For Knee Pain What To Eat
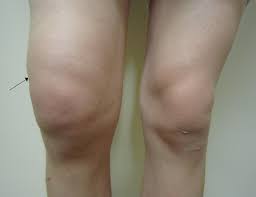
Introduction: Knee pain can greatly interfere with day-to-day activities, making it difficult to move freely or enjoy them. If a person has serious bone diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, gout (retention of uric acid in the knee), severe injury, or pain from vigorous exercise and workouts, they need to take medication and have a…