Iliopsoas Muscle Pain
What is Iliopsoas Muscle Pain?
Iliopsoas muscle pain refers to discomfort or strain in the iliopsoas, a critical muscle group responsible for hip flexion and stabilizing the lower spine. This muscle complex, consisting of the psoas major, psoas minor, and iliacus, is essential for activities like walking, running, and maintaining posture.
Pain in this area often arises from overuse, prolonged sitting, poor posture, or sports-related injuries. It can manifest as stiffness, reduced mobility, or sharp pain in the lower back, hip, or groin, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
- Iliopsoas muscle pain is suggested when you have pain at the front of the hip joint that radiates down your leg. This soreness might occasionally spread to the buttocks
- The femur’s lower trochanter is where the iliopsoas muscles are implanted.
Causes of the iliopsoas muscle pain?
It typically affects athletes and those who routinely engage in physical activity.
When engaging in everyday activities like jogging, these iliopsoas muscles are used repetitively.
Iliopsoas bursitis:
- The muscles around the hip joints are impacted by iliopsoas bursitis.
Hip Arthritis:
- Hip joint arthritis is another cause of this pain.
- Chronic conditions can occasionally cause this pain.
Iliopsoas muscle Tightness:
- The hip flexor muscle tension is the cause of this pain.
- Excessive and prolonged sitting causes tightness.
Injury :
- Whenever there is a hip joint injury, this muscle pain is also caused.
- Overuse and overloading of the muscles are the main causes of this ailment.
- Trauma is another factor that causes it.
Symptoms of the iliopsoas muscle pain?
- Muscle pain is a result of this damage.
- It is created to cause muscular swelling and spasms.
- You get pain at the front of your hip, which travels down your leg and into your buttocks.
- You wake up feeling stiff as well.
- The muscular pain location also shows pain & trigger points.
- You sense that your hip mobility is feeble.
- Additionally, you experience pain when engaging in certain activities, such as:
- while performing the workout.
- while going upstairs and downstairs.
- if you lift one or both legs and stretch them.
What is a diagnosis of the iliopsoas muscle pain?
- Contact a doctor if your pain is severe and does not go away after two to three days of basic therapy.
- For a correct diagnosis, the doctor is suggested to do certain tests following the evaluation.
Treatment of the iliopsoas muscle pain?
The RICE concept is recommended by the doctor as a main therapy or at-home remedy when you experience muscular pain.
- R-rest = When you have muscular soreness, you need to take a break from activities that cause it.
- I-ice = You apply ice to the region of pain for 20 minutes, allowing swelling and muscular pain to subside. You may also use frozen peas and an ice pack for ice treatment.
- C-compression = Compression bandages can also be used to relieve swollen and painful muscles.
- E-elevation: To relieve muscular pain and swelling, you must be raised to the afflicted leg with the aid of a pillow beneath the foot.
Pain medication for Iliopsoas muscle pain:
- To relieve muscular pain, you can also take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as Celecoxib and Naproxen.
- Your doctor will prescribe a stronger medication if you have had extreme pain following an exercise session.
- The doctor recommends taking an antibiotic medication while the illness is present.
- For muscular discomfort, the doctor is also recommended to administer a corticosteroid injection.
- Applying pain-relieving gel and spray, such as volini gel and spray, to the area of muscular soreness and swelling is another option.
Hot & cold therapy:
- You may also apply hot and cold compresses to the region of muscular soreness to ease pain.
- It is used every few hours during the day for 15 minutes at a time.
Physical Therapy Treatment:
The doctor has recommended physical therapy as a treatment for muscular pain if it does not go away after home remedies and painkillers.
You can get relief from pain, edema, spasms, and muscular stiffness with physical therapy treatment.
Massage:
- The therapist is suggested to use massage treatment to relieve muscular pain when trigger and sensitive points are present in the affected area.
- After two to three days of adhering to the RICE principle, massage is administered when you feel as though the pain has subsided.
- With the aid of oil, a massage is administered for five to ten minutes.
- At home, massage is done three times a day.
Electrotherapy treatment:
If the RICE principle, pain medication, and massage do not alleviate the muscular pain, electrotherapy is utilized to relieve it.
An electrotherapy treatment is recommended by your therapist to relieve your pain, edema, and swelling.
A lot of electrotherapy machines are employed by the treatment therapist.
- Therapists use the US, or ultrasound treatment, to relieve muscular pain when trigger and sensitive points are present.
- This therapy is administered with the aid of gel & applied for 5 to 10 minutes on the region of pain.
- This treatment aids in the reduction of pain and edema.
- A pain therapist applies TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), IFT (interferential therapy), and SWD (short wave diathermy) to the painful location.
- Short wave diathermy, or SWD, is a type of heat treatment used to relieve pain in the affected region.
- Gel and electrodes are used to apply TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) and IFC (interferential current therapy) to the painful region.
- Ten minutes are spent applying this treatment to the painful region.
Exercise therapy for iliopsoas muscle pain:
You feel relieved of the pain after using the RICE concept for two to three days at home, receiving primary care, and taking painkillers.
The physical therapist suggests exercise treatment to alleviate muscular weakness and stiffness after you feel comfortable and relieved of your muscle pain. Stretching and strengthening exercises are part of the exercise treatment for muscular soreness.
Stretching exercises aid in both strengthening and releasing tense muscles.
Stretching exercise:
The physical therapist recommends stretching to relieve muscular stiffness after electrotherapy for two to three days to relieve muscle soreness.
When you feel comfortable and your pain has subsided, you use this stretching.
- Standing Hip Flexor Stretch
- Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
- lying hip flexor bed stretch
- Table Psoas Stretch
- Kneeling Stretch
- Butterfly stretch
- Pigeon stretch
- Knee to chest stretch
- Half-kneeling hip flexor stretch
Standing Hip Flexor Stretch:
- Next, Create a split and staggered posture by stepping your right foot forward.
- Tuck your pelvic bone in and contract your core muscles.
- You touch the right leg with your hands.
- Surely Holding your rear leg straight, steadily lunge forward with your right leg until your left thigh, groin, and hips start to stretch.
- After that, slowly go back to the beginning and switch sides.
Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch:

- Next, Change sides and slowly get back to the starting position.
lying hip flexor bed stretch:
- You’re While lying flat on your back on your bed, put your right leg closest to the bed’s edge.
- Next, slowly lower your right leg to the bed’s side.
- Your foot remains on the bed while your leg remains bent.
- Your hip flexor feels stretched.
- Bend your knee joint softly to increase the stretch’s depth.
- Then slowly go back to where you were before.
Table Psoas Stretch:
- With the knee joint pointing down, raise your right leg behind you and place it on the table.
- Make sure your leg is straight.
- To relieve any pressure from the table, you lay a folded towel beneath your knee joint.
- Hold on to Your right hand should be placed on the table before you.
- You have your standing leg bent slightly.
- When you notice a strain in your right hip, stop the stretching.
- Then slowly go back to where you were before.
Kneeling Stretch:
- Bring your right foot forward until your right knee is just above your right ankle joint after you begin kneeling with both knees on the floor.
- Maintaining the alignment of your hips and shoulders is essential.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
- For a more thorough stretch, contract and release your hip flexors.
Butterfly stretch:

- As you sit on the floor, you put your feet’s soles together.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Pigeon stretch:

- One knee joint is 90 degrees bent in front of the body when you are sitting, with the heel facing the opposing hip.
- Next, extend the second leg as far behind the torso as you can.
- Try gently moving them back and forth, hip to hip.
- Next, repeat on the opposite side.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Knee to chest stretch:
- Your legs are spread out on the floor while you lie on your back.
- Bend one knee joint slowly in the direction of your chest.
- Surely Pull your knee joint as near to your chest as you can without feeling uncomfortable while maintaining a flat back.
- Next, Squeeze your glute muscle and extend your straight leg as far as you can.
- Then go back to where you were before and do it with the other leg.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Half kneeling hip flexor stretch:
- Surely When performing this exercise, maintain a tall trunk.
- To feel a slight stretch at the front of your hip joint, try gently sliding your right knee joint back.
- Next, contract your right glute muscle as though you were pulling forward and moving your hip joint or trunk closer to your left foot.
- Create a small pelvic tilt by tucking your hip joint.
- For 30 seconds, maintain this stretching position.
Strengthening Exercises:
Following two to three days of electrotherapy and massage to relieve muscular pain, the physical therapist suggests strengthening exercises to relieve muscle weakness.
It is usually recommended to perform this strengthening exercise when you are comfortable and want to relieve pain.
All of these strengthening exercises relieve pain and weakness in your muscles.
- Glute Bridge
- Runner’s Lunge
- Hips Elevated
- High Lunge
- Half Frog
- Hero Pose
- Supported Side-Plank Reach
- Lying hip rotation
- Sidekick
- Hip raises
- Leg raises
- Frankensteins
- Hanging Leg Raise
- Bridging Psoas March
- Romanian Chair Leg Raises with Dumbbell
- boat pose
- lunge
Glute Bridge:
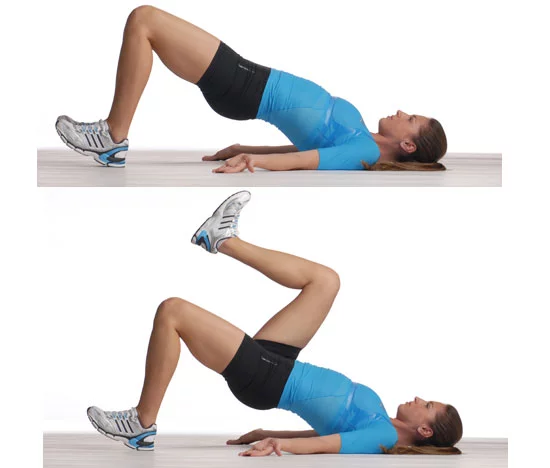

- Your arms are by your sides, your knees are bent, and your feet are flat on the ground while you lie on your back.
- Then, to build a bridge between your knees and shoulders, contract your glutes and raise your hip joint.
- Elevate your hip joint until the iliopsoas muscles in both legs feel stretched.
- Lower your hip joint a little when you have lower back pain, but maintain a tight gluteal muscle.
Runner’s Lunge:

- Next, Your hands should rest on your thigh.
- Press the top of your rear foot into the ground for a deeper stretch.
- Repeat this action on the other side after holding for two to three minutes in the exercise posture.
Hips Elevated:
- Next, raise your hip joint by placing a foam roller and block beneath your hip joint and lower back.
- You must maintain your head and shoulder joints lying on the floor.
- Next, pull your left knee closer to your chest, bend it, and put your arms over your shin.
- Hold for ten seconds throughout this workout.
High Lunge:

- You have your hands by your sides and your feet shoulder-width apart as you stand.
- Bend your right knee joint to a 90-degree angle so that it is directly above your right ankle joint and step your left foot a few paces behind you.
- Then raise your arms straight up.
- Hold for ten seconds throughout this workout.
Half Frog:
- Stretch your legs behind you while resting on your stomach to begin this workout.
- Place your forehead on your hands’ backs.
- Flex your right foot and bend your right knee joint such that it remains parallel to your right hip joint.
- Next, To get your right inner thigh as near to the mat as you can, press your right knee joint into the floor.
- Hold for ten seconds throughout this workout.
Hero Pose:
- This workout is With both knee joints on the floor, begin by kneeling.
- Lower yourself onto the block and roller by bending your knee joint.
- Surely Maintain the tops of your feet pushed against the ground and your knees together.
- Your shoulder joint is just above your hip joint as you sit upright.
- Lean back a little and walk your hands behind you with the fingertips facing your toes for a deeper stretch in this position.
- Next, For one to two minutes, hold this position.
Supported Side-Plank Reach:
- To begin this exercise, place both knees on the floor and begin by extending your left leg out to the side.
- Immediately behind your right shoulder joint, place your right palm on the floor.
- Next, Rotate your shoulder joint so that it is parallel to the wall in front of you, and press the outside edge of your left foot into the ground.
Lying hip rotation:

- Your knee joint is bent and your feet are flat while you lie on the floor.
- Next, Place one ankle joint on top of the other.
- In and out, rotate the hip joint.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Sidekick:

- One leg should be raised out to the side when standing.
- Perform this exercise ten times on each side, on both sides.
- Try introducing little weights to the ankle joint as the strength improves.
- Additionally, you are clinging to a wall for support if necessary.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Hip raises:
- Both of your feet are firmly planted on the ground close to your buttocks as you lie there.
- Next, attempt to raise one leg straight up while maintaining a parallel thigh.
- Lift your hip joint off the floor.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Leg raises:

- Next, Return to all fours after lifting one foot back toward the sky.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Frankenstein:
- You take a stride forward with your left foot while standing erect with your arms by your sides.
- Without arching your back, try to swing your leg as high in the air as you can.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Hanging Leg Raise:
- Initially When your legs are stretched, hang from a pull-up bar high enough so that your feet do not touch the floor.
- As you pull your legs out and up towards your chest without utilizing any momentum, aim to bend your hip and knee joints at the same time while maintaining a solid overhand grasp.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Bridging Psoas March:
- First, wrap a little band around your footballs.
- Then, with your torso straight and your toes pointed upward, place your heels on an elevated platform.
- Try to raise your hip joint while using your glutes and core.
- You must prevent your butt from drooping at the hip joint.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Romanian Chair Leg Raises with Dumbbell:
- First, place a light dumbbell firmly between your feet and adjust yourself on the Roman chair.
- Surely With your forearms resting on the pad, maintain an erect posture and press your lower back on the backrest.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
Boat Pose:
- To avoid placing pressure on your tailbone, carefully lean back and tuck it under.
- Try extending your legs into the air as you’re reclining back, and remove any arching in your spine to achieve a neutral posture.
- Keep your shoulders down, raise your chest, and hold for a while.
Lunge:

- You must maintain an erect trunk throughout the exercise.
- Directly above your right ankle joint should be your right knee joint.
- After that, return to standing and repeat with your left leg in front of you.
- For ten seconds, maintain this workout stance.
FAQs
Is cycling beneficial to the psoas muscle?
After six months of competitive training, the researchers found that the experienced cyclists’ psoas muscles were much larger than those of the males who had no training. About 14% of our pedaling power is generated by hip flexion as we raise the pedal during the upstroke.
When using Iliopsoas, how do you sit?
Make sure your hips are level with or slightly higher than your knees if you must sit. This will assist keep the psoas from shortening and somewhat enhance its posture.
How can psoas pain be resolved?
Activities for Relaxing Tight Psoas
Flex and Lunge Stretches: Place yourself in a lunge position and let your rear knee drop to the floor. Push your body forward a little till you feel a small stretch while keeping your spine straight.
Which posture causes the psoas to relax?
When performed on a hard surface, the pose is most effective. Aiming to flatten your spine toward the floor is NOT a good idea.
Will the pain from psoas ever go away?
Patients should take every precaution to prevent this result since muscle tissue repairs very slowly. After they heal, psoas muscle tears will leave scars that will result in chronic pain and weakness. Furthermore, the muscles that surround the psoas may potentially sustain damage.
Does walking help those with tight hip flexors?
To prevent tension, I advise shifting positions every 30 to 45 minutes, or sooner if necessary, says Kimberly Baptiste-Mbadiwe, a physical therapist at HSS.
What not to do if you have psoas pain?
Some psoas syndrome sufferers must temporarily alter their activity regimen. For instance, you might have to limit yourself to narrower workout ranges or weightlifting postures. Running on hills or slopes should be avoided by certain individuals.
How can someone with tight psoas sleep?
To alleviate hip and lower back discomfort and lessen the curvature of your spine, place a cushion beneath your knees. To maintain your hips in a neutral posture, make sure the pillow beneath your knees is sufficiently thick. For your head and neck, use a supporting cushion, but make sure it’s not too high.
Can the iliopsoas be massaged?
In addition to the tissues that cover it, the iliopsoas appear to be highly sensitive to pressure, and pain is nearly always unpleasant. To perform it correctly and without inflicting a great deal of suffering, it requires patience and care. It’s simply too much massage pressure for a lot of individuals.
How does the iliopsoas muscle feel when it is strained?
A quick, acute pain or tugging feeling is typically experienced by patients who have an iliopsoas strain. This pain might be in the groin or the front of the hip. This happens when someone pulls their knee toward their chest when walking, ascending stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
Does heat help with psoas pain?
Exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the psoas can assist support the lower back and lessen muscular tension.
How can iliopsoas pain be relieved?
These objectives are achieved with the use of medicine, ice, rest, and mild stretching. Pain, spasms, and inflammation can also be reduced by using a pack of crushed ice in an ice bag wrapped with moist cloth for 20 minutes every one to two hours.
References
- Ladva, V. (2022, May 27). Iliopsoas muscle pain: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment & Exercises. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/iliopsoas-muscle-pain-treatment/
- Physiotherapist, N. P.-. (2024a, February 16). Iliopsoas Muscle: Origin, Insertion, Action, Exercise | Mobile Physio. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/iliopsoas-detail-know-your-muscles/
- Valand, B. (2022, October 30). iliopsoas muscle stretch Archives – Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/tag/iliopsoas-muscle-stretch/
- Physiotherapist, N. P.-. (2023, July 22). Iliopsoas tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/iliopsoas-tendonitis/