Jacobson’s Relaxation Technique
Jacobson’s relaxation technique also known as progressive muscle relaxation (PMR), is a method for releasing tension in the muscle and, as a result, reducing stress and anxiety.
It’s common to experience stress occasionally. However, if the stress increases or persists for an extended period, it suggests that the person may be carrying the tension in muscles. Someone can have tight muscles without even recognizing it.
Dr. Edmund Jacobson: American physician Dr. Jacobson created PMR in the 1920s. He thought that anxiety had a direct connection to tense muscles and that one might calm the mind by intentionally relaxing the muscles.
The key principle of this technique is that by systematically contracting and releasing particular muscle groups, you can increase your awareness of the differences between muscle tension and relaxation. You can identify and release tension more effectively because of this enhanced awareness.
This method may help someone manage the physical symptoms of stress if it is used on a daily basis. This method has been shown to have therapeutic advantages for conditions such as:
- High blood pressure
- Migraines
- Sleep issues
- Reducing Stress, Depression, and Anxiety
What is Jacobson’s Progressive Muscle Relaxation (JPMR)?
The relaxation method known as Jacobson’s progressive muscle relaxation (JPMR) involves methodically tensing and releasing various bodily muscle groups in order to lower tension and anxiety.
Basic Principles:
Muscle tension awareness: The foundation of JPMR is the idea that tense muscles are a typical physical sign of stress.
You can increase your awareness of the gap between these two states by consciously tensing and then relaxing your muscles.
Progressive approach: Typically, muscle groups are worked in order, beginning on the face and progressing down the body.
Controlled contraction: In order to tell the difference between tension and relaxation, a muscle group should be tensed by a forceful yet painless contraction.
Mind-Body Connection: JPMR highlights how closely your mind and body are related.
You can encourage mental relaxation by letting your muscles rest.
Inducing a relaxation response in the body is the aim of JPMR. The body shifts from an active, alert state to a more relaxed one as a result of the relaxation response. It results in several physiological alterations, including:
- Slower breathing
- Slower heart rate
- Hypotension
- Lower cortisol levels
- To reduce stress or anxiety, improve sleep quality, or relax stiff muscles, people might trigger the relaxation response.
- The JPMR method is also used by some as a type of meditation or at the conclusion of a yoga practice.
Uses of Jacobson’s Relaxation Technique
- Anxiety
- High blood pressure
- Lower back pain
- Migraine
- Tension in the muscles
- Stress-related neck pain
- Temporomandibular joint Pain (TMJ)
Reduction of Stress and Anxiety
Our bodies frequently tense their muscles in response to stress or anxiety. The “fight-or-flight” reaction includes this.
A persistent form of this muscular tension can cause pain, discomfort, and increased anxiety.
On the other hand, stiff muscles can also communicate with the brain in ways that intensify stress.
Additionally, it has been discovered that JPMR may assist individuals with COVID-19 in managing their anxiety, which may be beneficial for handling challenging circumstances.
Better Quality Sleep
JPMR can help people sleep deeper and fall asleep more easily by calming the mind and releasing tension in the muscles.
It’s very beneficial for people who suffer from sleeplessness.
During the postpartum phase, Women who had preterm babies were able to sleep comfortably because to JPMR.
Pain Control
Many forms of pain such as migraines and tension headaches, can be relieved by JPMR and
conditions that cause chronic pain, such as arthritis and back pain.
Chronic Neck Pain: Although JPMR can assist with tension-related neck pain, it might not be enough to treat chronic neck pain caused by underlying conditions.
If you experience persistent or severe neck pain, you should absolutely consult a healthcare professional.
Minimizes low back pain
Pain in the low back is another common condition. Although stress could worsen it, there are several potential reasons.
Performing this exercise for a few weeks might help lessen persistent low back pain.
It has been found by certain sources that pregnant women who get the PMR treatment while listening to music might have less low back pain.
Improved systolic blood pressure
By influencing the body’s stress response, progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) can really help reduce systolic blood pressure.
Hypertension, raises the risk of stroke and heart disease. PMR may assist, but stress might worsen the issue.
Reduces the number of migraine episodes
Stress and tense muscles can cause or worsen migraine headaches. progressive muscle relaxation, can lessen the occurrence of these.
The Link Between Tension and Migraines:
Stress as a Trigger: It is commonly recognized that stress can cause migraines. Hormones released by the body under stress can cause vascular alterations and increase muscular tension, It can both make migraines worse.
The Function of Muscle Tension:
Migraines can also be triggered by or made worse by tension in the skull, shoulders, and neck.
Pain may result from this tension’s disruption of blood flow and irritation of nerves.
The Benefits of PMR
- Stress Reduction: By triggering the body’s relaxation response, PMR successfully lowers stress. This lessens the release of stress hormones and helps to control the neurological system.
- Muscle Relaxation: PMR reduces tension in the neck and shoulders, which are frequently impacted by migraines, by methodically relaxing muscle groups.
- Improved Body Awareness: By raising awareness of tense muscles, PMR enables people to recognize and relieve tension before it causes a migraine.
Reduce the Pain of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a useful technique for treating the pain and discomfort that are frequently associated with temporomandibular joint (TMJ) issues.
PMR aids in the systematic relaxation of the jaw, face, and neck muscles.
Jaw function can be improved, and pain can be reduced by this release of tension in the muscles.
Stress management: PMR can lessen the frequency and severity of teeth grinding and pressing by lowering general stress levels.
By doing this, more TMJ tension may be avoided.
Encouraging Relaxation: By calming the neurological system, the profound relaxation that PMR produces might lessen the sense of pain.
By practicing PMR, people may become more aware of their bodies and better understand when they have tension in their jaw. This helps them release that tension.
How are Jacobson’s Relaxation Techniques performed?
Although Jacobson’s progressive muscle relaxation (JPMR) is a very easy method, it takes practice and concentration.
- Preparation: Find a Quiet Area. decide on an area where you won’t be disturbed.
- Reduce distractions and turn off the lights.
- Get at comfort: Sit comfortably in a chair or lie down on a level surface.
- Any tight clothes should be loosened.
- Anything that might be distracting should be taken out.
- Set the Intention: Breathe deeply a few times and concentrate on the here and now.
- Get ready for relaxation.
The Method:
Muscle Groups: Using JPMR, several muscle groups are methodically tensed and relaxed.
A typical order is:
- Calves of the feet
- The thighs
- The buttocks
- The abdomen
- The hands
- Arms
- Shoulders, Face, and Neck
- Focusing: Pay attention to a particular muscle region.
- Take a deep breath and tense those muscles for five to ten seconds.
- Tighten your muscles, but don’t strain them.
- Observe the feeling of tension carefully.
- Relaxing: Quickly relieve the tension in the affected muscle group by exhaling.
- As the muscles relax, take note of the sensation.
- Give the muscles ten to twenty seconds to fully relax.
- Pay attention to the differences between relaxation and tension.
- Repeat: For every muscle group, repeat the cycle of tensing and releasing.
- Doing the tensing and relaxing exercises for each muscle group two or three times might be beneficial. lowering the level of stress you produce each time.
- Breathing: Throughout the process, continue to take deep, steady breaths.
- Inhale when you’re tense, and exhale when you’re relaxed.
Completing:
- Scan Your Body: After working all of your muscle groups, pause for a moment to look for any tension that may still be there.
- Repeat the pattern of tensing and releasing if you notice any tense spots.
- Allow yourself to take in the feeling of complete relaxation.
- Before you resume your regular activities, stand motionless for a few minutes.
Whole-body relaxation method:
Meditation Illuminated: Easy Ways to Manage Your Busy Mind was written by Joy Rains. She suggests starting the relaxation treatment with a breathing technique before working your way up from your feet.
The feet
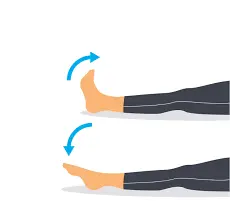
Turn your focus to your feet.
Curl your toes under and point your feet downward. Don’t strain as you softly tighten your toe muscles.
After a few minutes of noticing the tension, let it go and see the relaxation. Do it again.
Learn to recognize the difference between stressed and relaxed muscles.
From the foot to the abdomen, keep your leg muscles tight and relaxed.
The abdomen
Gently tighten your abdominal muscles. don’t strain.
Take time to notice the tension. After that, let it go and see the relaxation. do it again.
Learn to recognize the difference between your tight and relaxed muscles.
Neck and shoulders
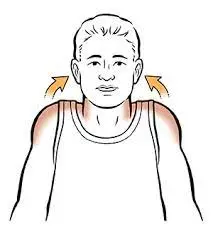
Shrug your shoulders gently, right up to your ears. Avoid straining.
Take a few seconds to feel the tension, let it go, and then enjoy the calm. Do it again.
Observe how the tight and relaxed muscles differ from one another.
Concentrate on your neck muscles, tensing and then relaxing them until you feel completely at rest.
Tips for Jacobson’s Relaxation Technique
- Gentle Tension: Make sure your muscles are tense, but don’t strain them. The intention is not to cause pain but to sense the tension. Be especially careful and adjust the workouts as necessary if you have any pain or injury.
Pay Attention to the Difference - Take note of how stress and relaxation differ from one another. This is essential for raising awareness.
- Breathing is essential.
- Sync the breathing exercises with your breathing. As you tense, take a deep breath; as you relax, release it completely.
- Holding your breath might make you more tense, so avoid doing it.
- The key to mastering JPMR is consistent practice. daily sessions, even if brief, can be helpful.
To make it simpler to utilize while you’re under stress, practice even when you’re feeling relaxed. - Consistent Practice: To become skilled in JPMR, regular practice is essential. daily sessions, even if brief, can be helpful.
- To make it simpler to utilize while you’re under stress, practice even when you’re feeling relaxed.
- Go Methodically: Regardless of whether you begin with your head or your feet, go through the muscular parts in a regular order.It will help you maintain your concentration.
- Pay Attention to Your Body: Stop exercising right away if it starts to hurt.
If needed, you can change or exclude certain muscle groups. - Guided Recordings: Use guided audio recordings when you first start. This can help that you’re doing the exercises correctly and help you maintain concentration.
- Mindful Awareness: As you work through the exercise, make an effort to pay closer attention to any persistent tension in your body.
- Integrate into Daily Life: After you feel at ease with PMR, you may start using it in regular basis. For instance, you can quickly do a mini-relaxation exercise if you have shoulder tightness while working.
There are several alternative relaxation methods available if the JPMR approach is ineffective, such as:
- Meditation
- Breathing exercises
- Practices like yoga, tai chi, or qi gong that include visualization
- Self-hypnosis
- Relaxation with biofeedback assistance
- Massage
FAQs
What are the benefits of progressive muscle relaxation?
Muscle tension is one of the ways the body reacts to worry or stress in daily life. One technique that aids in easing that tension is progressive muscle relaxation.
What is the JPMR duration?
Each intervention lasted for twenty minutes.
What is the relaxation method used by Jacobson?
Progressive muscular relaxation (PMR), another name for Jacobson’s relaxation method, is a form of therapy that involves tensing and relaxing muscles in a particular order.
Is anxiety a result of tense muscles?
Chronic muscular tension contributes significantly to anxiety in many persons. It should come as no surprise that psychological stress generates tension in the muscles, but the opposite is also true: psychological stress causes tension in the muscles. This is excellent news since it indicates that anxiety may be reduced by easing tense muscles.
What does JPMR aim to achieve?
One method of relaxing is progressive muscle relaxation or PMR. One by one, you must tense and then release your muscles. This aids in the physical release of tension, which may reduce anxiety and stress.
References
- Tanushri. (2023b, September 15). Exploring Jacobson’s Progressive Muscle Relaxation (JPMR). Mind and Brain Hospital. https://mindandbrainhospital.in/blog/unlocking-tranquility-exploring-jacobsons-progressive-muscle-relaxation-jpmr/
- VA.gov | Veterans Affairs. (n.d.). https://www.va.gov/WHOLEHEALTHLIBRARY/tools/progressive-muscle-relaxation.asp
- Mushtaq, B., & Khan, A. A. (2018). Jacobson Muscle Relaxatation Technique (JPMR) (20 min). JOJ Nurse Health Care, 8(1), JOJNHC.MS.ID.555726-JOJNHC.MS.ID.555726. https://doi.org/10.19080/JOJNHC.2018.08.555726
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024, February 26). Progressive muscle relaxation. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progressive_muscle_relaxation
- Goldman, R. (2020, July 21). What is Jacobson’s Relaxation Technique? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/what-is-jacobson-relaxation-technique
- Manas. (n.d.). Jacobson’s progressive muscle relaxation. https://manas.org.in/jacobsons-progressive-muscle-relaxation