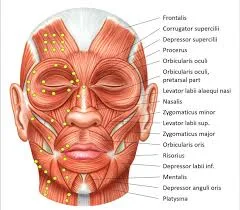
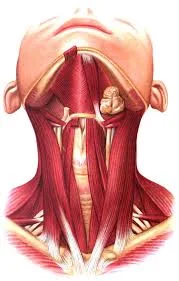
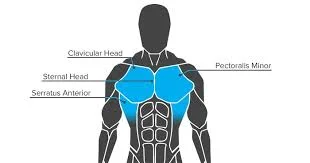
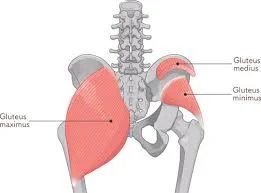
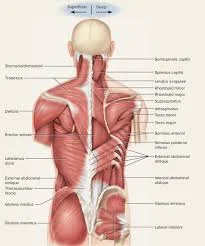
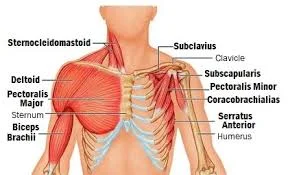
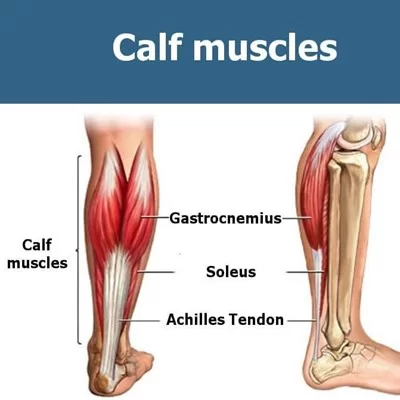
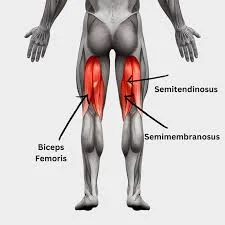
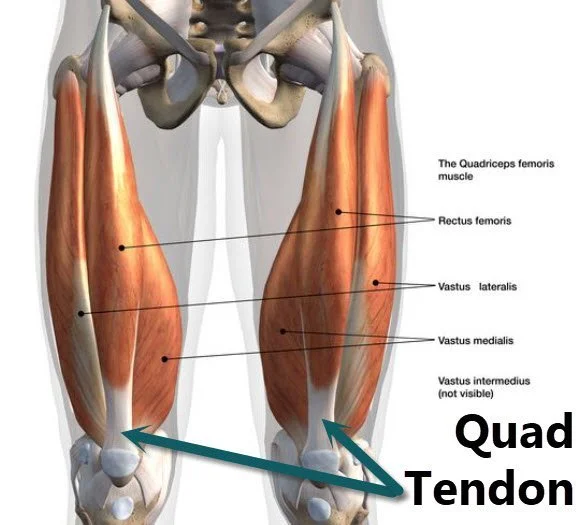
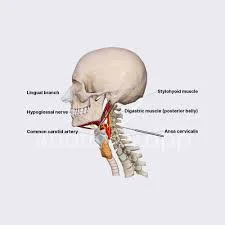
Facial muscles
Introduction The facial muscles, also known as craniofacial muscles, are a group of approximately twenty flat skeletal muscles that are located beneath the skin of the scalp and face. The majority of them originate in the skull’s bones or fibrous structures before spreading to the skin. The facial muscles are a collection of striated skeletal…