses. Chronic, all-over discomfort at particular pressure locations is experienced by those who have fibromyalgia Trusted Source. Ankle and rear upper thigh discomfort are common locations for leg pain.
- Thigh pain is one of the body parts affected by a variety of arthritis kinds. Although it can spread either up or down, osteoarthritis pain is typically localized in the hip and knee joints.
Blood clots
- Another source of quadriceps pain could be a blood clot in a blood vessel. Often known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), this painful condition could be severe if it converts into emboli.
- Individuals who experience prolonged periods of inactivity, smoke, have poor circulation, have cardiovascular disease, are pregnant, or are overweight are more likely to develop deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Signs and Symptoms of Quadriceps Muscle Pain
- Pain in the front leg, soreness, or sharp pain that gets worse with movement and goes away with rest.
- Pain is from moderate to severe and you may experience a throbbing discomfort, walking pain, especially on hills or inclines, and soreness while trying to sit up straight
Muscle Weakness
- weakness is seen in the quadriceps muscle.
Joint Stiffness
- It feels that the muscles in your thighs are tense.
- Stiffness that subsides with movement after sitting or being inactive
Swelling & Bruising
- Bruising, puffiness, and swelling are possible, particularly in cases of contusions or strains.
- Bruises may initially appear as a colored red, purplish, or black-and-blue skin coloration
Tenderness
- The discomfort experienced when bending one’s knee against opposition when sitting.
Difficulty inactivity
- Antalgic gait (limping), changed walking biomechanics, avoiding stairs, and squatting posture
Popping
- Pop or snap is present.
Poor Movement Patterns
- Faulty biomechanics of jumping and running.
Risk factors
Overuse: Sports like basketball, volleyball, soccer, tennis, and track and field events that require sprinting, jumping, and sharp changes in speed put more strain on the quadriceps.
Muscular Imbalances: The quadriceps are under additional strain due to tight hip flexors and hamstrings.
Weak gluteal preventing appropriate hip extension assistance
Trauma: The quadriceps muscles are immediately harmed by falls, accidents, or contusions.
Age: Over 40 years of age, patellar tendinopathy is more common, and tissue elasticity loss is associated with aging.
Other Factors
- Overweight or obese
- Vitamin/mineral deficiencies
- Autoimmune disorders
- Metabolic issues like diabetes.
- The greatest avoidable dangers are related to poor movement, overuse, and incorrect strength training.
pain while walking or after walking.
Your pain increases. - After treating your symptoms at home for a few days, they don’t go away.
Your varicose veins are quite painful.
Diagnosis
- A comprehensive history will be taken by the health care provider (a physician or therapist) prior to doing a physical examination.
- Part of the discomfort is explained by certain diagnoses made in the clinic, but other problems need to be recorded.
Imaging studies
- X-rays: Examining the anterior thigh aids in detecting any related fractures in the patella or femur.
An X-ray will also reveal a bony growth that develops inside the muscle if Myositis Ossificans is present. - In certain cases, an MRI may be required for a quadriceps/patellar tendon integrity diagnosis.
- blood examinations – The measurement of creatine phosphokinase, or CPK, levels are used to diagnose major muscle injury.
History
- Encouraging harm or excess trouble going up or down stairs Playing sports.
- Additional health-related factors.
Physical Examination
A comprehensive assessment consists of:
- Feeling for soreness and edema
- examination of the range of motion
- Manual quadriceps muscle testing
Evaluating the walking pattern
Special tests (patellar grind, for example)
Treatment Plan for Quadriceps Muscle Pain
Medications
- Oral NSAIDs can be used.
- Acetaminophen is used for minor strains of the quadriceps.
- Anti-inflammatory topicals reduce the symptoms of tendonitisChronic tendinopathy may be treated with PRP or cortisone injections.
For acute phase
Initially following a quadriceps contusion, strain, or tendon injury, treatment focuses on the P.R.I.C.E. protocol –
P- Protection
R- Rest
I- Ice for cooling
C- Contraction tapping and splinting
E- Elevation
the P. R.I.C.E approach
PROTECTION: Preserving the damaged area safe from further harm and movement is crucial. By doing this, excessive stress can delay the healing process or result in more harm intended to be avoided.
Rest: You need to stop or change the activity that may have caused the pain. Any activity that could put stress on the affected area should be avoided. This will lessen blood flow to the area and prevent more damage from happening.
Ice: Cold compresses can help in reducing swelling. Using ice for ten to fifteen minutes each day will help in reducing swelling.
Compression: Apply an elastic medical bandage on the thigh to reduce swelling and manage painElevate: The goal of elevating and supporting the damaged body part is to reduce blood pressure, which in turn stops bleeding. Additionally, since gravity is now helping, it promotes lymphatic and venous drainage.
Role of Physiotherapy in quadriceps Muscle Pain:
- Your pain is initially reduced by the therapist using manual treatment and electrotherapy.
- Then, they meticulously create a program specifically for you, taking into account all of your objectives and needs.
GOALS FOR TREATMENT:
- Reduce muscle pain
- Reduce muscle swelling
- Increases muscle strength
- Improve joint’s total range of motion
- Restore the patient’s confidence
- Restore patients’ full functional activity
Phase – 1
PRICE PROTOCAL CONTINUE
Electrotherapy
- Pain-reducing modalities SWD (short wave diathermy) TENS & IFC
- In the event of any tender spots or edema, US [ultrasound] is used.
Heat Therapy
- Heat therapy can be beneficial in relieving discomfort and relaxing the affected area’s muscles. Heat-resistant towels or packs work well for this.
- Cryotherapy can help lessen swelling and inflammation by using ice packs and giving the affected area cold water baths.
TENS
- TENS is helpful in relieving pain.
Massage
- increase blood circulation to the muscle.
- A physiotherapist can target certain sore spots with a variety of treatments, including trigger points or deep tissue massage.
Exercises for quadriceps pain
Stretching exercises for quadriceps muscle pain:
Importance Quadriceps muscle Stretch
- A comprehensive post-workout stretch session is essential if you want to maximize the effects of your exercise, no matter whether you’re preparing for an hour of heavy leg activity.
- Dynamic stretches before a boxing match also help to improve your muscles’ flexibility and range of motion, which will help you move around your opponent more deftly and deliver blows with more power.
- Quadriceps helps to increase knee ROM, Each time your knee bends and straightens, your quadriceps are worked.
- Nearly every leg movement involves your quadriceps; they collaborate with other muscles like the hamstrings and glutes to provide effective running, jumping, and balance.
- Some common exercises for the quadriceps are lunges, leg presses, and squats. Any workout that stimulates the fast- or slow-twitch muscle fibers in your leg muscles is generally considered a quadriceps exercise.
Standing Quadriceps Stretch
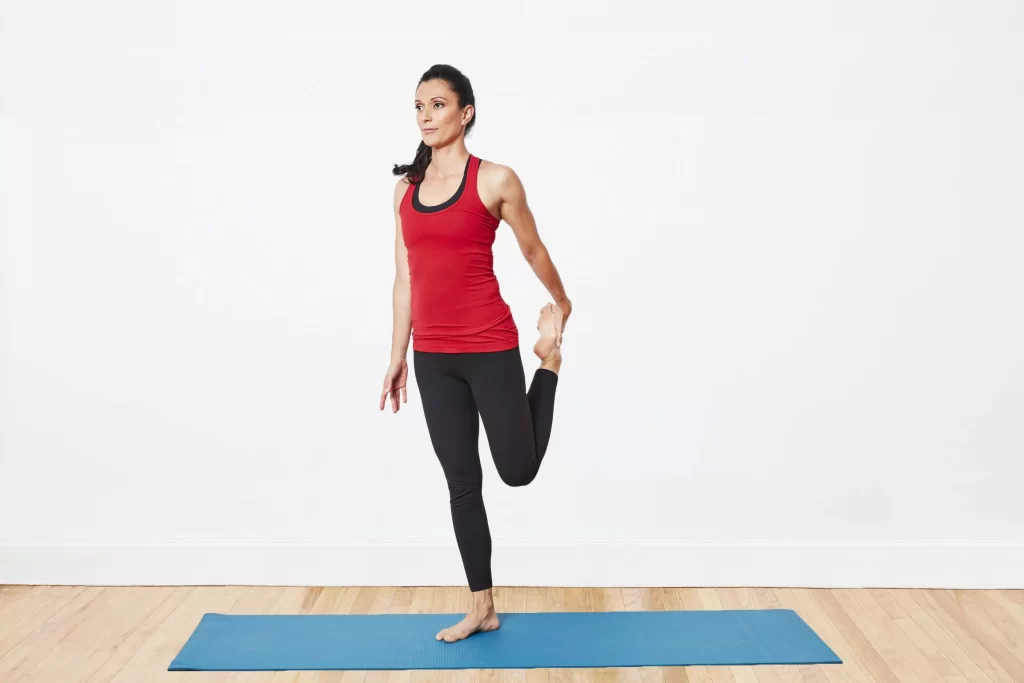

- It’s something you can do before a running activity, at the gym, or even at home. The standing quad stretch is something you can do if you can locate a spot to stand.
How to do it is as follows:
- To help with balance while standing, grab on the floor or chair back.
- now you need to hold your lower foot to move it towards your buttocks
- Hold the same position for thirty seconds.
- Go back to your upright position.
- Repetition:- 4-5 times on both leg
Side-Lying Quadricep Stretch

- You can pay more attention to the stretch in your quads when you’re on the floor in a supported position.
- To extend your quadriceps, try this:
- Turn over on your side.
- hold your ankle as shown in the picture.
- Keep your position for thirty seconds.
- Return to your initial position.
- Repetition: 3 to 5 times
Prone Quadricep Stretch
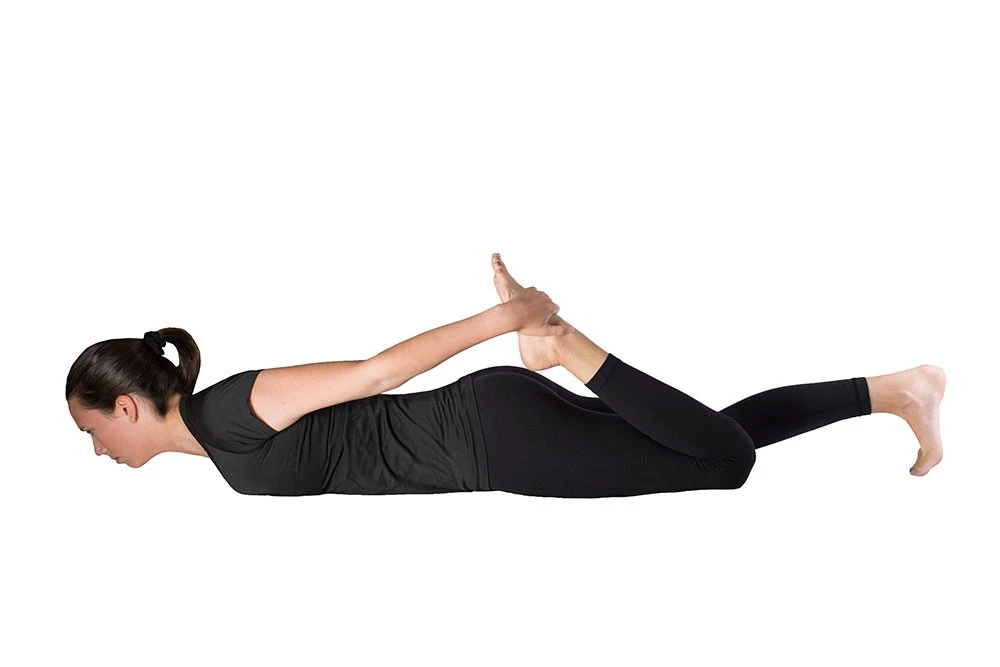

- Stretching your quadriceps is another benefit of lying on your stomach.In this posture, the floor stabilizes your pelvis to minimize slipping and enhance flexibility.
- To stretch your quadriceps while prone:
- Place yourself on your stomach.
- As far as possible, flex your knee back. hold from your lower leg.
- Hold your position for thirty seconds. Go back to where you were before. Proceed through each leg’s steps four to five times.
- In case when you are facing difficulty in performing this exercise you can use a towel as an eg. Even if you have trouble reaching your ankle, this might still help you get a good stretch in your quadriceps.
Kneeling Quad Stretch
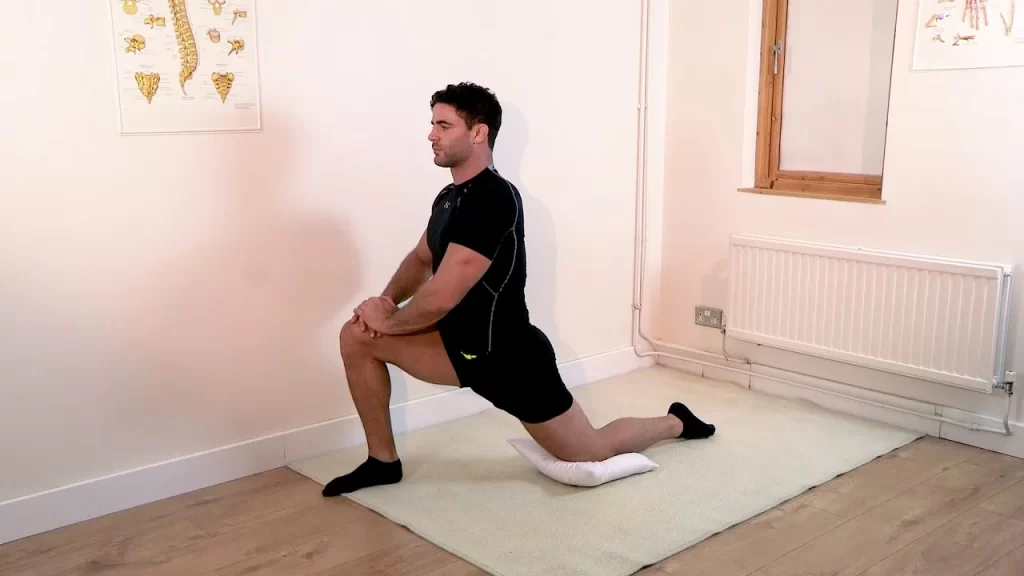

- In order to extend your quadriceps while maintaining a neutral hip and pelvic alignment, try this more difficult stretch.
- or the quad stretch while kneeling.
- Put your left knee down.
- Point your right leg in front.
- Stretch your quadriceps as you bend forward while maintaining a straight upper torso.
- For 30 seconds, hold on.
- Repetition: 3-4 times on both leg
Crescent Pose / High Lunge

- Maintain a wide at the hips spacing between your legs while standing erect on a mat. Put your right foot forward. To drop into a lunge, bend your left leg while maintaining a square hip and forward posture.
- Lean slowly forward from your left knee.
- Take a deep breath, raise your arms above your head, and maintain a straight posture with your palms facing each other.
- Sensation along the length of your left quad.After holding for a few long breaths, switch sides.
Pigeon pose

- Adopt the posture that you see in the picture.
- Raise your right leg such that the outside of your knee is directly behind your wrist. put your foot close to your hand as shown in the picture, and your lower leg should be resting on the floor.
- As you bring your upper body down toward the mat, notice how deeply your thighs and hips are stretched.
- Continue on the opposite side.
Strengthing exercise for quadriceps
Static Quadriceps Exercise (SQE):
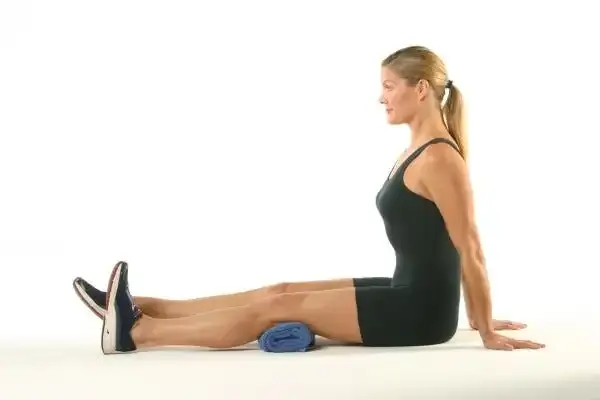

- Position for exercise: Sitting on the floor.
- your right knee and press it down.
- As directed, hold for 5 to 10 seconds. Then unwind.
- Do as directed, or repeat ten times.
- Repetition : 3 times per day
Straight Leg Raises
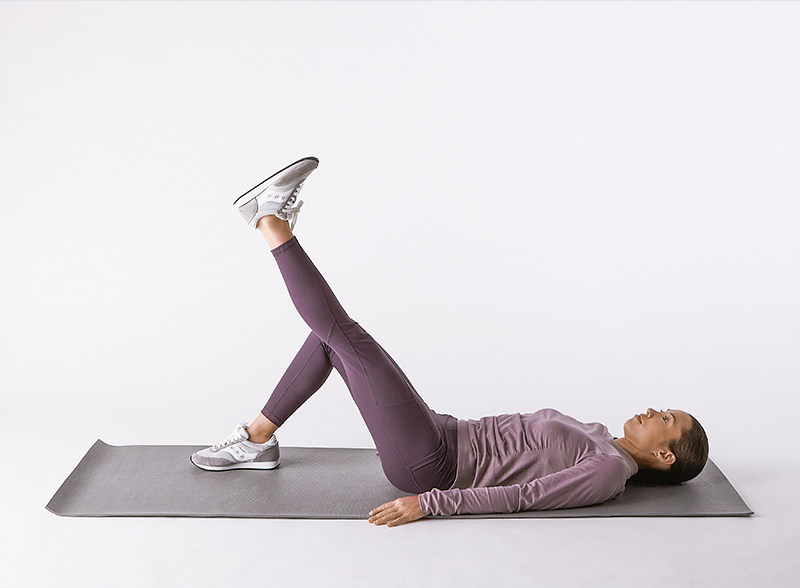

- A quick and easy technique to get your quadriceps functioning properly is the straight leg raise. This is how you do it.
Your unaffected limb (the one that wasn’t injured or had surgery) should be bent to a 90-degree angle Remain on the surface with your foot flat the opposite leg straight and don’t flex your knee. - Elevate the affected leg and progressively tighten the muscles in your front thighs. Five seconds of holding. Lower your leg to the floor slowly. Release, then do it 10 or fifteen more times.
Sitting leg lifts
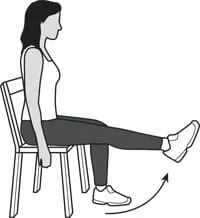
- Position for exercise: sit on the chair
- Raising one leg and bending it at the knee.
- Stretch your ankle to your side after lifting your leg, then drop it back down.
- Make careful to move slowly
- Repetition should be performed on both legs.
- Continue till the set amount of times.
Short Arc Quadriceps exercise
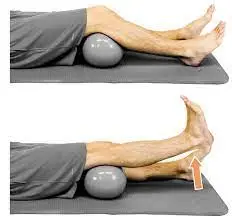
- Here’s how you can do it:
- Place yourself on your back. To extend your knee, use a folded pillow or bolster.
Your raised knee should be straightened gradually. - Your toes should be pointing upward while you contract your quadriceps. For five seconds, hold it firmly.
Lower your leg gradually.
15 times over, repeat.
Standing half squats
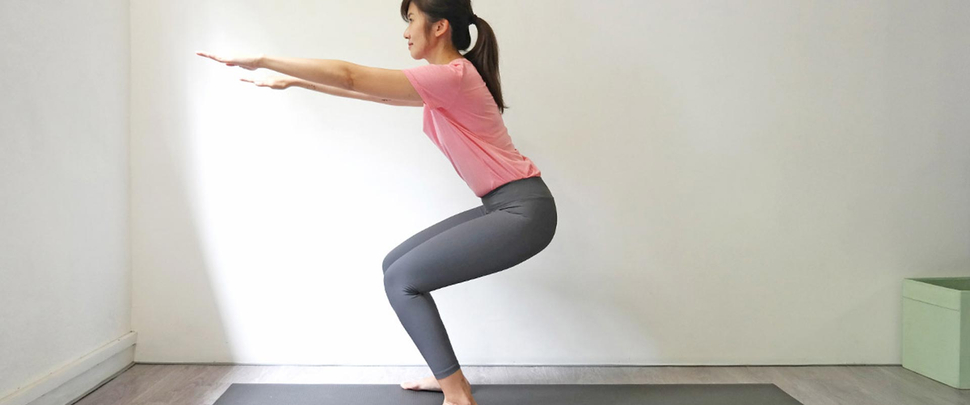

- Place your feet shoulder-width apart as you stand. Like you were going to take a seat in a chair, slowly lower yourself by about ten inches.
- Holding 5-10 seconds
- For one set, repeat ten times. Take a minute or two to rest. Repeat a set of ten.
Step-ups
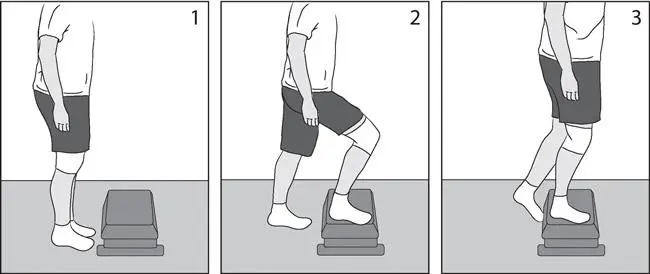
- In this exercise, we are using a stool or stepper. Put one foot on the stepper.
- Maintain position: 10-12 seconds
- Then return to normal position.
- Take the second foot off the platform and place it on the ground.
- Repetition: 5-10 on both legs
Wall Sit

- This exercise is performed near the wall.
- maintain your balance by keeping your arms at your sides or extending them forward.
- Make sure your glutes and core are working as you hold this position for however long you choose.
- Finally, to get up, apply pressure on your feet.
- Repeat after a 20–30 second break.
Knee to Chest

- From a reclined position, raise one leg to your chest.
Hold the thigh below the kneecap. - muscles will be stretched.
- Holding time: 15-30 sec.
- Repeat 3-4 times
How to prevent quadriceps muscle pain?
Warm Up and Cool Down
- Always warm up properly before exercising. Gentle muscular stretches for your quadriceps and light walking or running can help the tissues become ready.
- Removing waste and lactic acid that might cause discomfort by cooling down with low-intensity exercises increases circulation.
Train at the Proper Frequency and Intensity
- Maintaining recuperation capacity and avoiding tissue overload and breakdown is possible with enough rest in between training days.
Wear Proper Equipment
- In cases of patellofemoral problems and anterior thigh tendinopathies, knee braces may be advised in order to enhance patellar tracking and reduce offload forces. Avoid overusing After working out, complete the rest.
Complications of quadriceps pain
Myositis Ossificans:
- The quadriceps muscle, a large muscle, gets wounded throughout the healing process, and the body adds additional calcium to the area.
- The ailment known as myositis ossificans is characterized by pain and reduced range of motion, or ROM, in the afflicted limb.
Compartment syndrome:
- The anterior compartment of the leg contains the quadriceps muscle group, which is susceptible to secondary causes of injury. Occur due to Crush injuries or femur fractures, In order to release pressure and stop irreversible damage to the muscles and nerves, compartment syndrome requires releasing the compartment surgically.
- Loss of knee mobility and weakness are further complications.
- include complications such as blood clots, infections, and wound disintegration when performing surgery
FAQs
What do you do at home to relieve pain in your quadriceps muscles?
The RICE therapy is used at home to treat most cases of discomfort in the quadriceps muscles.
If the patient’s pain worsens while they are at home, the medical professional must be informed.
If the leg is numb, the acute pain and swelling have not decreased after five or six days, or the knee joint cannot be stretched or straightened, you should always seek emergency medical assistance.
Is pain in the quadriceps muscles preventable?
Quadriceps muscle discomfort can be avoided, but you’ll need to take some precautions.
Always take care when participating in sports to prevent injuries to the anterior thigh. Avoid letting the exercise become too repetitive and damage the tendon.
To avoid straining the quadriceps muscle, avoid stretching it.
Does stretching relieve pain in the quadriceps?
yes, it reduces the tightness of the quadriceps muscles.
How do you make your quadriceps stronger?
Exercises such as:
1)Straight leg raises.
2)Short arc quads.
3)Wall slides.
4)Chair pose.
5)Terminal knee extensions.
6)Step-ups.
7)Split squats.
8)Walking lunges.
References
- Physiotherapy, R. J. (n.d.). Quadriceps Pain | Quadriceps Pain. Copyright 2024. All Rights Reserved. https://rjphysio.co.nz/conditions/quadriceps-pain/Ref
- Quadriceps Muscles: Anatomy & Function – Knee Pain Explained. (n.d.). Knee-Pain-Explained.com. https://www.knee-pain-explained.com/quadriceps-muscles.html
- Felman, A. (2023, November 28). Why do I have pain in my upper thigh? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321001
- Leg pain. (2023, April 25). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/leg-pain/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050784
- Pt, L. I. (2022, October 14). 3 Essential Quad Stretches. Verywell Fit. https://www.verywellfit.com/quadricep-stretches-2696366
- Cpt, A. A. (2024, January 28). 5 Ways to Stretch Tight Quads. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/tight-quads-test-296858
- Inverarity, L. (2023, August 31). 11 Quad-Focused Exercises for Strength and Muscle Building. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/quad-strengthening-exercises-2696617
- Quadriceps Exercises – What You Need to Know. (n.d.). Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/cg/quadriceps-exercises.html