Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Pain
Latissimus dorsi muscle pain is suggested when you experience pain in the lower back, mid-to-upper back, base of the scapula, or rear of the shoulder joint. In the painful location, you experience pain, swelling, and spasms. The RICE method, painkillers, and physical therapy are used to alleviate this pain.
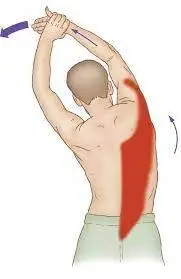
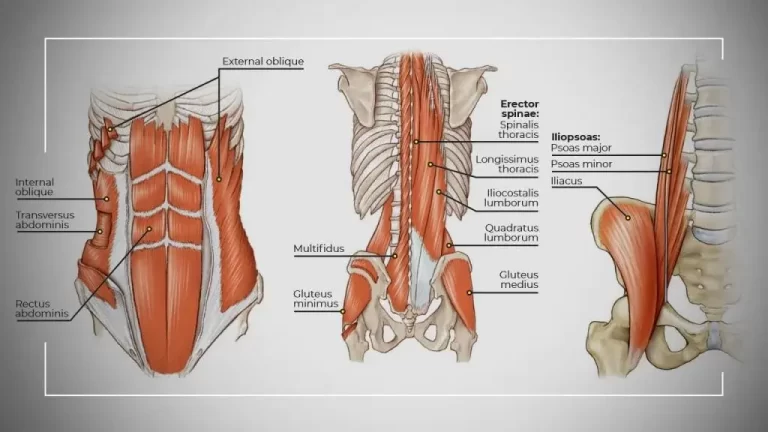
Anatomy of the latissimus dorsi muscle?
- One of the biggest muscles in the back is the latissimus dorsi.
- This muscle’s role is to span the width of the back and aid in shoulder joint movement regulation.
Causes of the latissimus dorsi pain?
- This latissimus dorsi muscle is employed in pushing and throwing movements.
- The body is accustomed to using bad techniques throughout the exercise.
- if the workout is performed without a warm-up.
The following are some activities that can cause latissimus dorsi pain:
- Shoveling snow
- Tennis
- Chin-ups and pull-ups
- Gymnastics
- Swimming
- Reaching forward or overhead repeatedly
- Baseball
- Chopping wood
- Rowing
- When you are accustomed to having bad posture in your daily life, which results in slouching posture, you also have pain in the latissimus dorsi muscle.
- This latissimus dorsi muscle injury occurs in uncommon instances.
- Commonplace actions that cause latissimus dorsi muscle soreness include pushing against a chair’s armrests in order to stand.
- when you open up your chest to breathe.
Symptoms of the latissimus dorsi muscle injury?
- An injury to the latissimus dorsi muscle can cause pain in the lower, middle, and upper back, among other areas of the body.
- the shoulder joint’s rear.
- which radiates down to the fingers and the inside of the arms.
- The agony gets worse when the person tosses something or stretches their hands in front of them, lifting them above their head.
Additional symptoms consist of:
- You’re having trouble breathing.
- A tingling sensation in the lower arms
- Lower back and middle back tendinitis
- Additionally, you experience trigger points and tenderness in the painful spot.
- You experience muscle tension, edema, and spasms.
When should you see a doctor about this muscular ache?
- If you are unable to pinpoint the cause of your back pain using certain symptoms, such as
breathing difficulties or abdominal pain - A fever
- when significant pain persists after initial treatment.
Treatment of latissimus dorsi pain?
RICE principle:
When you first experience muscle pain, your doctor will advise you to use the RICE principle to relieve the pain and swelling in your muscles.
- R-rest = Occasionally, take a break from using your shoulder and back joints and avoid any physical activity that causes pain.
- I-ice = To alleviate muscle pain and swelling, apply ice to the affected area for 20 minutes. To avoid ice burn, always apply to the ice using a towel.
- C-compression = Compression bandages can also be applied to the area of pain to reduce swelling and spam.
- E-elevating: Sit up straight and position the pillows behind your shoulders and upper back to raise yourself to the painful area.
Pain medication:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), can also be used to relieve muscle soreness.
- Your doctor will give a stronger medication if you have experienced extreme pain.
- In order to relieve muscle pain and swelling, you can also apply volini gel and spray to the affected area.
Physical Therapy Treatment:
Pain, edema, spasms, and muscle stiffness can all be relieved with physical therapy.
Massage, electrotherapy, stretching, exercise, strengthening exercises, and yoga are all part of the physical therapy treatment.
Massage:
- It is recommended that a therapist massage the affected area when muscular pain appears in delicate areas.
- For five minutes, this massage is performed to the sore spot on the muscle using oil and powder.
A circular motion is used to apply this massage. - A messenger is also used to administer this message.
Electrotherapy treatment
You can alleviate your pain, swelling, and spasms with electrotherapy.
There are too many machines used in the electrotherapy treatment.
- Use US (ultrasound therapy) to relieve muscle pain when trigger and tender points are present.
- This gel-assisted treatment is administered to the painful area for five to ten minutes.
- A pain therapist applies TENS, IFT, and SWD to the painful location.
- Short wave diathermy, or SWD, is a type of hot therapy used to relieve pain in the affected area.
- Gel and electrodes are used to apply TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) and IFT (interferential therapy) to the painful area.
- Ten minutes are spent applying this therapy to the painful area.
Stretching:
- Best Active Lat Stretches
- Active floor stretch
- Exercise ball stretch
Best Active Lat Stretches:
- Shoulder and back joints must remain against the wall.
- Avoid arching your back.
- The patient must maintain constant contact with the elbow joint.
- Push the elbow joint forward and overhead.
- Try separating the hands while keeping the elbow joint together to extend the stretch.
Active floor stretch:
- Next, stretch the left arm by reaching out through the fingertips while leaning the weight onto the right arm.
- The side of the patient’s torso feels stretched.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this posture.
Exercise ball stretch:
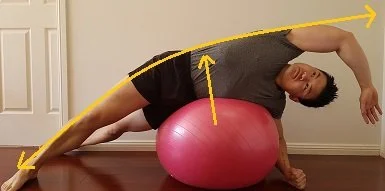
- This workout begins with all four limbs in front of an exercise ball in a tabletop position.
- For support and stability, apply pressure on the grounded arm.
- Roll the ball forward by using your core muscles to extend your arm straight out.
- After that, stretch the other side as well.
Exercise:
You can get rid of muscle weakness and soreness by exercising.
- One Arm Row on One Leg
- Lat Pulls With Bands
- Foam rolling exercise
- Wall press
One Arm Row on One Leg:
- Move the weight from the hip joint to the right leg and tip for the starting position.
- For balance, hold against a wall.
- Pull the elbow joints up into a row from this posture, then slowly lower them down.
- To maintain the majority of your weight on the front leg, lower your leg and rest softly on your toes when you feel unsteady.
Lat Pulls With Bands:
- You may also use a door holder to hold the band and fasten it in a doorway above you if you want to make this exercise more difficult.
- As an alternative, draw the elbow joint down toward the rib cage by holding the band overhead and squeezing the back.
- Put more effort into your workout and bring your hands closer together to grasp the band.
- Do this workout 12–16 times.
Foam rolling exercise:
- The patient is keeping their spine neutral while lying on their right side with the foam roller beneath their lat.
- Surely Bend the left knee joint however it feels comfortable while maintaining a straight right leg.
- Next, From side to side, roll.
- Keep rolling like this for a minute.
- On the other side, repeat this exercise.
- Do it three times a day.
Wall press:

- The patient is positioned facing a wall and about two feet away from it.
- Position the hands’ palms at hip height against the wall.
- Do it three times a day.
Strengthening exercise:
You can strengthen the muscles with this workout.
- Barbell Rows
- Dumbbell Pullovers
Barbell Rows:

- Lowering the torso too much might strain the back, especially when the weight is substantial.
- To protect the back, the knees must remain bent.
- Next, perform 12–16 repetitions of this exercise.
Dumbbell Pullovers:
- The first step in this workout is to hold a weight straight up overhead in the bridge posture.
- Surely Maintain a straight arm position with a slightly bent elbow joint.
- After that, reduce the weight until it is roughly head-level or as low as the patient feels comfortable.
- Next, perform 12–16 repetitions of this exercise.
Yoga
- Upward Salute
- Eagle Pose (Garudasana)
- Cat-Cow
- Downward-Facing Dog
- Upward-Facing Dog
- Child’s Pose
Upward Salute:
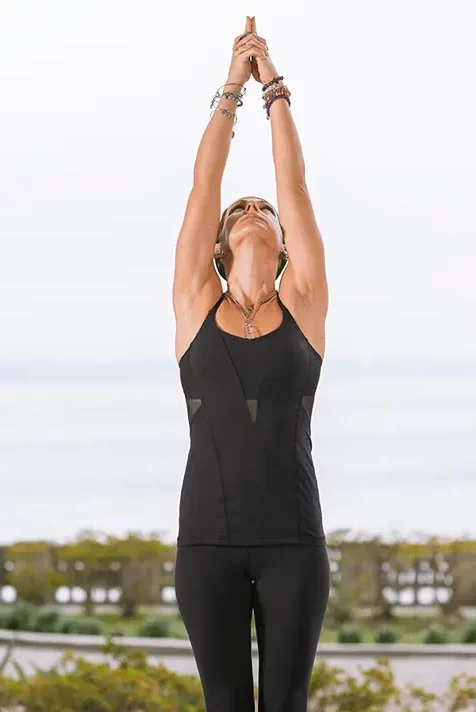

- Beginning in Tadasana (Mountain Pose), place your heels slightly apart and balance your weight evenly on both feet.
- Next, raise both arms in the direction of the ceiling.
- Maintaining the spine in alignment, contracting the core, and slightly tucking in the tailbone.
- You should bend slightly backward once you are comfortable.
Eagle Pose (Garudasana):
- Rhen Both arms should be extended parallel to the floor and straight ahead.
- Make sure the right arm is above the left by crossing the arms in front of the upper body.
- Bend your elbows.
- Raise both forearms.
- Breathe deeply while pressing your palms together.
- Then, concentrate on the shoulder and back joint release.
- After that, switch the arms and do this yoga stance three times.
Cat-Cow:
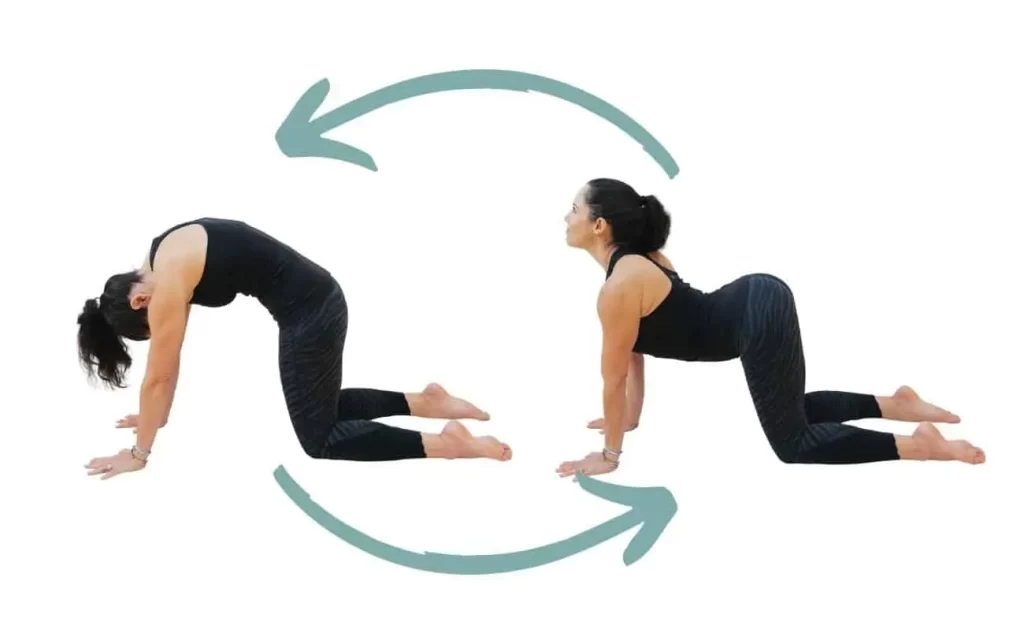
- With a neutral spine, begin this exercise on your hands and knees.
- Take a breath, raise your seatbones, push your chest forward, and let your belly drop to the floor to enter Cow Pose.
- As you release your breath, round your spine outward and tuck your tailbone in to enter Cat Pose.
- Then, in a relaxed attitude, let the head drop toward the floor.
- Throughout both motions, apply firm pressure to the arms and observe how the shoulder joint blades shift position.
- Do this yoga stance three times.
Downward-Facing Dog:
- Beginning on all fours, place the knee joint beneath the hip joint and the wrists beneath the shoulder.
- Raise the heels toward the floor and straighten the legs.
- It is OK to maintain a modest bend in the knee joint when the hamstring muscles are tense.
- Additionally, when you require more length, the patient is walking with their hands forward.
- Next, firmly press through the hands while concentrating on spreading across the shoulders and collarbones.
- Do this yoga stance three times.
Child’s Pose:

- From Downward Dog, inhale deeply and release it.
- Pull the hips back to the heels as you release the knee joint onto the floor.
- Place the forehead down on the ground.
- With the knee joint somewhat wider than the hip joint, you can also unwind in this position.
- Move the fingers as far forward as you can to increase the stretch.
- Before returning the fingers to the middle and relaxing in this position, walk them to each side.
What are Preventions for latissimus dorsi muscle pain?
- Always keep your posture straight and refrain from slouching.
- Throughout the day, especially before and after physical activity, make sure to stay hydrated.
- To relieve any tightness in your shoulders and back, you can also consider getting a massage once in a while.
- Before working out or participating in sports, make sure you warm up and stretch correctly.
- After working out, always perform the cool-down.
- Receiving massages on occasion.
FAQs
What are the latissimus dorsi trigger points?
There are upper and lower trigger points for these muscles. About two fingers below the nipple is where the upper trigger point is located. Draw a line horizontally and continue until you reach the edge of your back. Check for sensitivity in this region.
How is the tightness of the latissimus dorsi measured?
Ask your patient to raise their arm to 90° flexion and place it in scapulation in order to examine their latissimus dorsi. After that, you can palpate the muscle and urge the patient to extend and medially rotate their arm while applying resistance.
How can my latissimus dorsi be strengthened?
The Weighted Pull-up, Meadows Row, and Wide Arm Reverse Pulldown are three of the best lat exercises. broad Arm Reverse Pulldown: While seated at the Lat Pulldown machine, squeeze your shoulder blades together and grasp the bar with a broad underhand grip.
What causes pain in the latissimus dorsi?
Muscle strain: Overuse from sports like golf, skiing, and rowing that call for repetitive upper-body movements can lead to latissimus dorsi muscle soreness. Overuse, particularly if you don’t warm up adequately before the exercise, might result in tendinitis or muscular strain.
How is your latissimus dorsi stressed?
Lean your elbows against the table or shelf. To feel a stretch around the armpits of both shoulders, slightly lower your knees and move your hips back without moving your arms. The latissimus dorsi muscle will be stretched as a result; you will notice a strain under your armpit and in the direction of your shoulder blade.
How is the latissimus dorsi taped?
The medial strip should be applied without stress toward the final costovertebral joints and then vertically down to the third lumbar vertebra’s transverse process. Apply the lateral strip in the direction of the fourth lumbar vertebra’s transverse process without applying any tension.
How can the pain in the latissimus dorsi be stopped?
These consist of:
utilizing appropriate form when exercising and playing sports.
preventing the muscle from being overused.
After warming up and before cooling down, gently stretch.
maintaining hydration.
receiving massages on occasion.
How is latissimus dorsi pain tested for?
Testing of Muscles
The forearm is subjected to resistance during abduction and mild flexion. When the upper extremity is flexed into an overhead posture, such as reaching for an article on a high shelf, the back will lengthen and rotate if the latissimus dorsi is short or tight.
How is the latissimus dorsi massaged?
Your latissimus dorsi muscle can be massaged using this foam roller technique. Roll about on a foam roller while lying down until you locate a sore region. As you move your arm from in front of you to above your head, hold that position. As you rotate the arm above your head, rotate it externally.
How does pain in the latissimus dorsi feel?
You may have pain in several areas following a latissimus dorsi strain, such as the lower, middle, and upper back, the back of your shoulders, and the base of your scapula. Additionally, you might experience pain from the inside of your arm down to your fingertips.
How long does it take to recover from a strain of the latissimus dorsi?
Depending on the strain, recovery times can vary; Grade 1 infections normally take two to three weeks, while Grade 2 strains typically take at least a month. However, grade 3 injuries can have significantly longer healing times and frequently necessitate surgery.
How may the pain in the latissimus dorsi be relieved?
Physical therapy and rest are typically used to treat latissimus dorsi pain. To aid with the pain, you can also take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or aspirin.
References
- Ladva, V. (2024a, November 25). Latissimus dorsi muscle pain: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/latissimus-dorsi-muscle-pain/#google_vignette
- Jyoti. (2022, July 13). latissimus dorsi muscle function Archives – Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/tag/latissimus-dorsi-muscle-function/#google_vignette