Levator Scapulae Muscle Pain
What is the Levator scapulae muscle pain?
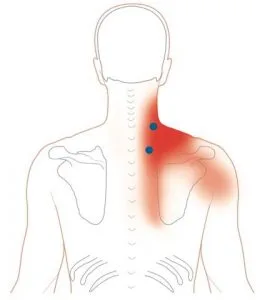
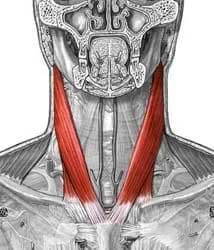
Levator scapulae Muscle Pain is characterized by pain at the upper medial angle of the scapula.
A muscular strain that causes the neck to become rigid and tight is known as levator scapulae muscle pain. The cause of this muscular pain is muscle soreness.
Medication, physiotherapy, and the rice principle are used to relieve this muscular soreness.
Anatomy of the levator scapulae muscle?
The levator scapulae muscle is located in the scapula’s medial border, which extends from the superior angle to the point where the spine and scapular medial border meet.
The lower part of the levator scapulae muscle is situated deep within the Sternocleidomastoid muscle, close to the mid-portion and splenius capitis, and deep to the trapezius. This levator scapulae muscle is raised to the scapula and rotates to the inferior angle medially while your spine is stabilized.
This muscle is usually used in conjunction with other muscles, such as the pectoralis minor and rhomboids, which are created when the scapula rotates downward.
The levator scapulae rotate to the same side and flex the cervical spine laterally when your shoulder joint is fixed. However, when both shoulder joints are not fixed, the levator scapulae muscles simultaneously contract in equal amounts, which prevents the cervical spine from rotating and flexing laterally.
Causes of Levator Scapulae Muscle Pain?
One of the most frequent causes of Levator Scapulae Pain is extended sitting, usually with poor posture.
Inflammation of the levator scapulae muscle is caused by persistent stress and strain that is given to overload and perform repetitive movements.
- Poor posture:
- Poor sitting posture is exemplified by sitting at a computer with a rounded shoulder that creates a “hunch back” stance.
- This poor posture causes pain or soreness in the levator scapulae muscles.
- Tendinitis:
- One of the causes of levator scapulae muscle pain is levator scapulae tendonitis, which is an injury to the muscle caused by everyday strain and physical stress.
- Increased muscular tension and tightness are the results of this kind of strain.
- Repeated movement:
- when the muscle is used repeatedly through repetitive contractions.
- Without treatment, it results in a decreased range of motion (ROM) in the arms, shoulders, and neck as well as tension headaches.
- It has been accompanied by bodily problems like depression or fatigue.
- Cervical spine dysfunction
- Drops
- Whiplash from accidents
- Muscle injuries arise from repetitive arm movements.
Other factors that contribute to levator scapulae pain include:
- For the entire day With the head turned, working on the computer
- Wearing a shoulder strap when carrying bulky luggage
- Stress on an emotional and mental level
- malfunction of the cervical spine.
- If the air conditioner and ceiling fan are used to keep the muscles cool as you sleep
- If you spend too much time holding a phone between your ear and shoulder.
Signs and Symptoms of levator scapulae muscle pain?
- Soreness in one area of the body causes pain in the levator scapulae muscle, which then spreads to other areas in widely different locations.
- You have stiffness in the muscles of your neck, over your shoulders, or in the space between your shoulder blades.
- You suffer from neck aches and have trouble rotating your head and raising your neck while you’re in the supine position.
- You sense The bottom part of the Levator Scapulae muscle has two trigger sites.
- Just above the scapula’s superior angle lies the lower trigger point for muscular soreness.
- One to three inches above it is the higher trigger point for muscular pain.
- Pain is transmitted laterally to the shoulder blade from both trigger sites, which are situated too deeply inside the upper trapezius muscle.
- Additionally, you have swelling and spasms in the vicinity of the sore muscle.
- Additionally, you experience arm weakness and numbness.
- Additionally, you get muscular tightness.
What effect does the levator scapulae muscle have on the posture of the head and neck?
- Maintaining the shoulder blade, which is positioned to encourage a vertical alignment of the head on the neck and avoid forward head posture.
- Because of this, it is difficult to keep the joint stable while maintaining good neck posture.
- The cervical spine is frequently subjected to dynamic opposing motions, such as typing, peering down at a phone, and sitting at a desk, which needs the muscles and bones to move both independently and together to maintain the activity.
- A lot of folks have a slouched posture that does not support their lumbar region.
- Therefore, the effect of spinal alignment is worse if the person’s chair is not flexibly designed to meet ergonomic requirements.
- These slouched positions have a tendency to lengthen and stretch the levator scapulae muscle by pushing the shoulder blade higher and downward.
- To make up for the loss of stability, the muscles get tenser as they lengthen.
- Pain and a lack of tension integrity in the joint complex, to which the muscle belongs, are typically linked to tension.
What effect does the levator scapulae discomfort have on the scapulohumeral rhythm?
- The amount of pressure applied to the muscles rises in order to stretch them.
- When the levator scapulae are too tight, the mid-upper corner of the scapula bone also becomes chronically raised.
- When a muscle weakens as a result of too much strain, the surrounding muscles start to have a similar impact and must also overexert themselves to compensate for the soft area.
- The scapula bone struggles to rotate upward when the arm is raised, thus it remains in a downward rotation.
- Compression in the subacromial area occurs as the arm attempts to raise, leading to problems with the glenohumeral joint.
- As a result, the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis designed to stabilize the shoulder joint socket are often affected in the early stages of rotator cuff degeneration.
- If the illness goes undiagnosed, it impacts the neuromuscular system and results in the loss of vital arm motor abilities in the arms or shoulder joints.
Diagnosis of levator Scapulae muscle pain?
- You should call your doctor right away if you have significant neck pain and discomfort.
- The physician is attempting to determine the cause of the muscular soreness by evaluating the cervical spine.
- The first doctor questions you about your muscular pain and tries to figure out why or what’s causing it.
- In the observation, the portion examines swelling & any color changes in the muscle pain.
- Part of the palpation detects spasms and edema.
- The examination portion looks at muscular strength and range of motion.
- Following an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will provide muscle therapy based on your situation.
Treatment of the levator scapulae muscle pain?
RICE principle:
The RICE concept should be followed by the doctor when you are experiencing muscular pain in its initial stage.
- R-rest = Whether you get neck pain, you should take a few days off and use a small cushion for support. You should also keep your neck in a neutral posture whether using a computer, a phone, or a television. You may relieve tension and muscular overload by getting enough rest.
- I-Ice = You may also apply an ice pack and frozen peas, but you must place them between the skin and the ice and monitor the redness of the skin.
- C- C-compression = In order to relieve pain and swelling, C-compression is also given to the region of pain using a compression bandage.
- E-elevation = This muscle cannot be elevated as doing so might induce neck pain.
Pain medication:
When you experience pain, you take an anti-inflammatory medication, which is a type of painkiller that lowers pain as a first line of therapy and at home.
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and diclofenac, are the most common anti-inflammatory treatments; nevertheless, the effectiveness of these medications varies according to the intensity of the pain.
Additionally, volini gel and diclofenac gel are administered to the painful region to relieve it.
Physical Therapy Treatment
Massage, electrotherapy, stretching, and exercise are all part of the physiotherapy treatment, which helps to lessen pain and swelling.
Massage:
- The trigger points and delicate spots of the aching muscles are massaged.
- Oil and powder are administered to the painful region to assist massage it.
- The application lasts for five minutes.
- You can reduce swelling and soreness with this massage.
Electrotherapy treatment :
SWD, TENS, IFT, and the US are all part of the electrotherapy treatment, which helps you reduce pain and swelling.
- The therapist applies the US = ultrasound treatment to the painful pain region in order to relieve the trigger points and tenderness.
- The therapist applies SWD (short wave diathermy), IFT, and a TENS machine to the painful region in order to reduce the pain and swelling.
- The painful region is treated with this equipment for ten minutes.
Stretching :
This stretching aids in the release of muscular tension and spasms.
Levator scapulae muscle simple stretching:
- With both hands at their sides, the patient is sitting up straight.
- Next, lift your right arm forward and extend your hand over your back, grabbing your right shoulder blade and pressing downward.
- Rotate the head 45 degrees to the left, or roughly halfway toward the shoulder joint, while holding everything else in place.
- Next, tilt the chin down until the right side of the neck, or the back, feels well stretched.
- The left hand is raised to the back of the head and gently dragged down a bit more to extend the stretch.
- On the opposite side, repeat this practice.
Neck Flexion Stretch:
- This stretching begins in a neutral posture with your shoulders down and your chin up.
- The back of the patient’s neck feels somewhat tense.
- Bring the arm over the head, hold the back of the head with the hand, and gently lift the head from behind to extend the stretch. Make sure the chin is directed toward the right knee joint by turning the head to the right.
- Lower your chin to your knee.
- On the side of the back of the neck, the patient has a little strain.
- Placing the left arm behind the back and toward the right hip joint will increase the stretch.
Lateral Neck Flexion Stretch:
- Drop the shoulder joint and keep the chin up.
- The right ear should then be slowly dropped toward the right shoulder joint.
- Care must be taken to avoid lifting the left shoulder.
- The side of the patient’s neck feels somewhat tense.
- Take hold of the left side of the head and gradually draw it toward the direction of the right shoulder.
Cat-Back Stretch (Cervical Spine Extention):
- Arch their back, relax their neck muscles, and slowly lower their head.
- Hold for a little while, then do this stretching three times.
Exercise :
Shoulder Shrug exercise (Scapular Elevation):
- After a few seconds of holding this exercise, return the shoulder joint to its initial position.
- After that, do this exercise several times.
Head Rolls exercise / Cervical Spine Rotation:
- It is necessary to lower the shoulder joint or maintain the chin raised.
- Do this exercise again, but in the other way.
Head Swings:
- Surely Drop the shoulder joint and keep the chin up.
- Return the head to its neutral posture.
Strengthening exercise:
Dumbbell Shrugs:
- The patient is instructed to stand with their feet shoulder-width apart for this exercise.
- Next, grasp a dumbbell in each hand.
- Do the three sets of fifteen repetitions twice a week.
Lateral Raises:
- The patient is Place your feet shoulder-width apart as you stand.
- then using each hand to grip a dumbbell.
- Lower the arm to dumbbells after raising it laterally until the elbow and shoulder joints are level.
- Do the three sets of fifteen repetitions twice a week.
Conclusion
In summary, levator scapulae muscle pain is a common but treatable ailment that is frequently caused by injuries, stress, bad posture, or overuse. Usually, it shows up as stiffness, decreased range of motion, and pain in the neck and shoulders.
In addition to professional interventions like physical therapy, massage, or medication if necessary, effective treatment combines self-care techniques including relaxing, stretching, applying heat or ice, and making ergonomic modifications.
People can lessen pain and lower the chance of recurrence by treating the underlying reasons, adopting good posture, and doing regular stretching and strengthening exercises. A healthcare professional should assess persistent or increasing symptoms in order to rule out underlying diseases.
FAQs
Which exercise makes the levator scapulae stronger?
Using the levator scapulae, slowly shrug your shoulders in the direction of your ears. Hold for two to three seconds before lowering your shoulders gradually.
How is the levator scapulae stretched?
To begin, take a seat comfortably with your shoulders relaxed. Tuck your chin into your chest and tilt your head 45 degrees to one side so that it seems as though you are staring at your underarms. Pull your head down a little with the arm of the side you’re facing.
What kind of pain does the levator scapulae muscle experience?
A headache might result from neck pain that spreads to the brain. Pain and limited mobility, particularly decreased side flexion and cervical flexion to the opposite side. Tightness and/or deep, aching pain around the neck or shoulder blade on the upper back.
How much time does it take for a levator scapulae strain to heal?
When a neck strain occurs outside of a fall or collision, it may heal naturally and the symptoms go away in a week or so. It may take up to 12 weeks for more serious injuries to fully recover.
Is it possible to rebuild the levator muscle?
Although levator dehiscence can be caused by trauma, previous eye surgery, and contact lens use, the likelihood of this kind of ptosis rises with age. Surgery may be necessary to lengthen this muscle to improve its strength or to reattach this tendon when this issue arises.
How may levator scapulae pain be lessened?
Stretching: In addition to certain other therapy modalities, such as massage, a levator scapulae stretch is frequently beneficial. Adjustments to posture: If the issue was caused by bad posture, learning the right sitting posture might significantly improve the situation.
What is a weakening of the levator scapulae?
When the levator scapulae are too tight, the mid-upper corner of the scapula may also become chronically raised. This happens because if a muscle weakens from too much strain, it may start to affect other muscles in the area, forcing them to overwork in order to compensate for the weak place.
Is it possible to strengthen the levator muscle?
Lifting the Eyelids: This exercise, which targets the levator muscle directly, involves elevating the eyelid while creating resistance with a finger above the eyebrow.
How can someone who has levator scapulae pain sleep?
If at all possible, you should avoid sleeping on your stomach. Your neck is positioned awkwardly while you sleep on your stomach, which might exacerbate your pain.