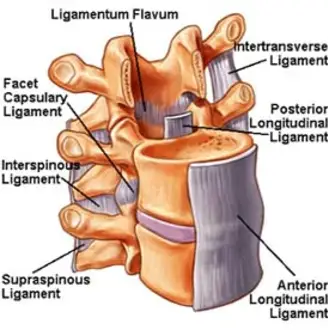
Annular Ligament Injury
What is a Annular Ligament Injury?
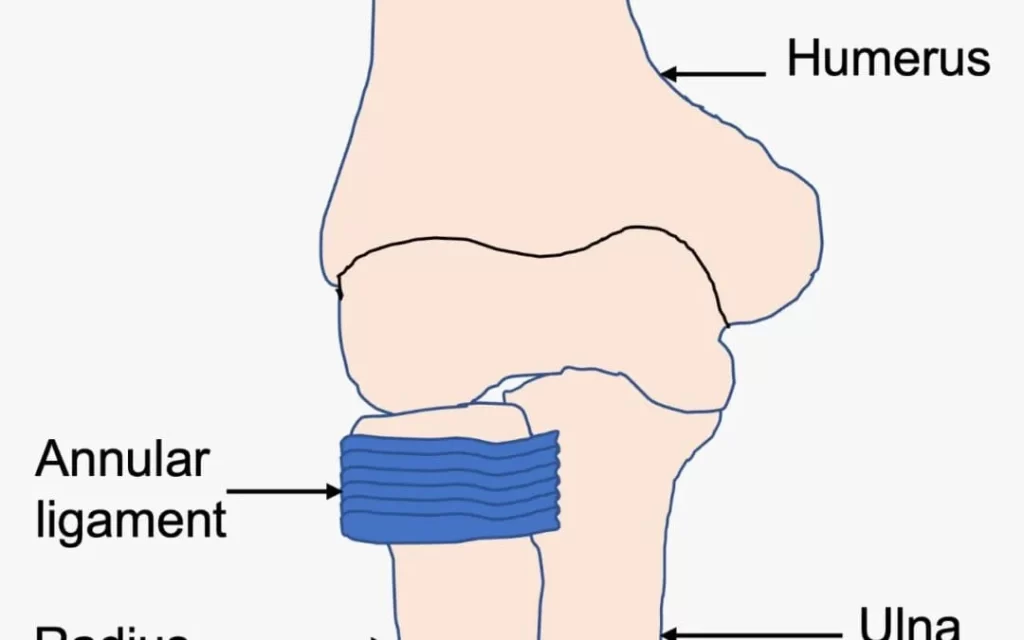
An annular ligament injury involves damage to the strong band of tissue that encircles the head of the radius, securing it to the ulna and stabilizing the elbow joint. It often results from trauma, such as a fall or sudden pulling motion, commonly seen in young children (referred to as nursemaid’s elbow).
Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and restricted movement in the elbow. Treatment typically involves rest, immobilization, and physical therapy, with severe cases occasionally requiring medical intervention.
Causes of Annular Ligament Injury
Numerous actions that strain the elbow joint might result in annular ligament injury. The following are a few typical reasons for annular ligament injuries:
- Repetitive motions: The annular ligament and surrounding tissues may be severely strained by sports like tennis or baseball that require repetitive actions of the elbow joint. This can raise the chance of injury and cause the ligament to deteriorate over time.
- Trauma: The annular ligament may be harmed by trauma to the elbow joint, such as a fall or a direct impact on the arm. Activities involving high-impact or contact sports are more likely to cause this kind of injury.
- Overuse: Ankle ligament problems can also result from excessive elbow joint use, such as lifting heavy weights or typing a lot. This is due to the fact that these activities continuously pressure the ligament, which over time may result in inflammation or tearing.
- Inappropriate technique: Inappropriate technique can also raise the risk of annular ligament injuries when engaging in specific activities, such as lifting weights or playing sports. This is due to the fact that improper form can cause the elbow joint and surrounding tissues to experience more stress.
Therefore, it’s critical to take precautions against annular ligament injuries by utilizing appropriate techniques when performing tasks, taking breaks to relax and stretch the elbow joint, and getting medical help if you experience any pain or discomfort.
Symptoms of the Annular Ligament Injury:
Depending on how severe the injury is, annular ligament injuries can present with a variety of symptoms, but some typical ones include:
- Elbow Pain: One of the most typical signs of an annular ligament injury is elbow joint pain. When engaging in activities that strain the elbow joint, one may experience either dull or severe pain.
- Swelling: Another typical sign of annular ligament damage is swelling around the elbow joint. In addition to mild to severe swelling, the affected area may also be heated or red.
- Stiffness: Another sign of an annular ligament injury is stiffness in the elbow joint. It may be challenging to move the arm or carry out specific tasks due to the mild to severe stiffness.
- Weakness: Another sign of annular ligament damage is weakness in the affected arm. This could be the result of ligament damage or soreness, which can make it difficult to move the arm normally.
- Clicking or popping: Another sign of an annular ligament injury is clicking or popping sounds in the elbow joint. The ligament may be torn or otherwise damaged, which could result in aberrant joint movement.
In order to identify the cause and obtain the proper therapy, it is crucial that you seek medical assistance if you have any of these symptoms.
Risk factors of the Annular Ligament Injury:
A ring of tissue called the annular ligament helps hold the forearm’s radius bone in place within the elbow joint by encircling its head. Despite being a robust and resilient structure, the following risk factors can raise the possibility of an annular ligament injury:
- Overuse: The annular ligament may sustain damage as a result of repetitive motions of the forearm and elbow, such as those found in sports like tennis or golf.
- Trauma: The annular ligament may stretch or rupture as a result of direct trauma to the elbow joint, such as a fall or impact.
- Age: Our tissues lose their elasticity and become more vulnerable to damage as we age. An annular ligament injury may be more common in older persons.
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to sustain injuries because their ligaments are thinner or more brittle from birth.
- Bad posture: Bad posture can increase the strain on the elbow joint and the ligaments that surround it, such as the annular ligament.
- Poor technique: When playing sports or engaging in other physical activities, poor technique might raise the risk of harming the annular ligament and other elbow joint tissues.
- Medical disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are two examples of disorders that can weaken the annular ligament and increase its vulnerability to damage.
- A diet deficient in vital nutrients, such as protein and vitamin C, can weaken bodily tissues and raise the risk of injury to the elbow joint’s annular ligament and other components.
To lower the chance of an annular ligament injury, it is imperative to be aware of these risk factors and take action to lessen them. This could entail keeping a healthy posture, exercising with appropriate form, and making sure one eats a diet that is both balanced and nourishing.
Diagnosis of the Annular Ligament Injury:
Imaging tests and a physical examination are usually required to diagnose an annular ligament injury. The physician will assess the affected arm and elbow joint during the physical examination, searching for indications of pain, stiffness, and edema. In order to assess for weakness or instability, they could also move the elbow and arm joints in various directions.
An annular ligament damage may also be diagnosed by imaging studies like MRIs, ultrasounds, or X-rays. While MRI or ultrasound can demonstrate the extent of ligament injury, X-rays can assist in ruling out other disorders such as fractures or dislocations.
In order to check the annular ligament and surrounding components, the doctor may also perform an arthroscopy in certain cases. This procedure entails putting a tiny camera into the joint. This can assist in determining the best course of treatment and offering a more thorough diagnosis.
Therefore, to identify annular ligament damage and choose the best course of treatment, an understanding of physical examination and imaging tests are usually utilized.
Treatment of the Annular Ligament Injury:
Medical Treatment:
RICE, or rest, ice, compression, and elevation, is the standard conservative treatment for an annular ligament injury. This may lessen the wounded area’s pain and swelling.
Avoiding activities that worsen the pain and resting the affected arm can help stop the annular ligament from getting worse. To lessen swelling and inflammation, use cold compresses or ice packs on the area for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, multiple times a day.
Using a brace or bandage to compress the injured area can also assist in reducing swelling and provide support. Reducing edema and accelerating healing can also be achieved by elevating the arm above the level of the heart.
To assist manage pain and inflammation, doctors may also prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) or painkillers like acetaminophen.
To help increase the affected arm’s strength, flexibility, and range of motion, physical treatment may also be suggested. In addition to manual therapy methods like massage or joint mobilization, this may entail activities to strengthen and stretch the muscles surrounding the elbow joint.
A brace or splint may be advised in some situations to immobilize the affected arm and promote the healing of the annular ligament. If conservative treatment is insufficient or there is a chance of more harm, this can be required.
Physical treatment may also be recommended to assist improve the strength, range of motion, and flexibility of the affected arm. This could involve exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles around the elbow joint in addition to manual therapy techniques like massage or joint manipulation.
In certain cases, it may be recommended to use a brace or splint to immobilize the affected arm and encourage the annular ligament to recover. This may be necessary if conservative treatment is not enough or if there is a risk of further damage.
Physical Therapy Treatment:
Exercises, manual therapy methods, and other modalities are commonly used in physical therapy treatment for annular ligament injuries in order to assist decrease pain and inflammation, increasing the range of motion, and restoring function to the injured arm.
To ascertain the amount of the damage and create a customized treatment plan, the physical therapist will first do an understanding evaluation of the injury. This could consist of:
- In order to allow the annular ligament to heal during the acute phase of the injury, the physical therapist may advise immobilizing the injured arm with a brace or splint and resting it.
- Ice therapy: Applying cold compresses or ice packs to the affected region might help to reduce swelling and pain.
- Manual treatment: Manual therapy methods including stretching, joint mobilization, and massage can help ease elbow joint muscular tension and increase range of motion.
- Exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the elbow joint can assist increase stability and stop additional injuries.
- Exercises for range of motion: These exercises can assist increase the affected arm’s flexibility and range of motion.
- High-frequency sound waves are used in ultrasound therapy to encourage healing and lessen pain and inflammation in the affected area.
- Electrical stimulation: This technique can be used to increase muscular strength and function and lessen pain.
- To guarantee the best outcomes, the physical therapist will keep an eye on patients’ development during the course of treatment and modify the plan as necessary. Most patients with an annular ligament injury can anticipate a major improvement in their quality of life, function, and pain with appropriate physical therapy treatment.
How to prevent of the Annular Ligament injuries?
A mix of lifestyle modifications, appropriate form when exercising, and medical treatment of underlying issues are necessary to prevent annular ligament injuries. The following advice can help avoid damage to the annular ligament:
- Keep your posture correct: Bad posture can increase the strain on the elbow joint and the ligaments that surround it, such as the annular ligament. Maintain good posture when standing, sitting, and engaging in physical activity to avoid injury.
- Employ good technique when exercising: In sports or other physical activities, poor technique can raise the risk of injury to the elbow joint’s annular ligament and other components. Use the right form and technique for your chosen exercise on a regular basis to avoid injury.
- Before engaging in any physical activity, stretch your muscles to help them warm up and assist you avoid injury. To get your forearm, wrist, and elbow muscles ready for action, concentrate on stretching them.
- Develop stronger forearm muscles: These muscles can support the elbow joint and lower the chance of annular ligament damage. Include forearm muscle-focused activities in your training regimen.
- Wear the right protective gear: Wearing the right protective gear, such as elbow pads, can assist prevent injury if you engage in high-risk activities like rock climbing or contact sports.
- Handle underlying medical disorders: The annular ligament might become weaker and more prone to injury due to certain medical conditions including osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. To manage any underlying conditions that could raise your risk of injury, collaborate with your healthcare physician.
- Keep up a healthy, well-balanced diet: A diet deficient in vital nutrients, such as protein and vitamin C, can weaken bodily tissues and raise the risk of injury to the elbow joint’s annular ligament and other components. Maintain a healthy, well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains to help prevent injury.
You can lower your risk of elbow joint injuries, including those to the annular ligament, by adopting these lifestyle changes. See a doctor right away if you have elbow pain or discomfort in order to stop additional damage and encourage recovery.
Complications of Annular Ligament Injury:
- Chronic elbow instability
- restricted range of motion, especially while rotating the forearms (pronation/supination)
- Frequent dislocation or subluxation of the radial head
- Contractures or stiffness in the joints
- Changes in degenerative joints, such as early osteoarthritis
- Chronic pain or agony
- Nerve irritation or compression (rare, but possible in extreme situations)
Prognosis:
An annular ligament injury has a relatively favorable prognosis, particularly when diagnosed early and treated appropriately. Conservative measures like rest, immobilization, and physical therapy are effective in the healing of the majority of minor injuries.
With the right reduction and care, children with radial head subluxation (also known as “nursemaid’s elbow“) have a very good prognosis. Although surgery may be necessary for severe or recurring injuries, full-functionrecovery is usually the conclusion. Chronic instability or restricted range of motion may result from postponed treatment or recurrent injuries.
Conclusion:
Annular ligament injuries can seriously impede forearm rotation and general arm function. These injuries are typically caused by trauma or repetitive stress on the elbow joint. Restoring joint stability and avoiding long-term consequences requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate management, which can range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to surgery in extreme cases. Most people can fully recover and resume their regular activities with prompt care.
FAQs
Can an annular tear be healed with massage?
Many patients find that a range of conservative methods, such as physical therapy, hot or cold compresses, and painkillers, are effective in treating annular tears. Electrical nerve stimulation, hydrotherapy, massage, and epidural injections are possible additional forms of treatment.
Does an annular tear benefit from walking?
An annular tear can also be treated with exercise in addition to medicine. When the symptoms start to become worse, rest is crucial, but exercise is also necessary to maintain a strong and healthy spine. The important thing is to exercise without getting hurt any more.
How should an annular rip be treated?
Low-impact physical therapy and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually used to treat simple symptomatic annular fissures without disc herniation. Granulation tissue or nerve ending ingrowth, which is typically observed close to the dorsal root ganglia, may be the cause of chronic pain caused by annular fissures.
What causes an annular tear?
When a disc’s typically thick outer covering is pulled or torn due to tension, an annular tear results. A herniated disc is created when the soft inner “jelly” (nucleus pulposus) leaks out from the disc’s interior due to further stress on the disc following the formation of an annular tear.
Which motions are permitted by the annular ligament?
During supination and pronation of the forearm, the radial head rotates within the radial notch of the ulna, stabilized by the annular ligament.
How can an annular ligament tear be detected?
The doctor forcefully pronates the child’s wrist with one hand while holding the child’s elbow at a 90-degree angle with the other. The radial head is compressed by the doctor’s thumb, and when the radial head is reduced, a tactile click is frequently heard.
What is the annular ligament injury mechanism?
The radial head is held against the ulna by the annular ligament, which surrounds it. The annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and becomes stuck in the radiohumeral joint between the radial head and capitellum when axial traction is applied to a pronated forearm and extended elbow.
Can ligament injuries be helped by physical therapy?
Injuries to the knee ligament can significantly impact a person’s everyday activities and make it impossible for them to engage in activities they used to enjoy. Whether the injury has been treated conservatively or surgically, a course of physical therapy will help hasten the healing process and maximize recovery.
How is an injury to the annular ligament treated?
Resting the joint may be necessary as part of treatment for an annular ligament rupture in order to reduce pain and inflammation. Surgery to reattach or repair the ligaments may be required for severe injuries, such as tears in the ligaments. The degree of ligament damage will determine how much movement should be limited after the injury.
What precautions may be taken to keep the annular ligament from getting injured?
Wearing protective clothing during activities that put the elbow joint at danger, avoiding repetitive actions that strain it, and maintaining strong forearm muscles through exercise are all ways to prevent injuries to the annular ligament.
How are annular ligament disorders and injuries identified and managed?
A physical examination, imaging tests (such as MRIs or X-rays), and occasionally an arthroscopy are used to detect annular ligament injuries or disorders. Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment options may include physical therapy, surgery, immobilization, or rest.
Which disorders or traumas are frequently linked to the annular ligament?
Annular ligament tears, radial head subluxation (partial dislocation), and persistent elbow joint instability are common injuries or diseases related to the annular ligament.
What is the annular ligament used for?
Smooth forearm movement is made possible by the annular ligament, which stabilizes the head of the radius bone within the elbow joint.
In what part of the body is the annular ligament located?
The elbow joint contains the annular ligament, which is situated around the radius bone’s head.
The annular ligament: what is it?
The head of the radius bone is held in place within the elbow joint by a band of fibrous tissue called the annular ligament.
References
- Patel, D. (2023, August 19). Annular ligament – anatomy, structure, function. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/annular-ligament/
- Ormond, S. (2025, March 17). Annular ligament injury symptoms – Atlas Pain Specialists. Atlas Pain Specialists. https://atlaspainspecialists.com/annular-ligament-injury-symptoms/
- Chua, B. N. (n.d.). What is Elbow Annular Ligament Tear & Strain? https://phoenixrehabgroup.com/articles/physiotherapy/what-is-elbow-annular-ligament-tear-strain/