Potts fracture
Introduction
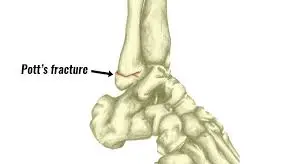
A Potts fracture refers to a type of ankle fracture that occurs when the fibula, one of the bones in the lower leg, breaks at the ankle joint. It is commonly caused by a sudden twisting motion or impact, often resulting from sports injuries, falls, or accidents. Treatment can range from immobilization and physical therapy to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the fracture.
This fracture may also involve ligament damage, making it a complex injury that affects both the stability and function of the ankle. Treatment can range from immobilization and physical therapy to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the fracture.
Small fractures surrounding the ankle and foot (e.g., Potts fracture) and straining or rupture of the muscles around the ankle (e.g., calf, peroneal, tibialis anterior) should also be considered when diagnosing ankle pain.
Mechanism of Injury
During actions such as landing from a jump (volleyball, basketball) or rolling an ankle, the tibia, fibula, and ankle joint are put under stress. Activities that require a fast change of direction, such as football and rugby, can also result in fractures around the malleoli.
A Potts fracture is frequently associated with other injuries, such as an inversion injury, ankle dislocation, or other fractures of the foot, ankle, or lower leg. Inversion injuries can cause both disorders, which include intense pain, swelling, and impairment to varied degrees.
Classification
They have been characterized in a variety of ways, including the mechanism of damage, joint stability, number of malleoli implicated, and fracture depth.
Henderson’s Classification
Types 1–3 are unimalleolar, bimalleolar, and trimalleolar. This does not address fracture patterns, mechanism of damage, or ligamentous injuries.
Lauge-Hansen’s Classification
This categorization is based on radiographic, clinical, and experimental data. It includes the following types:
- Supination-Adduction.
- Supination-External Rotation: causes rupture of the deltoid ligament, fracture of the posterior malleolus or posterior tibiofibular ligament, anterior tibiofibular ligament disruption, and spiral oblique fracture of the distal fibula.
- Pronation-Abduction: induces a transverse fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deltoid ligament, rupture of all syndesmotic ligaments or avulsion fracture of their insertions, and a brief, horizontal fracture of the fibula above the syndesmosis.
- Pronation-External Rotation:- If the stress is applied indefinitely, the posterior tibio-fibular ligament will tear or the postero-lateral section of the tibia may fracture.
- Pronation-Dorsiflexion.
Clinical Presentation
In extreme circumstances, weight bearing may not be possible.
In addition, disabilities such as flat feet are typical in Potts fracture cases. causing the person to walk in the wrong position and develop a flat foot.
Differential Diagnosis
There are several different diseases and injuries that might resemble a Potts Fracture in the absence of an apparent, acute injury.
- Acute Compartment Syndrome
- Lateral Ankle Ligament Tear
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Thrombophlebitis
- Syndesmotic Disruption
- Gout
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Talar Fracture
Diagnostic Procedures
Once diagnosed, it is common practice to classify the fracture using either the Lauge-Hansen classification based on the rotational mechanism of injury or the Danis-Weber classification system.
Treatment
One of the most crucial aspects of rehabilitation after a Potts fracture is that the patient rests sufficiently from any activity that causes them pain. Activities that put a lot of stress on the ankle, especially heavy weight-bearing activities like sprinting, leaping, standing, or walking, should be avoided.
For many weeks following surgery, a protective boot, brace, or plaster cast, as well as crutches, are utilized.
The massage is intended to prevent the production of heterotopic ossification. This is the process by which bone tissue develops outside the skeleton. Electrotherapy, taping and bracing, strength, flexibility, balance exercises, and hydrotherapy may all be used in the treatment.
Achilles tendon lengthening has been shown to be effective in treating difficult Potts fractures.
Various types of fixation devices, such as malleolar screws, malleolar tension band wire, fibula plate fixing, and syndesmotic screws, were employed.
Fixation of Lateral Malleolus: Lag screws alone can be used to repair an oblique fracture that is more than twice the diameter of the bone. Although displacement and shortening may still occur, carriage wires may still be added to the intramedullary device.
Anterior Malleolus: The front edge of the tibia is rarely fractured in isolation.
Prognosis
Patients with the most severe Potts fractures frequently recover completely with adequate treatment. Returning to activities or athletics normally takes a few weeks or months.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Potts fracture is a significant ankle injury that requires prompt and appropriate treatment to ensure proper healing and restore ankle function. With the right care, including immobilization, rehabilitation, or surgery when needed, most individuals can achieve a full recovery and return to their regular activities.
FAQs
What signs of a Potts fracture are present?
Potts fracture patients typically have pain, bruising, and edema when they touch the damaged bone area forcefully.
What signs of a Potts fracture are present?
Potts fracture patients typically have pain, bruising, and edema when they touch the damaged bone area forcefully.
What side effects may a Potts fracture cause?
A Potts fracture can result in long-term issues like persistent pain, ankle joint instability, and an elevated chance of developing ankle arthritis if it is not treated or is not treated appropriately.
References
- Khare, R., Kumar, N., Arora, N., & Khare, K. (1999). POTT’S FRACTURE. Medical Journal Armed Forces India, 55(4), 335–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0377-1237(17)30366-0
- Wikipedia contributors. (2022, September 6). Pott’s fracture. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pott%27s_fracture